Elaphoidella paraaffinis, Watiroyram, Santi, Sanoamuang, La-Orsri & Brancelj, Anton, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4282.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FF21414A-8B19-482F-9365-475058E7527E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6040680 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B224CF09-FFBE-9B6D-ECD1-F8EB3009F85E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Elaphoidella paraaffinis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Elaphoidella paraaffinis sp. nov.
( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 –6)
Type locality. Phra Kayang Cave , Lum Liang Subdistrict, Kraburi District, Ranong Province, southern Thailand ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
Material examined. Holotype: adult female, length 520 µm (access No.: NHMUK 2016.642), completely dissected and mounted on one slide. Allotype: adult male, length 480 µm (access No.: NHMUK 2016.643), completely dissected and mounted on one slide. Paratypes: three females with egg sacs and three males, stored in 70% ethanol (access No.: NHMUK 2016.644–649); four females with egg sacs and four males, stored in 70% ethanol (access No.: NPU 2016-001). All material was collected from Phra Kayang Cave (loc. typ.) by S. Watiroyram on 15 August 2015.
Etymology. The specific name paraaffinis , formed with the Greek prefix para (= near, beside), refers to the similarity of the new species with E. affinis . The species epitheton is a feminine singular adjective.
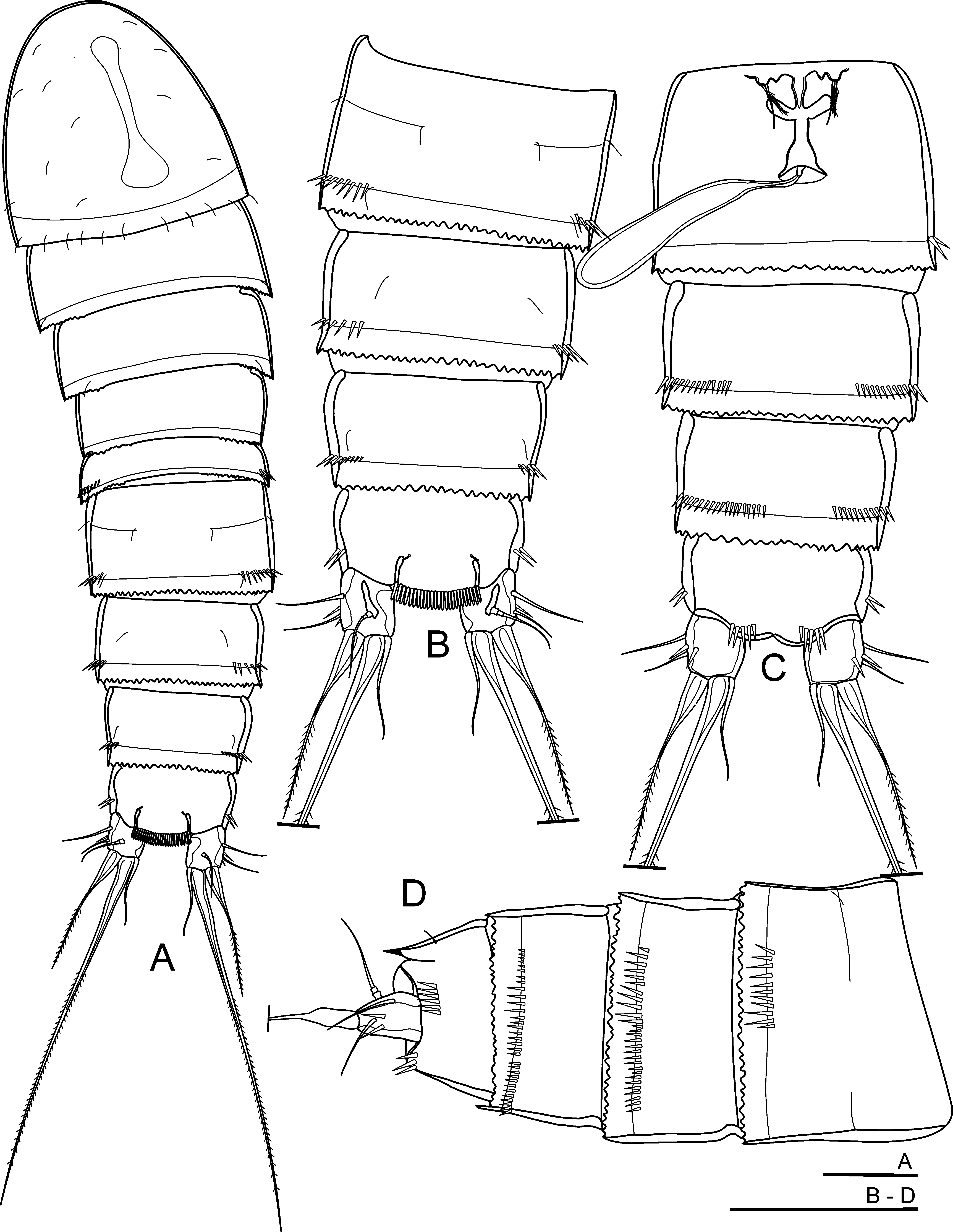
Description of female. Body length, measured from anterior margin of rostrum to posterior margin of caudal rami, 500–550 µm (mean = 530 µm, n = 5). Habitus elongated, subcylindrical, width evenly decreased from cephalothorax to last urosomite; preserved specimens colourless ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A). Naupliar eye not discernible. Cephalothorax with several pairs of sensilla, integumental window saddle-shaped, well discernible. Posterior margins of prosomites 1 to 3 and urosomite 1 serrated laterally; genital double-somite and urosomites 3 and 4 serrated along entire free margins. Somite of the genital double-somite completely fused ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B–D), about 0.8 times as long as wide, with row of strong spinules on distal dorso-lateral margin. Genital complex ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) with a large, bell-shaped median copulatory pore; seminal receptacles symmetrical, well developed. Urosomites 3 and 4 with row of robust spinules distally along dorsoventral margin. Anal somite ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B–D) with one pair of sensilla dorsally at base of anal operculum; transversal row of small spinules laterally; five strong spinules ventrally on posterior margin, near inner corner of base of each caudal ramus.
FIGURE 4. Elaphoidella paraaffinis sp. nov. Female: A, P1; B, P2; C, P3; D, P4; E, P5. Scale bar, 50 µm.
FIGURE 6. Elaphoidella paraaffinis sp. nov. Male: A, P1; B, P2; C, P3; D, P4; E, P5. Scale bar, 50 µm.
Anal operculum ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, D) large, with about 25 (range: 24–27) strong spinules along free margin; with an operculum margin reaching distal end of anal somite and spinules extending half of caudal ramus length.
Caudal rami parallel ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 B, C). Caudal ramus rectangular, as long as wide, with a small dorsal keel. Anterolateral accessory seta (I) absent. Setae II, III, VI, VII bare and thin. Anterolateral seta (II) inserted at about 1/ 3 of caudal ramus length. Posterolateral seta (III) inserted at 2/3 of caudal ramus length, slightly shorter than seta II, with two strong spinules near its base, inserted on ventral surface of caudal rami. Outer apical seta (IV) about four times as long as caudal ramus, spiniform, without a breaking plane. Inner apical seta (V) longest, swollen at its base, without a breaking plane. Inner accessory seta (VI) about 0.5 times as long as seta IV. Dorsal seta (VII) as long as seta II, inserted at half of caudal ramus length.
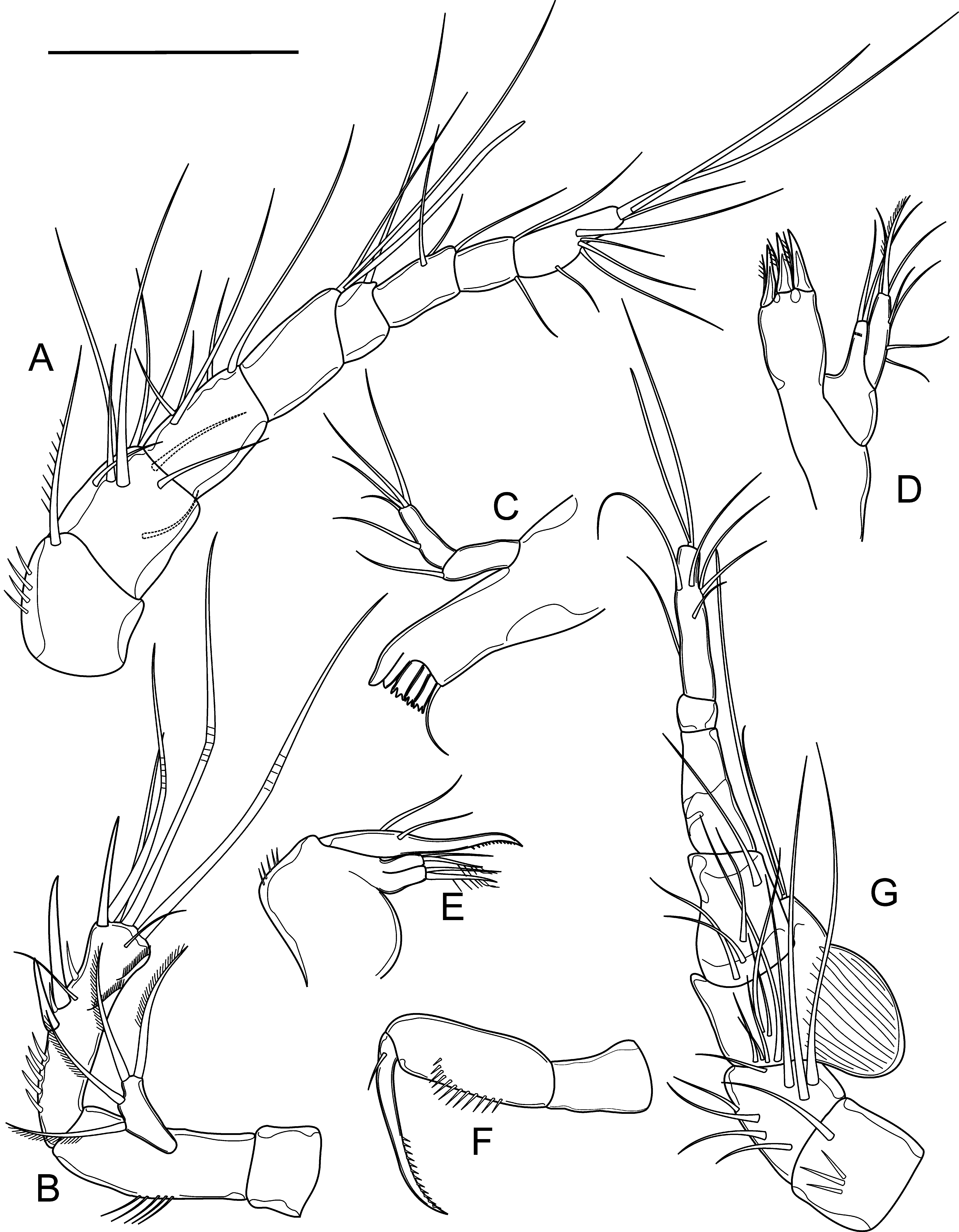
Antennule ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A) eight-segmented, not reaching posterior margin of cephalothorax. Aesthetasc on segment 4 reached middle of distal segment. Aesthetasc on segment 8 long and slim. Both aesthetascs fused with seta at its base (= acrotheck). Setal formula: 1, 9, 5, 2+aesthetasc, 1, 3, 2, 7+aesthetasc.
Antenna ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B) composed of coxa, allobasis, one-segmented Exp and Endp. Coxa slightly shorter than wide and unornamented. Allobasis about three times as long as wide, with five spinules along its outer margin. Exp with two apical and two subapical unipinnatae setae. Endp as long as allobasis, with two strong spines along outer margin at distal part; several strong spinules at proximal part of segment, and one strong spinule on each side of insertion of a distal lateral spine. Apically five elements: three geniculate setae, one normal smooth seta, one strong spine. External surface of Endp with thin seta inserted subapically.
Mandible ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C) robust, with five strongly chitinized teeth and one smooth seta on the dorsal side of gnathobase. Mandibular palp two-segmented; with seta on proximal segment and five setae on distal segment: four apically, and one laterally. All setae thin and smooth.
Maxillule ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 D) composed of robust praecoxa, coxa, and basis. Praecoxal arthrite with three strong spines and two short spiniform setae on arthrite base. Coxa with two smooth setae on cylindrical endite. Basis with one unipinnate and one smooth seta apically; Exp and Endp reduced to two smooth setae along inner margin of basis.
Maxilla ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 E) two-segmented; syncoxa with two endites, each with two setae. Basis drawn out into strong, beak-like apophysis, with few spinules distally; Exp and Endp reduced to two smooth setae.
Maxilliped ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 F) prehensile; comprising syncoxa, basis, and one-segmented Endp. Syncoxa unornamented. Basis about two times as long as wide, with a row of 12 spinules along its inner margin. Endp drown out into an unipinnate claw, as long as basis; with a small seta at its base.
P1 with three-segmented Exp and Endp; P2–P4 with three-segmented Exp and two-segmented Endp. An armature formula of P1–P4 is as follows (legend: inner-outer seta/spine; inner-apical-outer; Arabic numerals represent setae, Roman numerals represent spines):
Leg Coxa Basis Exopod Endopod
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 0-0 1-I 0-I 1-I 0-2+I-I 1-0 1-0 0-3-0 2 0-0 0-I 0-I 1-I 1- 2-II 0-0 2-2+I-0 ---- 3 0-0 0-1 0-I 1-I 2- 2-II 0-0 3- 1-I ---- 4 0-0 0-1 0-I 1-I 2- 2-II 0-0 2-1+I-0 ---- P1 Endp slightly longer than Exp (Fig. 4A). Coxa with rows of small spinules on its outer margin. Basis with thin inner seta and a slim outer spine; with spinules at base of both elements. Exp-1–3 similar in length, each with a strong outer spine. Exp-3 with a strong unipinnate spine and two long geniculate setae apically. Endp-1 long, slightly shorter than Exp-1 and Exp-2 combined, with unipinnate spiniform seta on inner margin. Endp-2 with thin and smooth seta on inner distal corner. Endp-3 with three setae apically: innermost seta thin, shortest; middle one geniculated, longest; outermost seta spiniform.
P2 (Fig. 4B) coxa ornamented as in P1. Basis with a spine and few spinules at its base. Exp-1 and Exp-2 with a strong spine on each of its outer margins. Exp-1 as long as Exp-2. Exp-2 with a long unipinnate seta on inner distal corner of this segment. Exp-3 2.5 times as long as wide; with two spines on its outer margin, two apical setae (outer seta unipinnate, inner one pinnate), and a long unipinnate seta on its inner margin. Endp-1 small, shorter than wide, without seta on its inner margin. Endp-2 2.5 times as long as wide, with a spine on its outer margin, two long pinnate setae apically and two short unipinnate setae on its inner margin.
P3 (Fig. 4C) coxa ornamented as P2; basis with thin and smooth seta on its outer margin. Exp-1 as long as wide; with a strong spine having a rounded tip on its outer margin. Exp-2 with a short smooth seta on inner margin and a strong spine with a rounded tip on outer margin. Exp-3 similar to P2 Exp-3, but with additional pinnate seta subapically on inner margin. Endp two-segmented, as long as Exp-1 and Exp-2 combined. Endp-1 small, shorter than wide, without seta on inner margin. Endp-2 about two times as long as wide, with a spine on outer margin, one long pinnate seta apically, one long pinnate seta and two short smooth setae on inner margin.
P4 (Fig. 4D) coxa with few spinules on outer margin. Basis with thin smooth seta on outer margin. Exp threesegmented, with one strong spine on outer margin of Exp-1 and Exp-2 and two strong spines on outer margin of Exp-3. Exp-1 about 1.3 times as long wide. Exp-2 as long as Exp-3, about 2.5 times as long as wide, with unipinnate seta on inner margin. Exp-3 with two unequal setae apically (inner pinnate, outer unipinnate), with one pinnate and one unipinnate seta on inner margin. Endp as long as Exp-1. Endp-1 small, shorter than wide, without seta on inner margin. Endp-2 two times as long as wide, with a spine and long pinnate seta apically and two unipinnate setae on inner margin.
P5 (Fig. 4E) Exp and baseoendopod well separated. Baseoendopod about as long as Exp, with four long, strong spiniform setae; second outer one (III) longest, followed by second inner one (II), innermost seta (I) and outermost seta (IV). Outer lateral seta on baseoendopod long and smooth. Exp small, sub-oval; with four strong spiniform setae; second inner seta (II) longest followed by second outer seta (III), innermost seta (I) and outermost seta (IV).
P6 ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) fused, small, forming a simple plate, with two subequal setae on each side of copulatory pore; inner one bare, and outer one pinnate.
Egg sac: holotype with 15 eggs; other females with 13–16 eggs (n = 5).
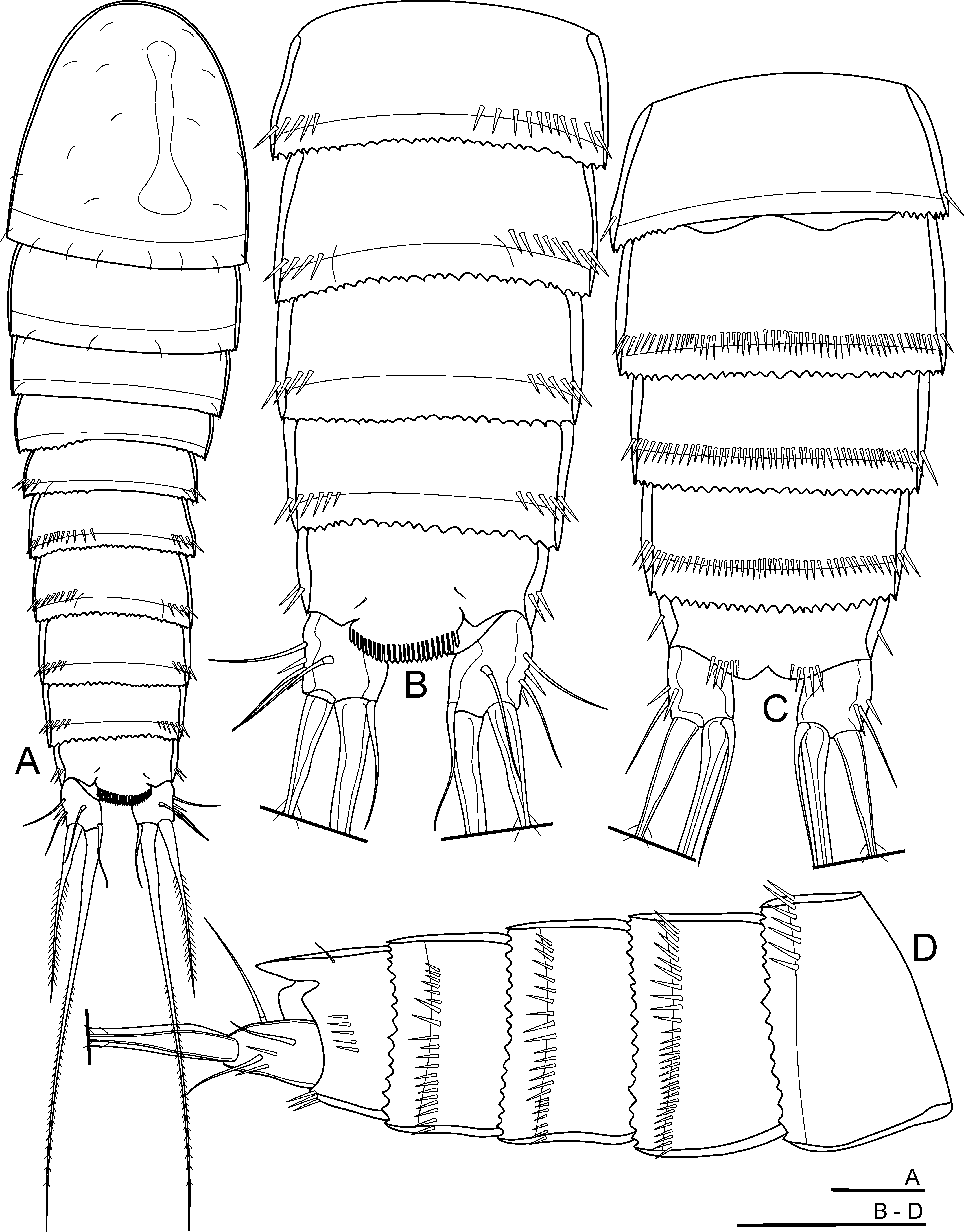
Description of male. Slightly smaller than female ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); body length, measured from anterior margin of rostrum to posterior margin of caudal rami, 460–500 µm (mean = 480 µm, n = 5); preserved specimens colourless; naupliar eye not discernible. Cephalothorax with a well discernible integumental window. Habitus similar to female; posterior margins of prosomites and urosomite 1 serrated laterally; urosomites 2–5 serrated along entire free margins. Urosomites 3–5 ventrally with a continuous row of unequal spinules along free margin ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 C). Anal somite, caudal rami, antenna, mouthparts and P1 similar to those of female ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 B–F, 5A–D, 6A). Anal operculum well developed, with about 23 (range 22–24) strong spinules on free margin, reaching middle of caudal rami ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 B, D).
Antennule ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 G) seven-segmented, with three strong spinules on first segment. Setal formula: 1, 8, 7+aesthetasc, 4, 0, 0, 7+aesthetasc. First aesthetasc cylindrical, slightly curved, with a rounded tip, reaching distal end of antennule. Distal aesthetasc shorter than proximal one, about 1.2 times as long as terminal segment. Both aesthetascs combined with a seta as an acrotheck.
P2 (Fig. 6B) coxa, basis and Exp as in female. Endp two-segmented, Endp reaching middle of Exp-2. Endp-1 small, shorter than wide, with no seta on inner margin. Endp-2 about 2.5 times as long as wide, with two long setae apically, reaching well above Exp-3; with two pinnate setae on inner margin: distal one as long as segment bearing it, longer than proximal seta.
P3 (Fig. 6C) coxa, basis and exopodite as in female. Endp three-segmented, as long as Exp-1 and Exp-2 combined. Endp-1 shorter than wide, with no seta on inner margin. Endp-2 with a short apophysis shaped in a harpoon-like tip, reaching middle of Exp-3. Endp-3 about two times longer than wide, with two pinnate setae apically (inner one as long as segment bearing it; outer one about three times as long as inner one).
P4 (Fig. 6D) coxa, basis and exopodite as in female. Endp two-segmented, short, as long as Exp-1. Endp-1 shorter than wide, with no seta on inner margin. Endp-2 about two times as long as wide; with a spine and pinnate seta apically, smooth spiniform seta on inner margin, and two strong spinules on outer margin.
Detailed ornamentation of P1–P4 as in Figs. 6A–D.
P5 (Fig. 6E) with a distinctly separated Exp and baseoendopod. Baseoendopodal lobe small, with smooth seta on outer margin. Exp small, as long as wide, with three spiniform and one smooth seta. Innermost (I) and outermost (IV) seta shortest, slightly longer than segment. Second inner (II) seta longer than second outer (III) seta, about four times as long as segment bearing it. Baseoendopod with no elements.
P6 ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 C) represented by a simple bilobate plate, with a smooth free margin.
Variability. Not found, except for anal operculum with 22–24 strong spinules along free margin in males and 24–27 in females.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.