Ablabesmyia (Sartaia) metica Roback, 1983
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.182745 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6232640 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BA8A18-6569-FFC5-FF68-32FA04754F5A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ablabesmyia (Sartaia) metica Roback, 1983 |
| status |
|
Ablabesmyia (Sartaia) metica Roback, 1983 View in CoL
( Figs 1–20 View FIGURES 1 – 7 View FIGURES 15 – 20 )
Material examined: BRAZIL: São Paulo State, São Carlos, UFSCar, Mayaca pond, 2 males with associated pupa and larva exuviae (slide-mounted in Euparal), 13.iv.2004, C.S.N. Oliveira; as previous except 2 males, 01.xii.2002, S. Trivinho-Strixino; São Paulo State, Luís Antônio, Estação Ecológica Jataí, Óleo pond, 2 males, 25.vii.2003, S. Trivinho-Strixino.
Diagnostic characters. The male lacks blade on the volsella (“aedeagal complex” Roback 1985), and the gonostylus is shorter and more sinuate than in other known Ablabesmyia species. In addition A. (S.) metica has lateral tufts of setae on the ninth abdominal segment.
The pupa has the aeropyle tube ending apically on the thoracic horn and the apical nipple is evident. It can be separated from other Ablabesmyia species in having shagreen on abdominal tergites consisting of simple spines in arches and thoracic horn with dense, fine, oval-type of reticulation.
The larva has palp with three segments, two sclerotized and one membranous. It can be separated from other Ablabesmyia species by having the margin of ligula concave and toothed, by having six apical setae on procercus and a procercus L/W of 3.2–3.7.
Male (n = 6)
Total length 2.06–2.74, 2.28 mm. Wing length 1.36–1.71. 1.47 mm. Total length / wing length 1.51–1.60, 1.55. Wing length / length of profemur 2.60–2.69, 2.65.
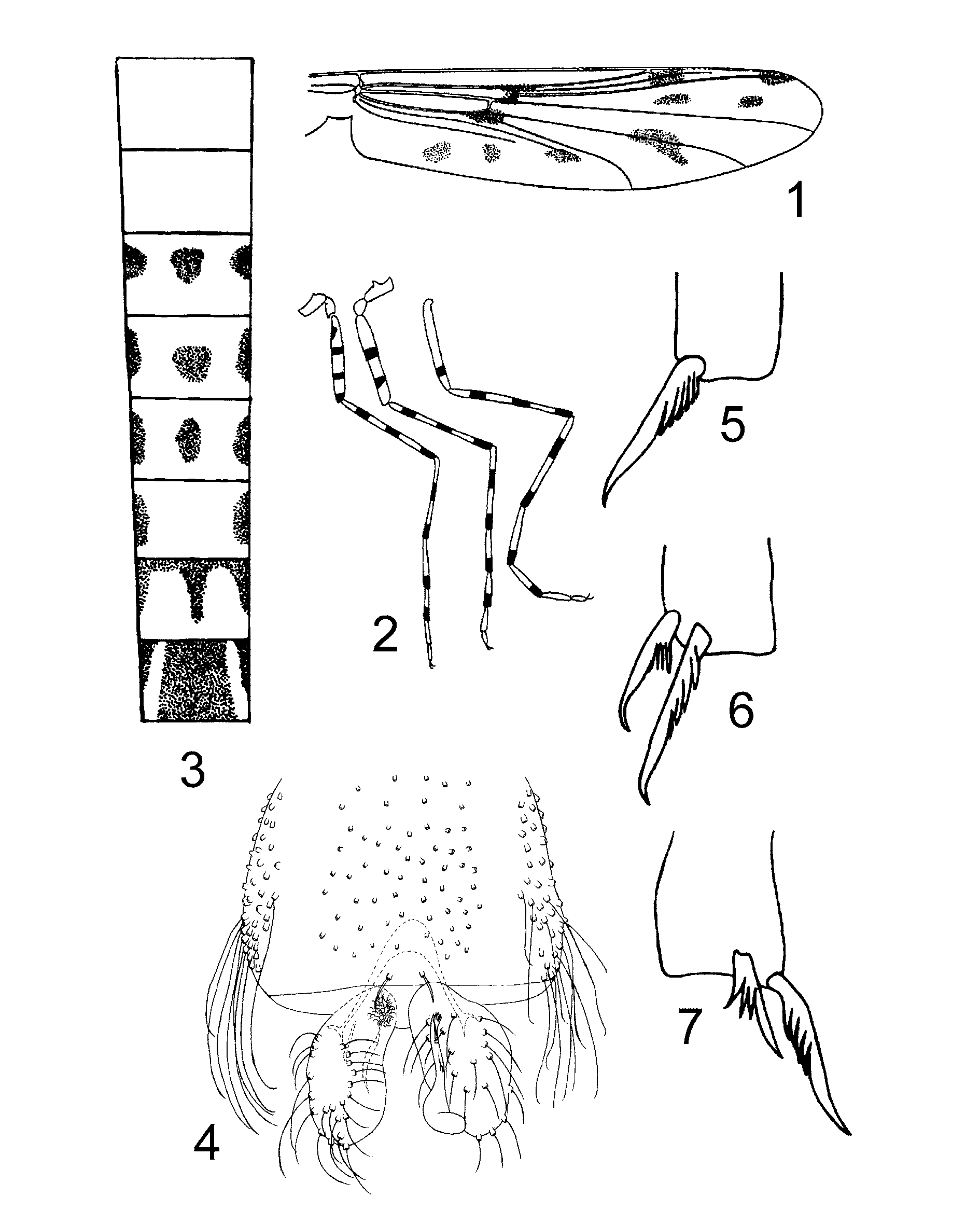
Coloration. Head and thorax brown. Wing membrane transparent, veins darker, with six brown spots and four dark brown spots on r-m, m-cu, R1-R3, and R4+5 as in Figure 1 View FIGURES 1 – 7 . Legs yellow with brown bands ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ). Forefemur with four bands: one incomplete sub-basal, two medially and one apically. Midfemur with two bands: one medially and one incomplete preapically. Hind femur with single preapical band. All tibiae with three bands: one sub-basal, one medially and one apically. First tarsomeres with two bands: one medially and one apically; second and third tarsomeres with single band apically; fourth and fifth tarsomeres entirely brown. Abdomen with brown spots ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ). Hypopygium yellow ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ).
Head. AR 1.24–1.47, 1.37; flagellum 800–1062, 907 µm long. Palp segment lengths (in Μm): 35–50, 48; 60–92, 77; 100–122, 113; 105–130, 119; 182–225, 207.
Thorax. Acrostichals 50, dorsocentrals 11–17, supraalars 8–10, humeral 1. Scutellum with 50–55 setae in double row.
Wing ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ) 0.45–0.50, 0.46 mm wide. Costal extension 83–146, 120 µm long.
Legs. Foretibia ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ) with single pectinate spur, 33–47 34 Μm long; midtibia ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ) with two pectinate spurs, 30–33, 33 and 47–55, 50 Μm long; hind tibiae ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ) with two pectinate spurs, 33–43, 35 and 52–55, 53 Μm long. Length and proportion of legs as in Table 1.
Hypopygium ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ). Tergite IX with two dorsal setae. Transverse sternapodeme 30–21 Μm long; phallapodeme 60–46 Μm long. Gonocoxite 105–140, 124 Μm long. Gonostylus 73–100, 86 Μm long, with slender subapical seta; megaseta 15–22, 18 Μm long, spoon-shaped. HR 1.10–1.86, 1.47.
Pupa (n = 2)
Coloration. Pale yellow. Thoracic horn with brown respiratory atrium.
Cephalothorax. Wing sheath 0.9–1.0 mm long. Thoracic horn (Fig. 8) oval, 318–407 Μm long, 181–233 Μm wide, reticulation of respiratory atrium indistinct, lumen homogeneous, preapical papilla and plastron plate absent, aeropyle tube sinuate with single membranous lobe, 110 Μm long with club-shaped apex (Fig. 9), basal lobe protuberant. Thoracic comb with 8–9 conical teeth. Frontal apotome dome-shaped as in Figure 10.
FIGURES 8–14. Ablabesmyia (Sartaia) metica Roback, 1983 , pupa. 8. Thoracic horn with basal lobe and medial row of teeth. 9. Apex of thoracic horn showing aeropyle tube. 10. Frontal apotome. 11. Abdomen, left: dorsal aspect, right: ventral aspect. 12. Shagreen. 13. Anal lobe and genital sac. 14. Setal arrangement on AIV, left: dorsal aspect with dorsal setae (D1-6), lateral seta (L1) and dorsal pore (DP), right: ventral aspect with ventral setae (V1 and V2) and lateral setae (L2).
Abdomen (Fig. 11). Tergites entirely covered with shagreen consisting of small spinules in arcs. (Fig. 12). Tergite I with elongate scar. Chaetotaxy of abdomen as in Figure 4 View FIGURES 1 – 7 . Segment IV (Fig. 14) with 7 dorsal setae, 2 lateral setae and 2 ventral setae. Tergites VI–VII with single protuberance on each side (Fig. 11). Segment VII with four taeniae, LS1 ratio 0.3 from anterior margin. Segment VIII with five taeniae, LS1 ratio 0.2–0.3 from anterior margin. Anal lobe (Fig. 13) 368–384 Μm long, triangular, with two taeniae, LS1 ratio 0.2–0.3 from anterior margin, inner margins with fine spinules. Male genital sac (Fig. 13) elongate, 200–203 Μm long.
4th instar larva (n = 2)
Coloration. Pale yellow. Apex of mandible, ligula and postoccipital margin brown. Most apical claws on posterior parapod yellow, 2 claws brown.
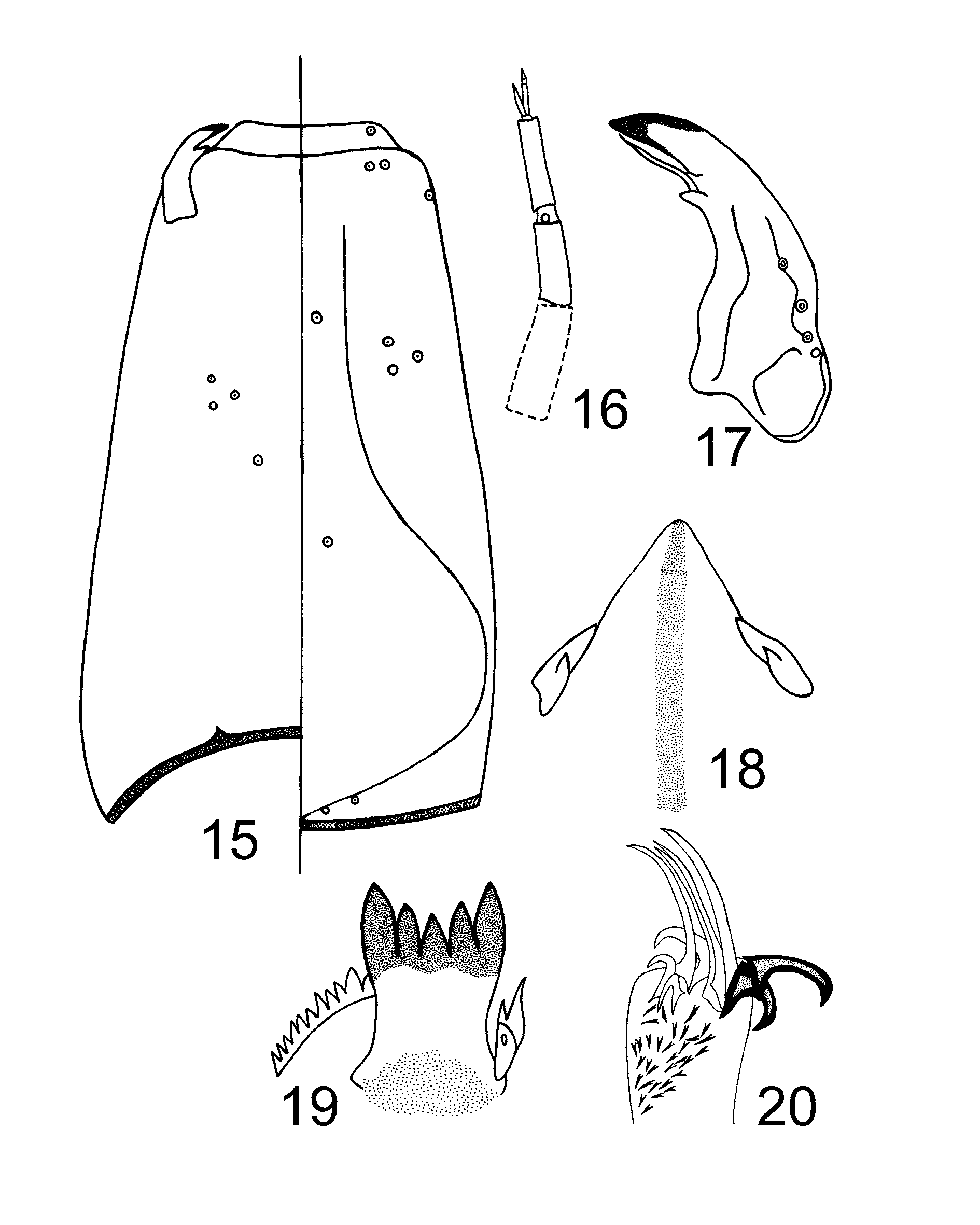
Head capsule ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ), elongate; cephalic index 0.68–0.70. Chaetotaxy as in Figure 15 View FIGURES 15 – 20 .
Antenna. First antennal segment 312–325 Μm long, with ring organ 175–181 Μm from base.
Maxilla ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ). Palp with 3 segments, palp segment lengths (in Μm): 20–44, 26–32, 32–35. Third palp segment membranous. Ring organ 46–75 Μm from base.
Mandible ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ), 112–120 Μm long, with 3 lateroventral setae. Sensilium campaniforme 86–90 Μm from apex. Basal tooth bifid with seta subdentalis, A1/MD 2.7.
Mentum ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ). Dorsomental teeth bifid and pseudoradula uniformly granulate.
Hypopharyngeal complex ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ). Ligula 52–62 Μm long, with concave row of 5 teeth. MA 24 Μm long; It/O = 0.8, Mt/O = 0.7–0.8. Paraligula bifid, 33–35 Μm long, inner tooth 29 Μm long, shorter than outer tooth. Pectin hypopharyngis with 12 teeth, the seventh and the tenth larger than others.
Abdomen. Without lateral fringe. Procercus 3.2–3.7 times as long as wide, with six 343–500 Μm long anal setae. Supraanal setae simple, 223–337 Μm long. Posterior parapods ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 15 – 20 ) with four hooked claws and eleven simple apical claws.
fe ti ta1 ta2 ta3 ta4
p1 553 600–615 461–470 307–323 230 123–138
p2 569–615 495–553 538–600 307–350 230–246 153
p3 569–575 661–668 630 338 246 169
continued.
ta5 LR BV SV BR
p1 95–107 0.76 2.05–2.13 0.76–0.77 2.24c p2 107 1.00 2.01–2.06 0.70–0.77 2.45
p3 123 0.94–0.95 2.12–2.13 0.81–0.82 1.50–2.45
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.