Garra kalpangi, Nebeshwar & Bagra & Das, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11609/JoTT.o1703.2353-62 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5A0E6018-1C49-487B-8DAA-E707CF1601DF |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/26B93981-2EA3-406C-B866-8EAFF43FB005 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:26B93981-2EA3-406C-B866-8EAFF43FB005 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Garra kalpangi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Garra kalpangi View in CoL sp. nov.
( Image 1 View Image 1 )
Material examined
Holotype: 18.vii.2005, 60.0mm SL, location 27025 ’54”N & 93046 ’42”E, altitude 843m, Kalpangi River at Yachuli (Brahmaputra River system), Lower Subansiri District, Arunachal Pradesh, India, coll. Kenjum Bagra, RGUMF-0006.
Paratype: 9 exs., same data as holotype, RGUMF-0007, 50.0– 72.4 mm SL ,
Diagnosis Garra kalpangi sp. nov. is characterized from
its congeners of the Himalayan foothills by the combination of characters:two pairs of barbels,a poorly developed proboscis represented by a squarish area in front of the nostrils and 16 circumpeduncular scales. It is closely similar to G. gravelyi , G. rotundinasus and G. elongata in having a weakly developed proboscis on the snout. Garra kalpangi sp. nov. can be differentiated from G. gravelyi in having branched dorsal-fin rays 8 (vs. 7), branched pectoral-fin rays 10– 12 (vs. 13), predorsal scales 10–11 (vs. 8–9), absence (vs. presence) of indistinct black spots at the bases of the branched dorsal-fin rays, absence (vs. presence) of lateral stripes on side of body. Garra kalpangi sp. nov. can be differentiated from G. rotundinasus in having branched pectoral-fin rays 10–12 (vs.13–15), lateral line scales 32–33 (vs. 36–37), scales between vent and anal-fin origin 3 (vs. 5), transverse scale rows above lateral line 3½ (vs. 2½), transverse scale rows below lateral line 3½–4 (vs. 2½–3), circumpeduncular scales 16 (vs. 12), absence (vs. subtle presence) of lateral stripe along lateral line. Garra kalpangi sp. nov. can be differentiated from G. elongata in having lateral line scales 32–33 (vs. 40–41), predorsal scales 10–11 (vs. 14–15), branched dorsal-fin rays 8 (vs.7), absence (vs. presence) of transverse groove at tip of snout, absence (vs. presence) of pleated papilliferous fold at corner of mouth, absence (vs. presence) of a wide submarginal band on dorsal fin, absence (vs. presence) of a longitudinal median black band on caudal fin.
Description
Measurements and counts taken from 10 specimens, 50.0– 72.4 mm SL are given in Table 1. General body
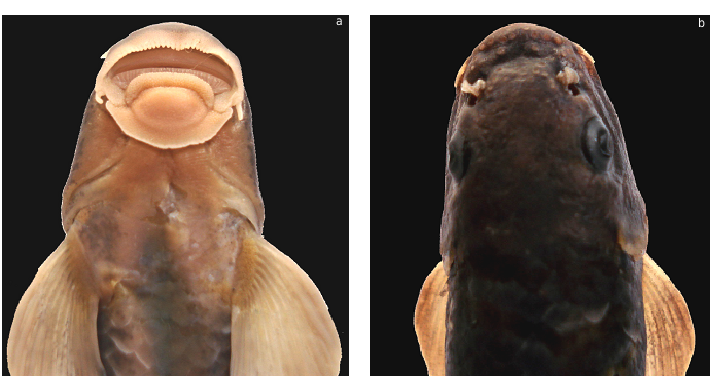
appearance in Image 1 View Image 1 and morphology of the mental adhesive disc and head dorsum are shown in Images 2a–b View Image 2 respectively.
Body elongate, compressed laterally, more on caudal peduncle region; dorsal profile smoothly arched to dorsal-fin origin, then straight from posterior end of dorsal-fin base to caudal–fin base; ventral profile flat from head to chest, then more or less round up to pelvic-fin origin, and straight from pelvic to caudal-fin base. Head small, more or less depressed with a convex interorbital space; height less than length; width greater than height. Snout blunt, without transverse groove on tip, with a few minute to large tubercles across its tip and lateral sides anterior to nostrils; sublachrymal groove free from lateral groove of rostral cap; a poorly developed proboscis represented by a squarish area in the front of the nostrils; rostral lobe absent. Eyes placed dorsolaterally in middle of head.
Two pairs of barbels; rostral ones anteroventrally located, shorter than eye diameter; maxillary ones at corner of mouth, shorter than rostral ones. Rostral cap well developed, moderately crenulated, and with a wide papillate margin; separated from the upper jaw by a deep groove and laterally continuous with lower lip by a flat papillate connective tissue. No upper lip in the form of papillose tissue and no papillose fold in the corner of mouth. Upper jaw entirely covered by rostral cap. Lower lip modified into a mental adhesive disc. Disc elliptical, shorter than wide; anterior margin modified to form a transverse, flat, fleshy and crescentic skin fold covered by numerous tiny papillae; anteriorly separated from lower jaw by a deep groove running along lower jaw and posteriorly bordered in a deep groove with central callous pad; lateral and posterior margin surrounding central callous pad papillate and free; posteriormost margin not reaching vertical from posterior margin of eye.
Dorsal fin with 2(4), 3(5) simple and 8(9) branched rays; last simple ray shorter than or equal to HL; distal margin slightly concave; originated closer to snout tip than to caudal-fin base, inserted anterior to pelvic fin; first and second branched rays longest, last branched ray not extending to vertical from anal-fin origin. Pectoral fin with one simple and 10(3), 11(3), 12(3) branched rays, reaching beyond midway to pelvic–fin origin; its length less than or equal to HL; subacuminate margin; fourth branched ray longest. Pelvic fin with one simple and 7(3), 8(6) branched rays, reaching beyond midway to anal-fin origin, surpassing the vent; its outer margin blunt; second branched ray longest. Anal fin short with 2(6), 3(3) simple and 5(9) branched rays; first branched ray longest, straight posterior margin; tip extending to base of caudal fin or slightly shorter; origin of anal fin closer to caudalfin base than to pelvic–fin origin. Caudal fin deeply emarginate; lobe tips pointed, 10 th ray shortest; lobes equally long or lower slightly longer.
Lateral line complete with 32(2), 33(7) scales. Scales in transverse row above lateral line 3½(9) and below lateral line 3½(8), 4(1). Circumpeduncular scales 16(9). Predorsal scales 10(6), 11(3); scales arranged regularly. Long axillary scale at base of pelvic fin reaching beyond its base. A row of 3 scales between vent and anal-fin base.
Total vertebrae 31(2); abdominal vertebrae 16(2); caudal vertebrae 12(2). Gill rakers thin and weakly developed 11(1), 12(1). Air chamber bipartite; anterior chamber oval; posterior one small and conical, about 2 ∕ 3 length of anterior chamber.
Colour in preservative
Dorsum and sides of head dark gray; head, chest, and abdomen yellowish. Dorsal, anal, pelvic, and pectoral fins grayish-white. Caudal fin light grayish with a thin, short marginal stripe each on tip of upper lobe dorsally and on tip of lower lobe ventrally; in three specimens, with more or less indistinct grayish wide band along middle rays. A black spot at the upper angle of gill opening.
Etymology
Name is given as noun in apposition after the name of the River Kalpangi in Yazali, Lower Subansiri District , Arunachal Pradesh from where the specimen was first collected .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |