Bosmina (Sinobosmina) fatalis Burckhardt, 1924
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.214313 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5680425 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B687AA-FFA4-5A56-25DC-9C32FB47FF11 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bosmina (Sinobosmina) fatalis Burckhardt, 1924 |
| status |
|
11. Bosmina (Sinobosmina) fatalis Burckhardt, 1924 View in CoL
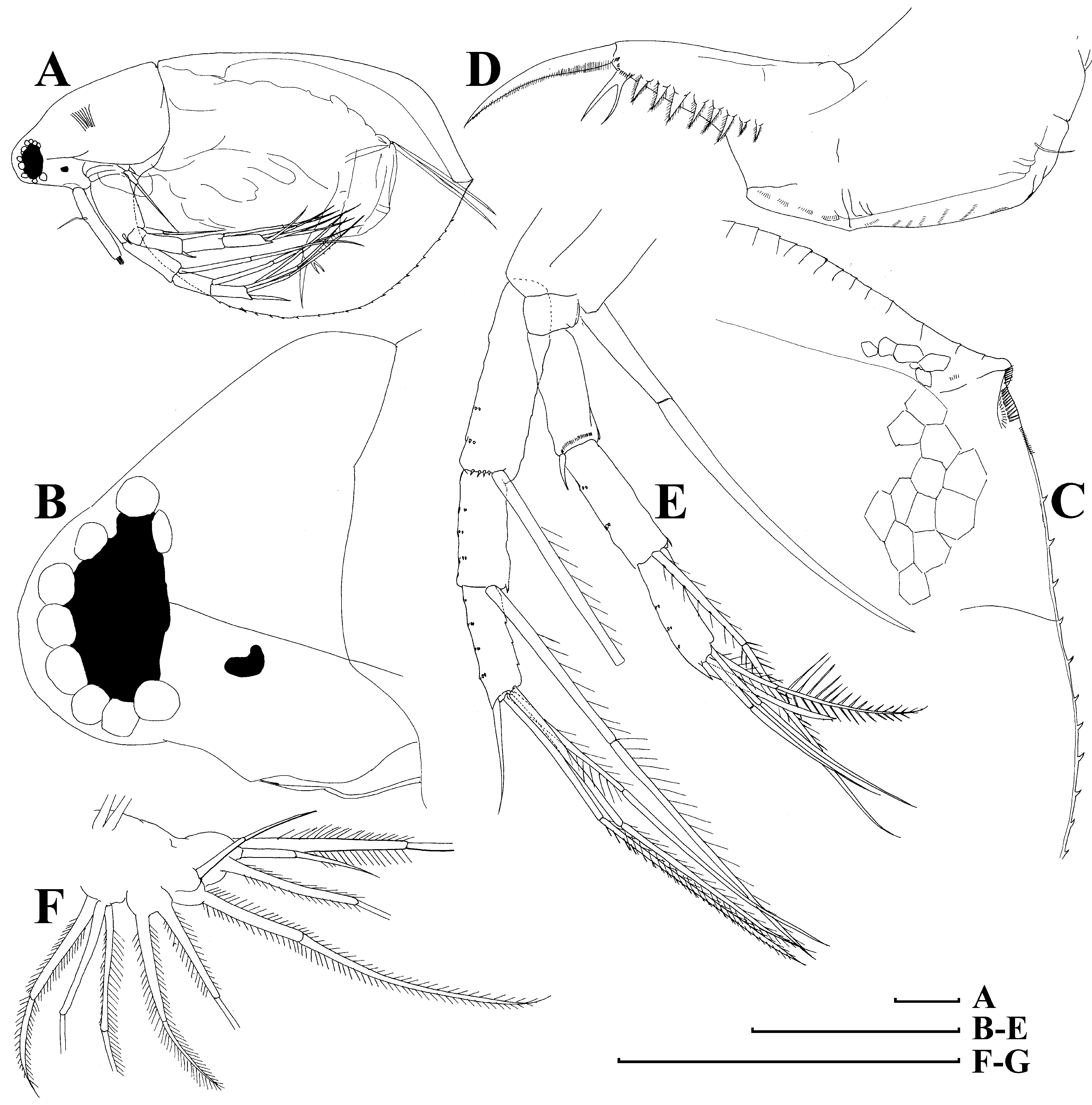
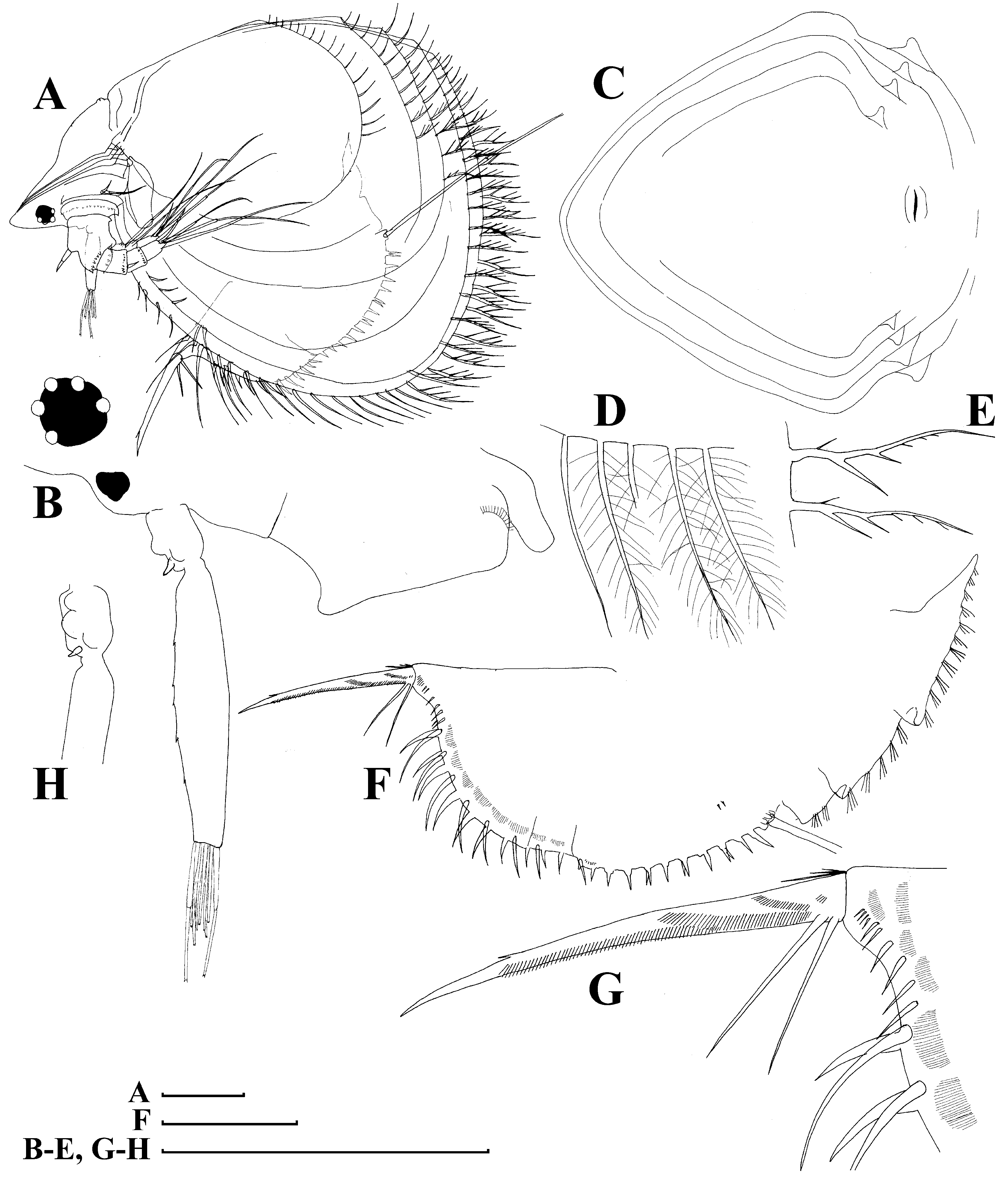
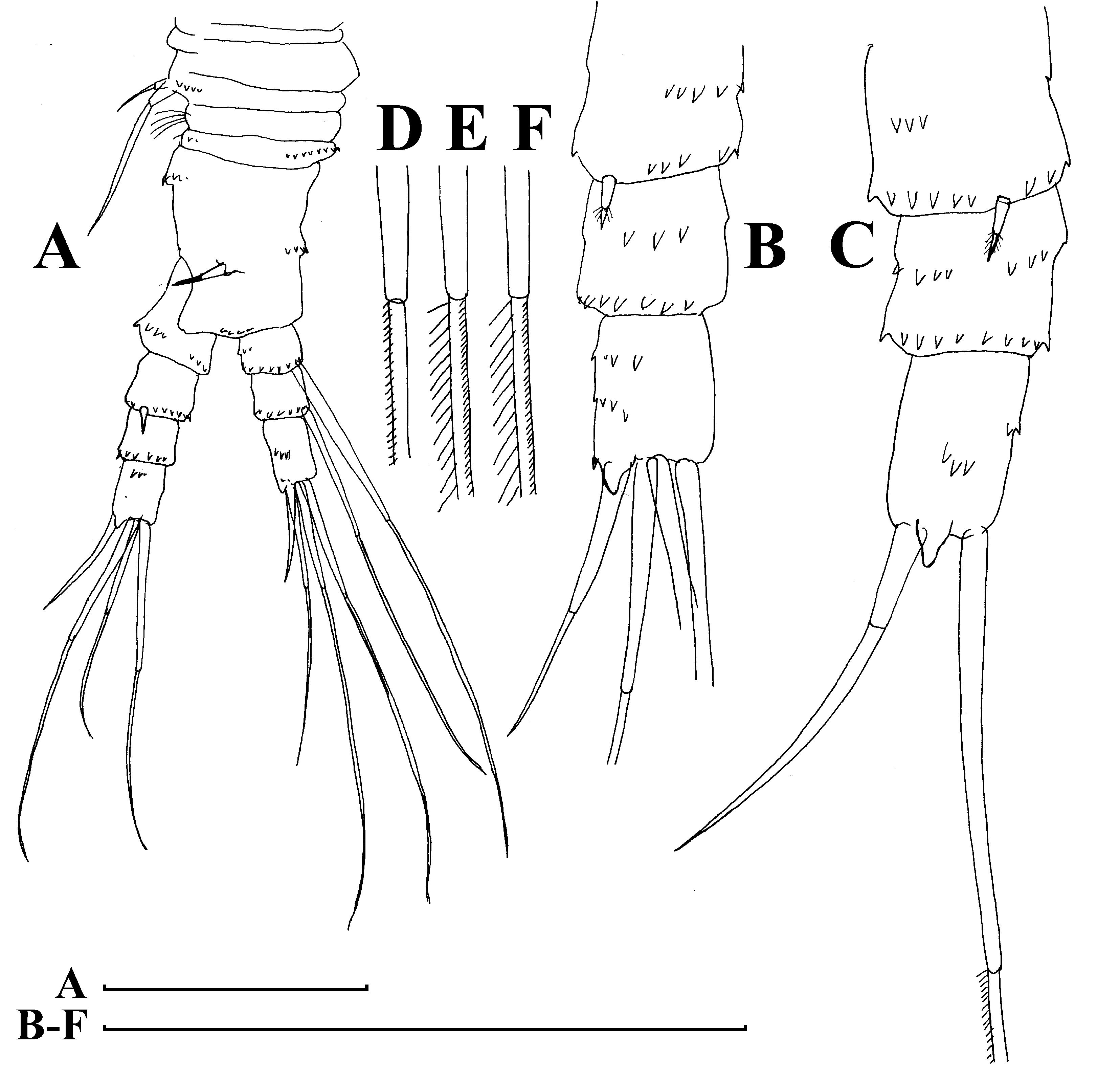
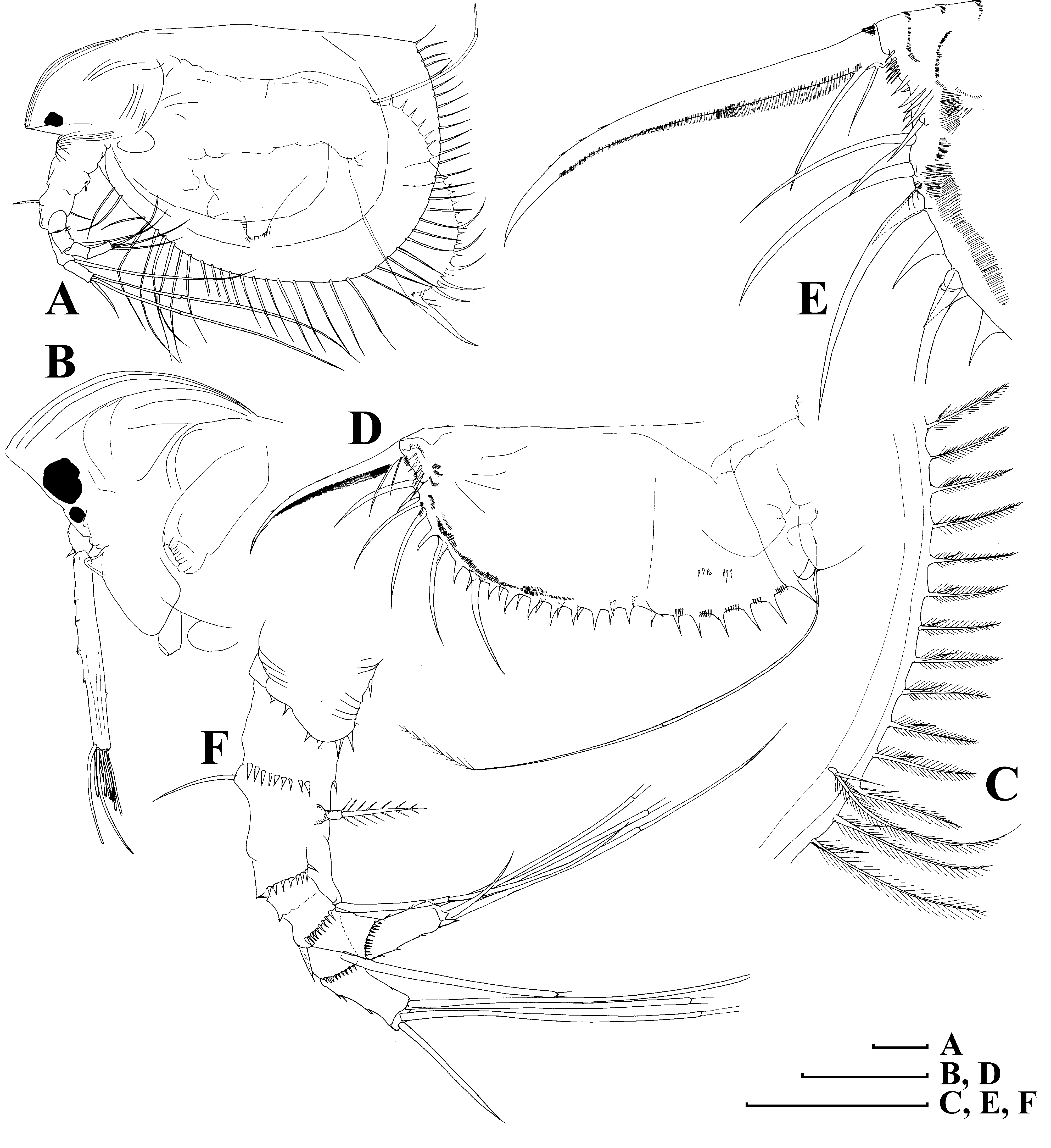
Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15
Synonymy. Bosmina fatalis Burckhardt, 1924 , p. 235–237, 240–241, Figs 10 View FIGURE 10 , 1–17 (except var. cyanopotamia ); Kořínek 1971, p. 289–292, Figs 9 View FIGURE 9 A–F, 10A–G; Chiang & Du 1979, p. 170–172, Fig. 112; Mizuno & Takahashi 1991, p. 153–154, Textfig.; Kotov 1997, p. 29; Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ; Tanaka 2000, p. 118–120 Figs 7–9 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 ; Kotov et al. 2009, p. 14–17, Figs 6–7 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 .
Type locality. Taihu Lake near Shanghai, China ( Burckhardt 1924).
Locality in Korea. 4 (see Fig. 1 and Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
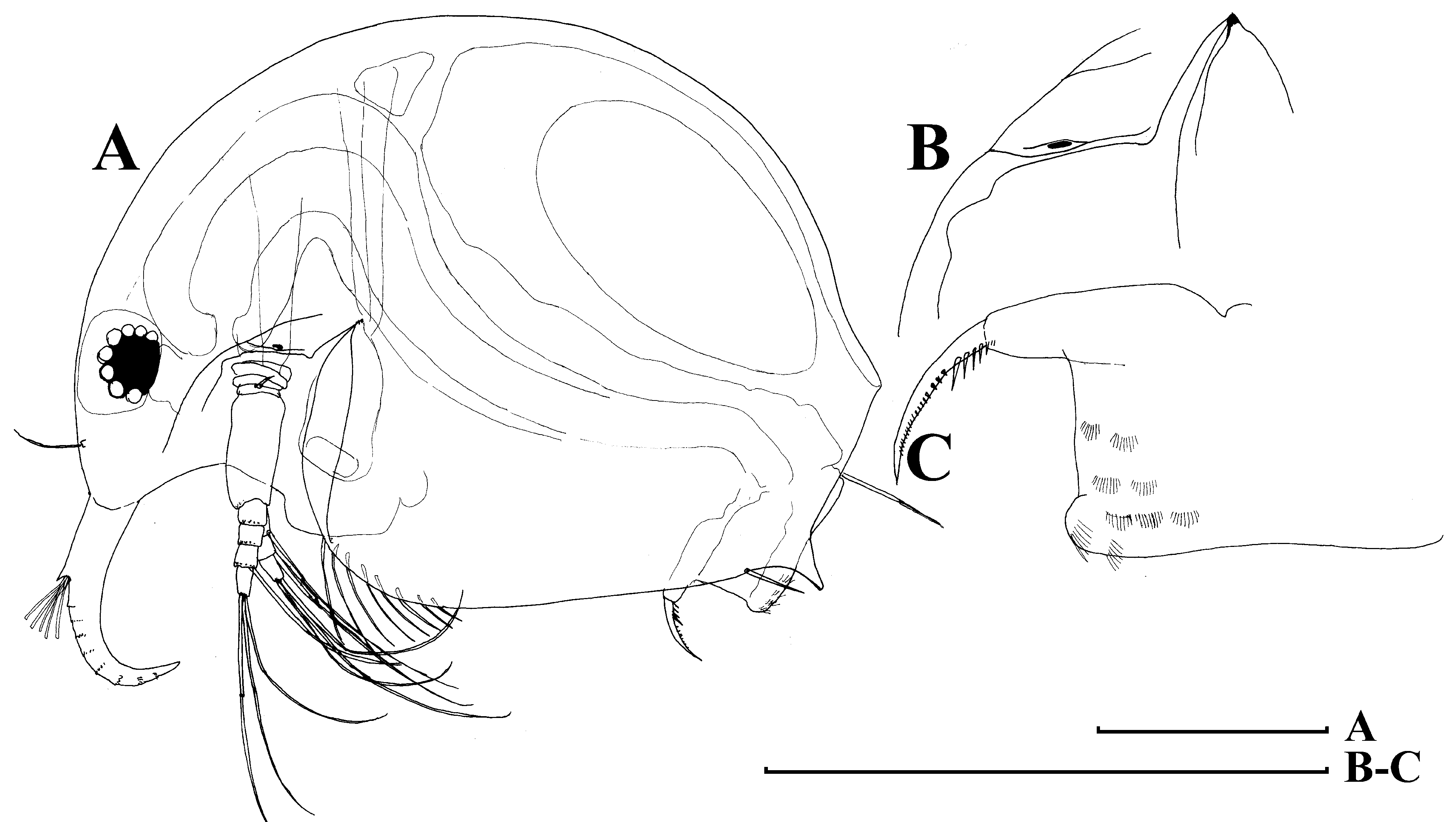
Parthenogenetic female. Body relatively short and wide in lateral view, dorsal margin with a weak depression anterior to brood pouch, posterior margin straight, its height less than half of body height, ventral margin almost straight, with a shallow depression anterior to mucro ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 A). Frontal head pore small, located far from ventral margin of head shield (as seen from anterior side) somewhat dorsally to level of antennular sensory setae ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 B). Lateral head pore small, ovoid, located in a bifurcation of reticulation near ventral margin of head shield, but not immediately near the margin ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 C–D). Labrum a fleshy appendage lacking significant projections, distal labral plate small. Ventral valve margin with a series of stout setae on its anterior portion, base of each located on internal surface of valve, “ seta kurzi ” located on internal side of valve anterior to abovementioned depression near mucro, which is strong, relatively long and lacking any incisions ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 E). Series of minute setules at inner side of valve near posterior valve margin. Postabdomen with width approximately equal along all its length, with ventral (although functionally dorsal) margin almost straight ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 F). Preanal margin long, slightly convex, with groups of setules distally. Distal (anal) margin truncated, postero-dorsal angle as a projection. Postanal portion as a cylindrical projection bearing paired postabdominal claws. Each claw regularly bent, with two pectens on concave (dorsal) margin; distal pecten consists of short, fine spinules, while proximal pecten consists of 7–9 rather strong and thin teeth. Postabdominal seta shorter than preanal margin. Antenna I fused with rostrum, rather long, its length from tip to tip of rostrum less then 0.5 body lengths. Antennular (frontal) sensory seta located on rostrum. Free section of antenna I (not incorporated into rostrum) consists of a pre-aesthetasc portion, fused with rostrum, and a slightly bent post-aesthetasc portion (Kotov et al. 2009). Both portions supplied with transverse series of fine denticles. Antenna II typical for the genus, six pairs of thoracic limbs as described by Kotov (1997). Size in our material 0.34–0.40 mm.
Notes. Kim & Yoon (1987) and Yoon (2010) found only Bosmina longirostris ( O. F. Müller, 1776) and B. coregoni Baird, 1857 in Korea. The most common species is Bosmina longirostris ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 A–C), belonging to the subgenus Bosmina (Bosmina) Baird, 1845 . But in a single locality we found B. fatalis belonging to the subgenus B. (Sinobosmina) Lieder, 1957. It differs in: (1) position of lateral head pore not immediately near the margin of head shield; (2) uniform thin setules in distal pecten on postabdominal claw. Even stronger differences are present between males of the two species (Kotov et al. 2009), but, unfortunately, males of B. (S.) fatalis are unknown from Korea, while males of B. longirostris were described by Yoon (2010).
B. (S.) fatalis View in CoL is common in the eastern half of China, Far East of Russia, Japan, Philippines, Cambodia and Thailand ( Chiang & Du 1979; Mizuno & Takahashi 1991; Maiphae et al. 2008; Kotov et al. 2009; Tanaka & Ohtaka 2010), and its presence in Korea was quite expected. This taxon is a Far Eastern endemic.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |