Metacostana, Domahovski & Cavichioli, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2023.889.2245 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:52E11625-6E26-4E4F-8B15-05195087BAB4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8271529 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F6AF5C63-2930-461A-AF9F-F55148F83EFE |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:F6AF5C63-2930-461A-AF9F-F55148F83EFE |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Metacostana |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Genus Metacostana View in CoL gen. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:F6AF5C63-2930-461A-AF9F-F55148F83EFE
Type species
Metacostana cornuta View in CoL gen. et sp. nov.
Diagnosis
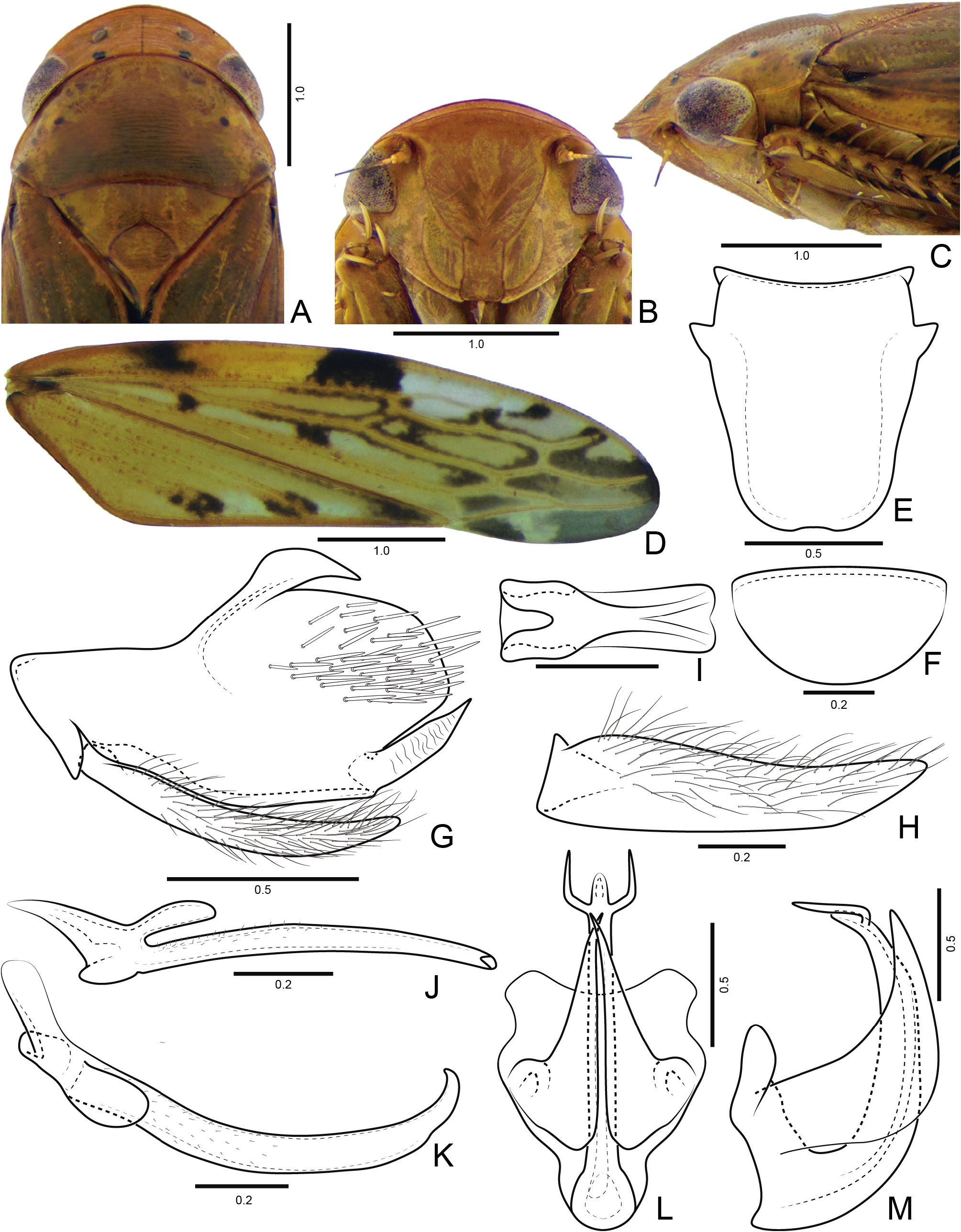
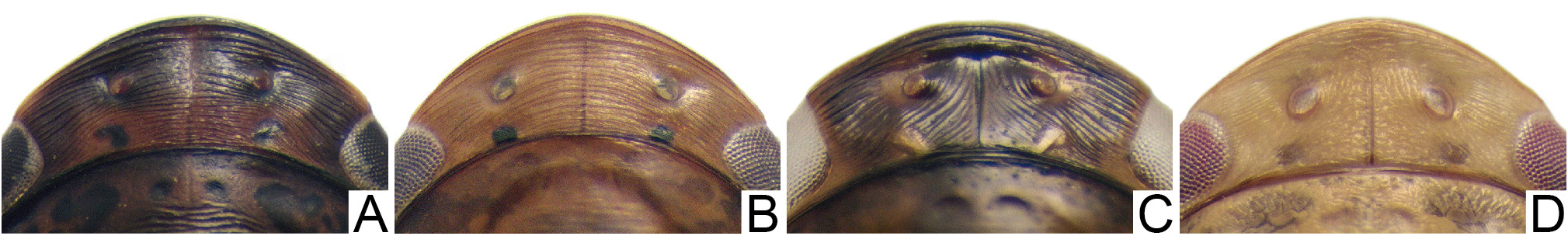
Head ( Fig. 26A View Fig ), in dorsal view, median length of crown less than half interocular width; crown surface with fine parallel transverse striations ( Fig. 25B View Fig ); ocelli equidistant between median line and eyes; in lateral view ( Fig. 26C View Fig ), crown-face transition thin, with three transverse carinae. Forewing ( Fig. 26D View Fig ) without extra crossveins. Metatibia row AD with intercalary setae between macrosetae. Male sternite VIII ( Fig. 26E View Fig ) long, fully hiding subgenital plates in repose. Male pygofer ( Fig. 26G View Fig ) with ventroposterior process. Subgenital plate ( Fig. 24H View Fig ) bearing filiform setae. Aedeagus ( Fig. 26L–M View Fig ) with apodemal processes. Female first and second valvulae of ovipositor ( Fig. 27D, F View Fig ) not broadened medially and curved ventrally. Second valvula ( Fig. 27F View Fig ) with weakly developed dorsal protuberance; dorsal margin ( Fig. 27F View Fig ) with prominent regular teeth on apical third.
Etymology
The new genus name is feminine and combines the prefix ‘meta’ (‘different’) + part of the name Costanana , a closely related genus of Gyponini .
Description
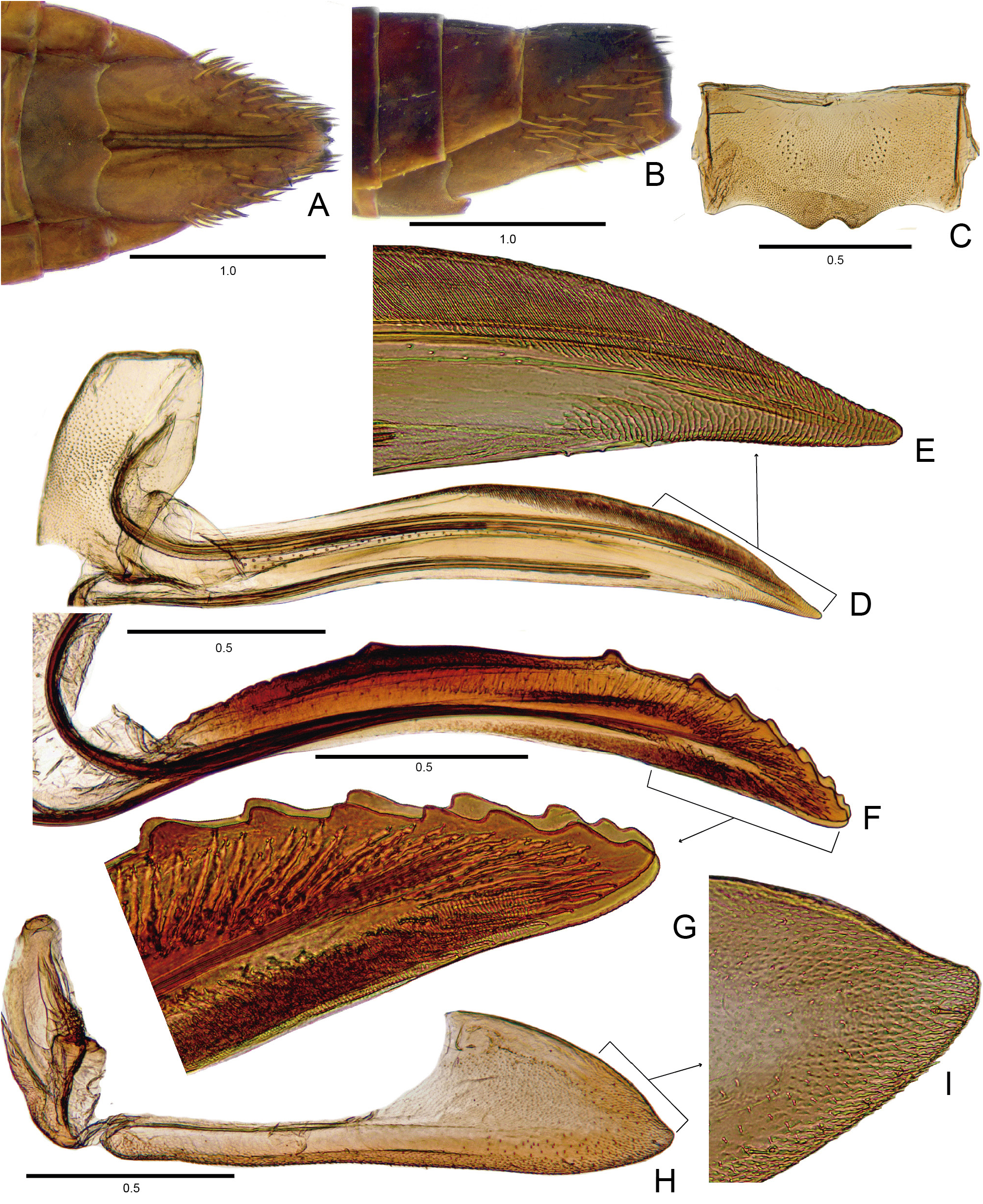
STRUCTURE. Head in dorsal view ( Fig. 26A View Fig ): slightly produced anteriorly, median length of crown less than half interocular width; crown surface with fine parallel transverse striations; anterior margin broadly rounded and parallel to anterior margin of pronotum, slightly extending over eye margin; transocular width of head narrower than humeral width of pronotum; ocelli equidistant between median line and eyes and slightly closer to anterior than posterior margin of crown; in frontal view ( Fig. 26B View Fig ), frons longer than wide, flat, not excavated below anterior margin of crown and with a few thin striations, texture shagreen; frontogenal suture distant from eye margins by maximum width of clypeus, not surpassing antennal ledge; antennal ledge carinated, obliquely downwards in relation to frons and extending over frons by short distance; epistomal suture indistinct medially; gena with ventrolateral margins slightly convex at midlength and weakly excavated near eye; maxillary plate produced ventrally as far as clypeus apex; clypeus not inflated, ca 1.5× as long as wide, lateral margins weakly divergent apically, apex emarginated; in lateral view ( Fig. 26C View Fig ), crown-face transition thin, with three transverse carinae. Pronotum in dorsal view ( Fig. 26A View Fig ): transversely striated except near anterior margin; lateral margins convergent anterad; in lateral view ( Fig. 26C View Fig ), moderately declivous; head and pronotum in continuous slope. Scutellum ( Fig. 26C View Fig ), not inflated. Forewing ( Fig. 26A View Fig ) without extra crossveins; venation distinct; M vein with segment after divergence between R+M and before cross vein m-cu 1, as long as length of m-cu 1; outer anteapical cell short, almost half length of central and inner anteapical cells; five apical cells (R1 vein present); appendix well developed and involving first and second apical cells; apex slightly tapered. Profemur elongated, approximately 3.5× as long as wide; AD, AM, and PD rows reduced and poorly defined, with exception of apical setae AD 1, AM 1 and PD 1 respectively; AV row with 3 short setae; PV row with only an apical seta present. Protibia, in cross-section, more or less cylindrical, with longitudinal carina adjacent to PD row weakly developed; AV row formed by long setae, gradually increasing in thickness and length towards apex; AD formed by many small undifferentiated setae; PD row with 3 long setae and intercalary undifferentiated setae; dorsal surface with apical setae AD 1 and PD 1 developed; PV row with 4 setae. Metafemur with setal formula 2:2:1. Metatibia rows PD, AD, and AV with 22–23, 12–13, and 14–15 macrosetae, respectively; AD row with intercalary setae between macrosetae; PV row with setae of apical half formed by sequence of 1 thicker and 3–4 thinner setae, ending with a thick seta. Metatarsomere I inner row of plantar surface with 5–6 setae, outer row very reduced in size; apex with 3 patellae flanked by 1 tapered lateral seta on inner and 1 on external corner. Metarsomere II pecten with 2 platellae flanked by 2 tapered lateral setae on inner and 1 on external corner.
MALE TERMINALIA. Male sternite VIII ( Fig. 26E View Fig ) long, fully hiding subgenital plates. Male pygofer ( Fig. 26G View Fig ) with ventroposterior process. Subgenital plate ( Fig. 26H View Fig ) not more membranous apically than basally, with filiform setae on ventral surface and outer margin. Connective ( Fig. 26I View Fig ) linear. Aedeagus ( Fig. 26L–M View Fig ) with apodemal processes.
FEMALE TERMINALIA. First and second valvulae of ovipositor ( Fig. 27D, G View Fig ) not broadened medially and curved ventrally. First valvula ( Fig. 27D View Fig ) with ventral interlocking device long, reaching the apical fourth. Second valvula ( Fig. 27G View Fig ) with weakly developed dorsal protuberance; dorsal margin ( Fig. 27G View Fig ) with prominent regular teeth on apical third.
Distribution
Southern Brazil.
Remarks
The crown of Metacostana cornuta gen. et sp. nov. transversely striated and the anterior margin defined are features present in the genera Acuthana , Costanana , Domahovana , Dumorpha , Delongiana Domahovski et al., 2020 , Nullana DeLong, 1976 , Ponana Ball, 1920 , Regalana DeLong & Freytag, 1975 , and some species of Polana DeLong, 1942 . Among these genera, the presence of apodemal processes on the aedeagus is shared only with Dumorpha , Ponana and some subgenera of Polana , and the male sternite VIII being well produced posterad, often hiding the subgenital plates, is shared with Acuthana , Costanana , Domahovana , Dumorpha and some species of Polana . Probably the unusual ventrally curved shape of the ovipositor will place Metacostana gen. nov. as sister group of Acuthana , which was the only known genus of Gyponini with this feature. The new genus can be differentiated from Acuthana by the color, with black and yellow maculae (uniformly yellowish-brown in Acuthana ), the absence of punctuations and reticulations on the forewings, the male pygofer with process on the ventroapical margin, the subgenital plate not tapered apically, the connective liner, the presence of apodemal processes on the aedeagus, the most strongly curved ovipositor, with smaller dorsal protuberance on the second valvulae, and the apex without denticles on the ventral margin. Unfortunately the ovipositor of females of Dumorpha is unknown, but the new genus can be separated by the color (pale yellow without black markings or only a few in Dumorpha ); the ocelli smaller and equidistant between eye and midline (closer to the eye margin in Dumorpha ), the presence of a process on the ventroapical margin of the male pygofer, the connective linear shape, and the atrial processes of the aedeagus being broader. Compared to Costanana , the new genus can be differentiated due to the metatibia row AD having intercalary setae between the macrosetae (also present in Dumorpha ), the presence of apodemal processes on the aedeagus and the different morphology of the female ovipositor.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Auchenorrhyncha |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Iassinae |
|
Tribe |
Gyponini |