Sinoxylon anale Lesne, 1897
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5091.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FA12D38D-EBF9-4EA1-A413-A203A9FF4EFB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5864056 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6D613513-FFD8-CB4B-FF03-FF29FDF8BFBC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sinoxylon anale Lesne, 1897 |
| status |
|
Sinoxylon anale Lesne, 1897 View in CoL
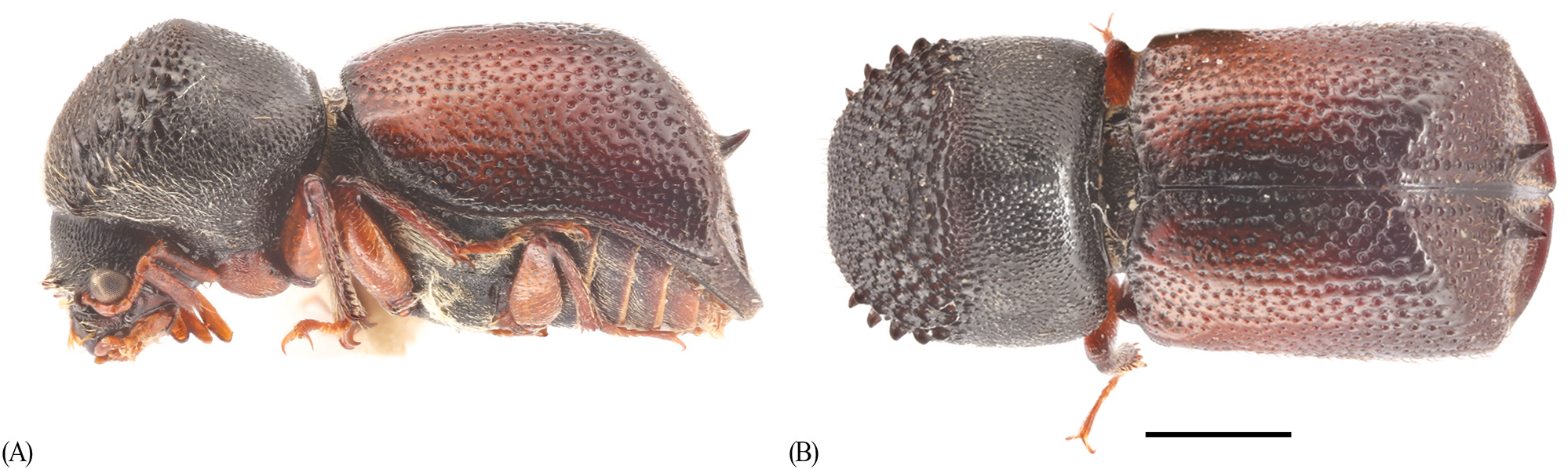
Fig. 25 View FIGURE 25 (A, B)
Sinoxylon anale Lesne, 1897: 21 View in CoL .
Distribution in China. Recorded from most of the southern Provinces including Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hunan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Yunnan ( Hua 2002).
Other distribution. Cosmopolitan in tropical and subtropical areas.
Host Plants. Recorded from numerous host trees and bamboos ( Beeson & Bhatia 1937; Hutacharern & Tubtim 1995). The adults can cause damage by boring into green shoots and twigs for maturation feeding or hibernation. The species is a major pest in rubber plantations in Thailand ( Kangkamanee et al. 2011), and economically important in India ( Beeson & Bhatia 1937).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Bostrichinae |
|
Tribe |
Sinoxylini |
|
Genus |
Sinoxylon anale Lesne, 1897
| Zhang, Yi-Feng, Meng, Ling-Zeng & Beaver, Roger A. 2022 |
Sinoxylon anale
| Lesne 1897: 21 |