Scrapter catoxys Davies, 2005
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.7667046 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CCD871AC-88F0-4E1B-929A-6AD042325468 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5BC1B4FF-758E-4E70-9001-184AB0317B32 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:5BC1B4FF-758E-4E70-9001-184AB0317B32 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Scrapter catoxys Davies |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Scrapter catoxys Davies View in CoL , sp. n.
Figs 13–17 View Figs 13–16 View Fig
Etymology: Gr. katoxys (very sharp). In reference to the acute, tapering final black flagellomere of the male antenna (Fig. V in key).
Holotype ơ: SOUTH AFRICA: Northern Cape: Springbok, Goegap Nature Reserve , hills, 8–10.ix.1992, F.W. and S.K. Gess ( AMGS) . Paratypes: 2 ơ with same label data as holotype.Additional material: 3 ơ and 2 ^with same label information as holotype.
Description:
Male.
Measurements (n = 3): head length 1.3 mm, head width 1.9 mm, lower interocular distance 0.9 mm, upper interocular distance 1.2 mm, interantennal distance 0.3 mm, antennocular distance 0.3 mm, length of clypeus 0.4 mm, length of eye 1 mm, width of eye (lateral view) 0.6 mm, width of gena (lateral view) 0.2 mm, length of facial fovea 0.3 mm, maximum width of facial fovea 0.06 mm, mesoscutum length 1.2 mm, mesosoma length 2 mm, forewing length 4.3 mm, length of pterostigma 0.6 mm, maximum width of pterostigma 0.1 mm, length of marginal cell beyond pterostigma 1 mm, length of marginal cell 1.2 mm, length of free-part of marginal cell 0.8 mm.
Vestiture: Hairy bee. Clypeus, supraclypeal area and lower paraocular area with thick, white, decumbent vestiture. Frons and upper paraocular area with erect, thick, white hairs. Scape with sparse, white hairs. Vertex with sparse, greyish, erect hairs. Gena with short, fairly dense, slightly decumbent, white hairs. Mesoscutum, scutellum and metanotum with sparse, erect, white hairs. Mes- and metepisterna with thick, long, white hairs. Propodeum with fairly dense, white hairs. Tergal discs with uniform, thick (although integument visible), short, white pubescence. T1–T4 with weak posterior, white, hair bands along marginal zone. S1 with scattered, inconspicuous white hairs. S2–S4 very weak, white, posterior hair bands.
Integumental colour:Mainly black. Protarsus, protibia and apical end of profemur yellow. Mesotarsus, proximal and apical ends of mesotibia and apical end of mesofemur yelloworange. Metatarsus, proximal and apical ends of metatibia and apical end of metafemur orange-brown.
Head: Clypeus shiny and smooth with heavy punctation (interspace <0.5 × puncture diameter), no clypeal sulcus. Supraclypeal area, frons and paraocular area with dense punctation (interspace <0.5 × puncture diameter). Facial fovea sulcoid, elliptical, shiny and smooth. Gena much narrower than eye (0.3:1) with fairly dense punctation. Frontal line weakly carinate. Ocellar triangle raised in anterior profile. Inner eye orbits diverging above, proportion of lower to upper interocular distance 0.8:1. F11 very distinctive, tapering to fine point (Fig. V in key), antenna moderately long reaching metanotum.
Mesosoma: Mesoscutum smooth and shiny with fairly dense punctation (interspace 0.5–1 × puncture diameter), median line weakly impressed, notaulus very weak. Mes- and metepisterna shiny and smooth with heavy punctation (interspace 0.5 × puncture diameter), episternal groove pitted throughout. Propodeum angulate and heavily punctate, propodeal triangle shiny, largely smooth with several longitudinal carinae on basal area (weakly or irregularly developed in some specimens), margins of triangle weakly pitted.
Metasoma: Tergal discs smooth and shiny with fairly dense micropunctation. T2 fovea elongate ovoid.
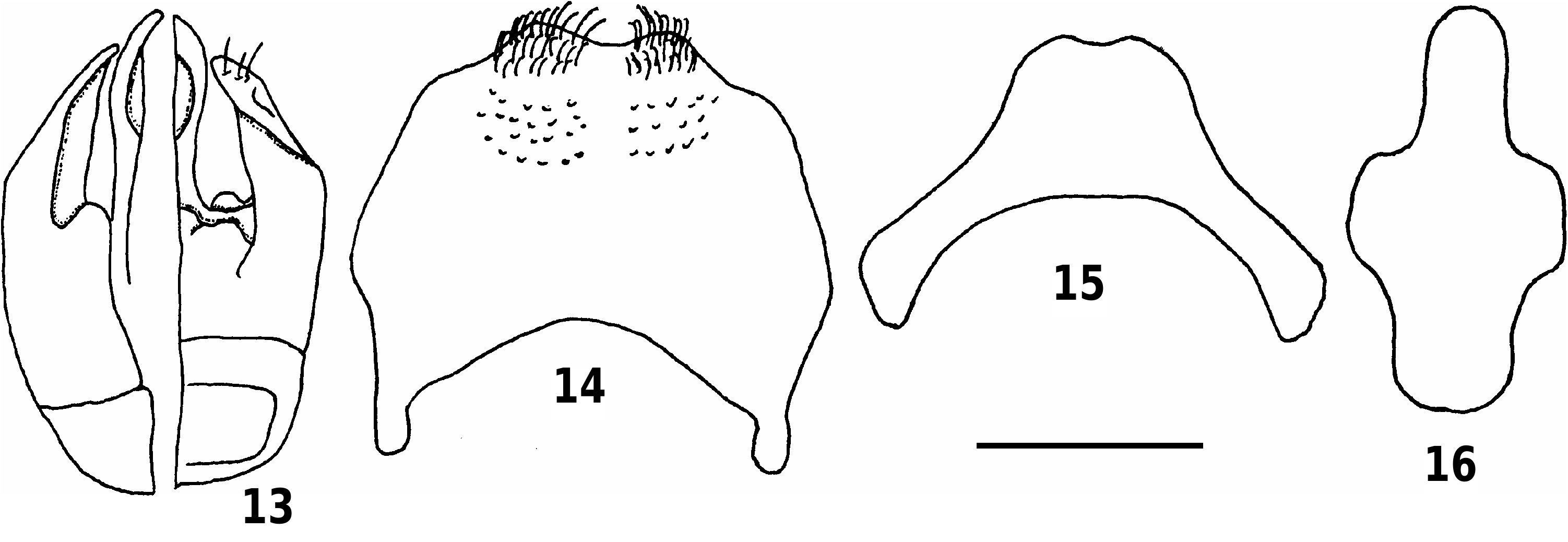
Terminalia: Gonobase large, gonoforceps curved inwards posteriorly, ventrally membraneous, penis valves narrow, curved inwards ( Fig. 13 View Figs 13–16 ). S6 weakly concave and hairy posteriorly, weakly concave anteriorly ( Fig. 14 View Figs 13–16 ). S7 essentially truncate posteriorly except for two very small, black, blunt projections ( Fig. 15 View Figs 13–16 ). S8 posterior disc region short, anteriorly round ( Fig. 16 View Figs 13–16 ).
Legs: Metabasitibial plate near-entire. Claws unusual, pro- and mesopretarsal claws deeply bifid but metapretarsal claws weakly toothed. Metabasitarsus elongate.
Female.
Measurements (n = 1): head length 1.4 mm, head width 1.9 mm, lower interocular distance 1.2 mm, upper interocular distance 1.3 mm, interantennal distance 0.3 mm, antennocular distance 0.4 mm, length of clypeus 0.5 mm, length of eye 1 mm, width of eye (lateral view) 0.6 mm, width of gena (lateral view) 0.3 mm, length of facial fovea 0.2 mm, maximum width of facial fovea 0.08 mm, mesoscutum length 1.2 mm, mesosoma length 2 mm, forewing length 4.2 mm, length of pterostigma 0.6 mm, maximum width of pterostigma 0.2 mm, length of marginal cell beyond pterostigma 1 mm, length of marginal cell 1.2 mm, length of free part of marginal cell 0.8 mm.
Vestiture: Clypeus sparse, white, bristly hairs. White, bristly, fairly long, rather dense hairs surrounding antennal sockets. Remainder of face sparsely hairy (hairs on vertex with slight gold tinge). Gena rather sparse, white, bristly hairs. Mesoscutum sparse, short, white hairs, pilosity somewhat thicker on scutellum and metanotum. Sides of mesosoma with rather sparse, white, bristly, long hairs. Terga sparse, inconspicuous, white hairs throughout disc and weak band of short, white hairs along marginal zone. Prepygidial fimbria thick, white, bristly hairs. Probasitarsus anteriorly with white, bristly, long hairs; posteriorly with brush of short, dense, golden hairs. Metatibial scopa completely white. S2 with long, white, plumose hairs; S3 thickish band of plumose, white hairs posteriorly; remaining sterna with scattered, short hairs.
Integumental colour: Mainly black. Protarsus and protibia yellow-orange; mesotibia proximally yellow; terga with brownish tinge.
Head: Clypeus sparsely punctate (interspace approximately 2 × puncture diameter), interspaces smooth and shiny. Facial fovea short, shallow ovoid. Supraclypeal area raised, sparsely punctate. Frons and paraocular area densely punctate (interspace <0.5 × puncture diameter). Frons and vertex not carinulate. Ocellar triangle raised in anterior profile. Gena smooth and fairly densely punctate.Antenna short, barely reaching tegula. F10 weakly pointed.
Mesosoma: Mesoscutum with dense punctation (interspace <0.5 × puncture diameter), interspaces smooth and shiny. Scutellum similar to mesoscutum, but punctation sparse anteriorly. Metanotum with dense punctation. Propodeum angulate; propodeal triangle strikingly smooth and shiny, a few short carinae on basal area. Sides of mesosoma with dense punctation (interspace <0.5 × puncture diameter), interspaces smooth and shiny. Episternal groove pitted throughout.
Metasoma: Terga smooth with fairly dense punctation (interspace approximately 1 × puncture diameter). T2 fovea elongate ovoid.
Legs: Metabasitibial plate entire, hairy. Claws simple.
Diagnosis: S. catoxys is a small, shiny, hairy, black bee ( Fig. 17 View Fig ); the metasomal tergal discs are noticeably covered throughout in fairly thick, white vestiture. Superficially, it resembles other hylaeiform Scrapter species, but the acutely pointed F11 is distinctive (Fig. V in key). In particular, S. catoxys resembles S. calx , but the colouration and structure of the antennae are different, the acute F11 being especially diagnostic of S. catoxys . Further, the gonostylus of S. catoxys lacks an expanded inner margin (present in S. calx ), the S7 of S. catoxys lacks posterolateral processes (present in S. calx ) and the metadistitarsi are elongate (not elongate in S. calx ). The ranges of S. calx and S. catoxys also appear allopatric ( S. calx is seemingly largely circumscribed to the Knersvlakte).
Distribution: Only known from Goegap Nature Reserve, approximately 12 km east of Springbok (Succulent Karoo biome).
Biology: Flight period is during September. The type series was collected on Cotula barbata DC. (Asteraceae) , which is a small, wiry annual bearing yellow, umbel-shaped flowers and is widespread in Namaqualand.
| AMGS |
Albany Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |