Agaricus punjabensis Qasim, A. Ashraf & Khalid, Phytotaxa
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.630.4.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10425709 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A687F4-EE1F-FFF9-FF45-FA4748FF51AC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Agaricus punjabensis Qasim, A. Ashraf & Khalid, Phytotaxa |
| status |
|
Agaricus punjabensis Qasim, A. Ashraf & Khalid, Phytotaxa View in CoL 252(1): 8 (2016) ( Figures 2f View FIGURE 2 , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Index Fungorum Number: 814981
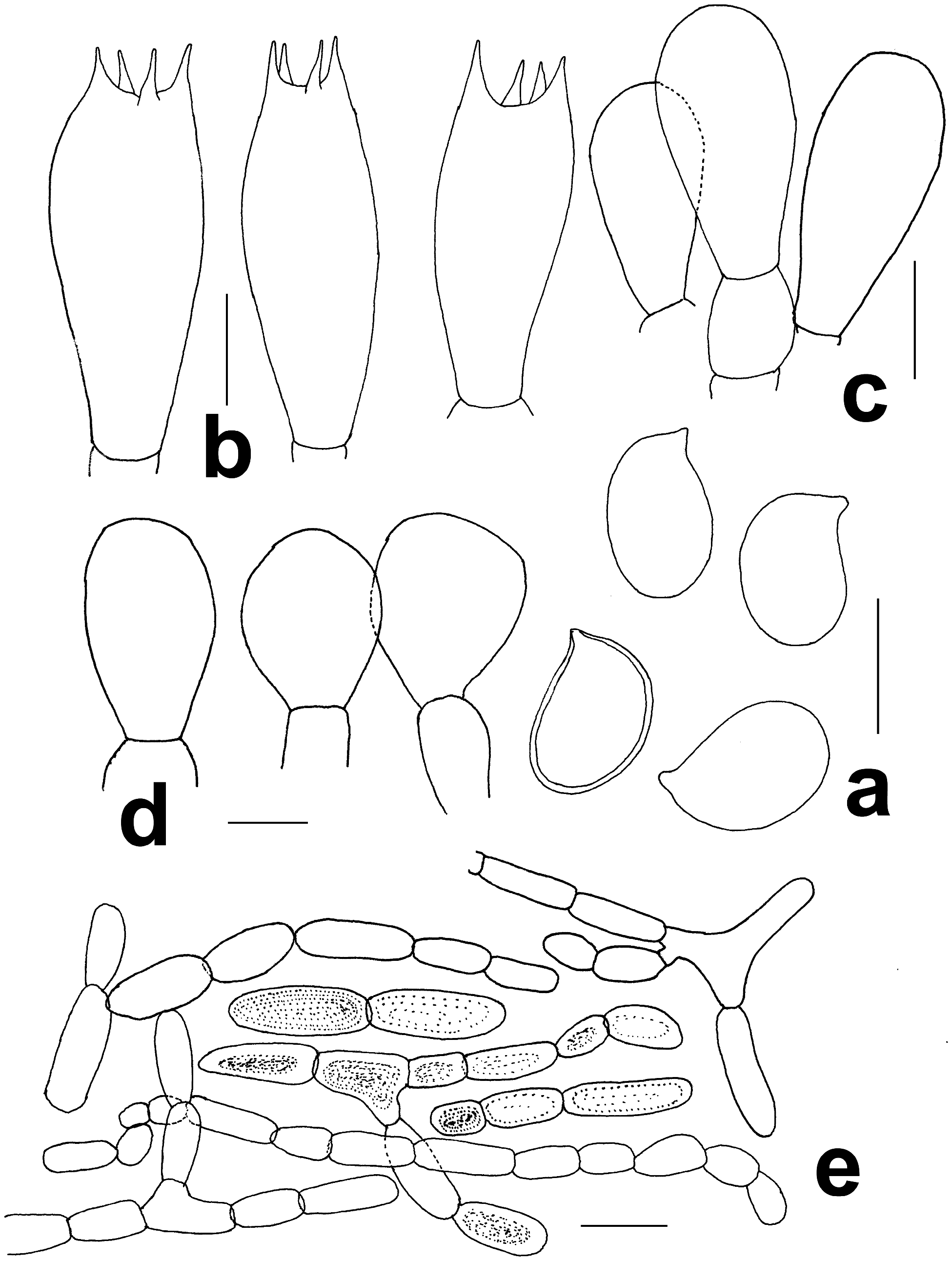
Pileus 42–75 mm in diameter, hemispherical to dome shaped when young, later slightly umbonate, then finally plano-convex with a depression around the umbo at maturity; surface dry, uniformly covered with innates, brownish grey (7F2) to dark brown (7F4) appressed fibrils on a white background, becoming radially fibrillose, splitting radially upon expansion; margin entire, slightly uplifted when mature, appendiculate with partial veilar remnants; context 7 mm thick at centre, white (1A1), fleshy, colour turns light yellow (1A4) on cutting. Lamellae free, 4–6 mm broad, very crowded; with 4–5 series of intercalated lamellulae, pinkish when young, becoming dark brown (6F8) on maturity; regular, edge even, concolorous. Stipe 40–80 × 5–12 mm, central, curved at the middle, surface smooth, white (1A1) to cream above the annulus, dark brown (6F5) below the annulus, dark greyish brown (6E3) at the base, light brown (6D5-6) near the annulus, colour turns light yellow (1A5) on cutting, marginate base (up to 16 mm) without rhizomorphs. Annulus superous, double, membranous, upper surface smooth, lower surface with scales arranged in a cogwheel, thick, 37 mm diam., white (1A1). Odour indistinct.
Basidiospores [35,1,1] (5.0–)5.9–6.8(–8.5) × (3.2–)4.1–4.7(–5.6) μm, X m = 6.4 ± 0.9 × 4.4 ± 0.6 μm, Q = 1.3– 1.6, Q m = 1.5 ± 0.07, ellipsoid, smooth, dark brown with KOH, thick-walled. Basidia 15–18 × 5–7 μm, clavate, hyaline, occasionally gluttulate, thin-walled, smooth, 4-spored, sterigmata 1.5–3 µm long. Basidioles 12–15 × 6–7 μm, clavate, hyaline, thin-walled, smooth. Cheilocystidia 11–16 × 6–8 μm, sub-clavate to sphaeropedunculate, hyaline, thin-walled, smooth. Pleurocystidia absent. Pileipellis a cutis, hyphae 7–10 μm broad, branched, short inflated cells with brown diffused pigments, thin-walled, smooth. Stipitipellis hyphae 5–7.5 μm broad, light brown with KOH, thin-walled. Annulus composed of long cylindrical hyphae, 6–8.5 μm broad, hyaline with KOH, not constricted at the septa, smooth, thin-walled.
Macrochemical reactions:—KOH reaction positive, pileus surface and context turning yellow (2A6), stipe surface and context changing to yellow (2A6); Schäffer reaction on pileus surface negative.
Habit and habitat:—solitary to gregarious, terrestrial on humus soil under a dicotyledonous tree.
Specimen examined:— INDIA: West Bengal, South 24-parganas District, Mathurapur, Halder Para, 22°7’14.85”N, 88°23’29.14”E, alt. 7.0 m asl., 04 August 2019, E. Tarafder, CUH AM758.
Remarks:— Agaricus punjabensis View in CoL was described for the first time in Pakistan ( Chen et al. 2016). The occurrence of this species in India represents its first record outside of Pakistan. The Indian collection matches quite nicely with the original protologue but differs in having larger basidiospores (5–8.5 × 3.2–5.6 μm vs. 3.5–5 × 2.5–3.5 μm).
Agaricus punjabensis View in CoL shares morphological features with A. endoxanthus Berk. & Broome , A. volvatulus Heinem. & Gooss. View in CoL -Font., A. moelleri Wasser View in CoL , and A. microvolvatulus Heinem. However View in CoL , A. endoxanthus Berk. & Broome has a stipe the surface of which is unchanging on bruising and much larger globose to clavate cheilocystidia (14–32 × 10–17 μm vs. 11–16 × 6–8 μm), pyriform, turbinate or subspherical ( Parra et al. 2013). Agaricus volvatulus Heinem. & Gooss. View in CoL -Font., has much smaller basidiospores (4.7–5.7 × 3.2–3.7 μm) and an absence to rare presence of cheilocystidia ( Heinemann 1956). Agaricus moelleri Wasser View in CoL differs by its entirely white stipe and much larger cheilocystidia (10–28 × 7.0–20 μm; Parra 2013). Agaricus microvolvatulus Heinem. View in CoL differs by its smaller basidiospores (3.8–4.8 × 2.8–3.3 μm) and much broader cheilocystidia (7.0–12.5 μm broad; Heinemann 1971).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Agaricus punjabensis Qasim, A. Ashraf & Khalid, Phytotaxa
| Tarafder, Entaj, Dutta, Arun Kumar, Karunarathna, Samantha C., He, Mao-Qiang, Tian, Fenghua & Acharya, Krishnendu 2023 |
Agaricus punjabensis
| Qasim, A. Ashraf & Khalid 2016: 8 |