Congochromis, STIASSNY & SCHLIEWEN, 2007
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1206/0003-0082(2007)3576[1:CANCGT]2.0.CO;2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9447E641-4CA3-4A29-9F1A-2D71F62411DD |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/26AC1267-F7CD-4B89-B9F7-DD8F78A932FE |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:26AC1267-F7CD-4B89-B9F7-DD8F78A932FE |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Congochromis |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Congochromis View in CoL View at ENA , new genus
Type species: Congochromis squamiceps (Boulenger, 1902) [Type locality: Lindi , Lindi River, Upper Congo, Zaire (Democratic Republic of Congo)] .
Included species: C. dimidiatus (Pellegrin, 1900) , C.
sabinae (Lamboj, 2005), C. pugnatus , n.sp.
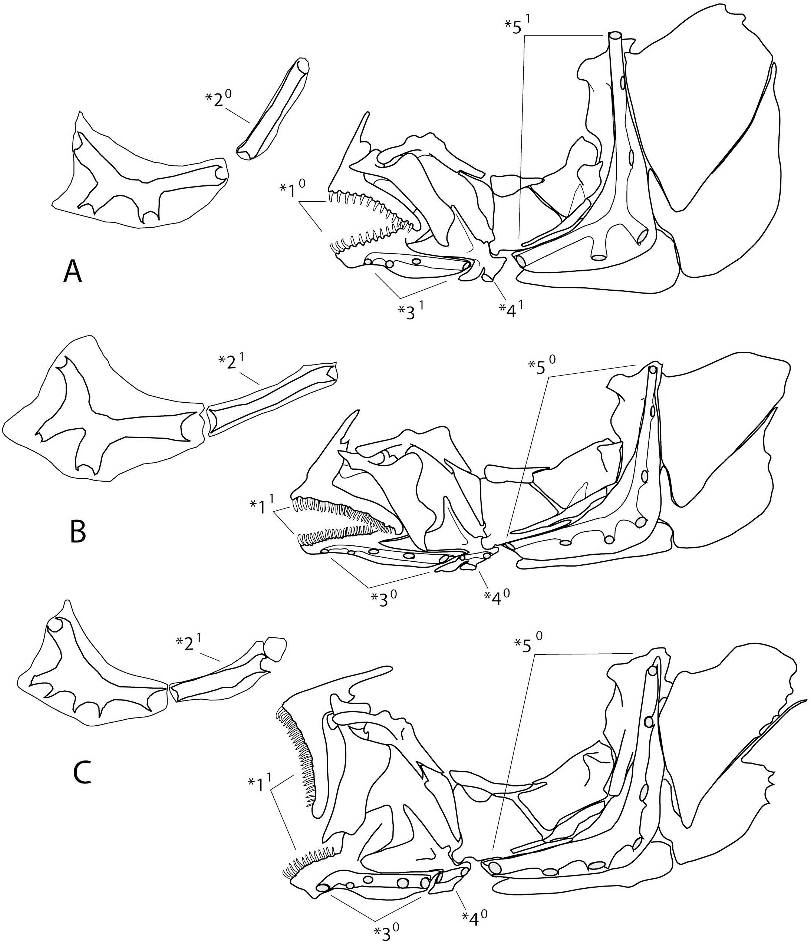
Congochromis is diagnosed by the following combination of apomorphic features: four pores in the dentary laterosensory canal ( fig. 1 View Fig , *3 1 vs. five pores, *3 0), absence of a laterosensory canal in the angulo-articular ( fig. 1 View Fig , *4 1 vs. *4 0), and six pores in the preopercle laterosensory canal ( fig. 1 View Fig , *5 1 vs. seven pores, *5 0).
The following combination of features distinguishes Congochromis from Nanochromis : only the last three to five pored scales of the upper lateral line are contiguous with the dorsal-fin base (vs. at least the posterior half of the upper lateral line contiguous); fully scaled nape, and partially scaled chest and cheek (vs. an asquamate nape, chest, and cheek); jaw teeth relatively robust unicuspids, not closely spaced (vs. extremely fine, closely spaced unicuspids); and the presence of a small, supraneural bone (vs. absence).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.