Stenochironomus gracilis, Dantas, Galileu P. S., Hamada, Neusa & Mendes, Humberto F., 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4117.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4274F17E-D096-4B30-8FD2-E66769F49708 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6073936 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E32D35-5100-3216-FF04-C934F27EFE5D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenochironomus gracilis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stenochironomus gracilis View in CoL new species
( Figs. 12–14 View FIGURE 12 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURE 14 )
Type material. Holotype male with pupal exuviae, BRAZIL: Amazonas state, Manaus, Presidente Figueiredo, Recanto da Pantera, 02°00'52"S, 60°01'43"W, 08.x.2013, on submerged leaf, G.P.S. Dantas, ( INPA).
Diagnostic characters. Male: thorax pale, except the ventral portion of preepisternum which is brown; anal point broad, light brown at basal half, pale at apex; abdomen with brown pigmentation on posterior margin of T III–IV; fore tibia with a brown band at apex, mid and hind femur with a brown band at base. Pupa: frontal apotome elongated; spur on T VIII with 2–3 teeth, the outer tooth larger than others; TII with a posterior row of small sized hooklets restricted to medial area of tergite, not divided medially; T V with three fields of shagreen separated by bare areas; T VII without shagreen; S VI with 3 LS setae.
Etymology. from latin, gracilis , meaning slender, referring to the general shape of the hypopygium.
Male (n = 1). Total length 3.37 mm. Wing length 1.58 mm. Total length/ wing length 2.13. Winglength/ length of profemur 1.66.
General coloration greenish. Head: eyes markedly metallic when alive or in alcohol; pedicel and flagellum brown. Thorax: pale, except the ventral portion of preepisternum which is brown. Legs: anterior leg most pale, with a brown band at apex of tibia; mid and hind legs most pale, with a brown band at base of femur; all coxa with a brown band. Wing: membrane with a medial light-brownish band (hard to see when slide-mounted). Abdomen: T III–IV with brown pigmentation restricted to posterior margin; TIX brown at the lateral margins, anal point light brown at basal half, pale at apex; gonocoxite and gonostylus pale.
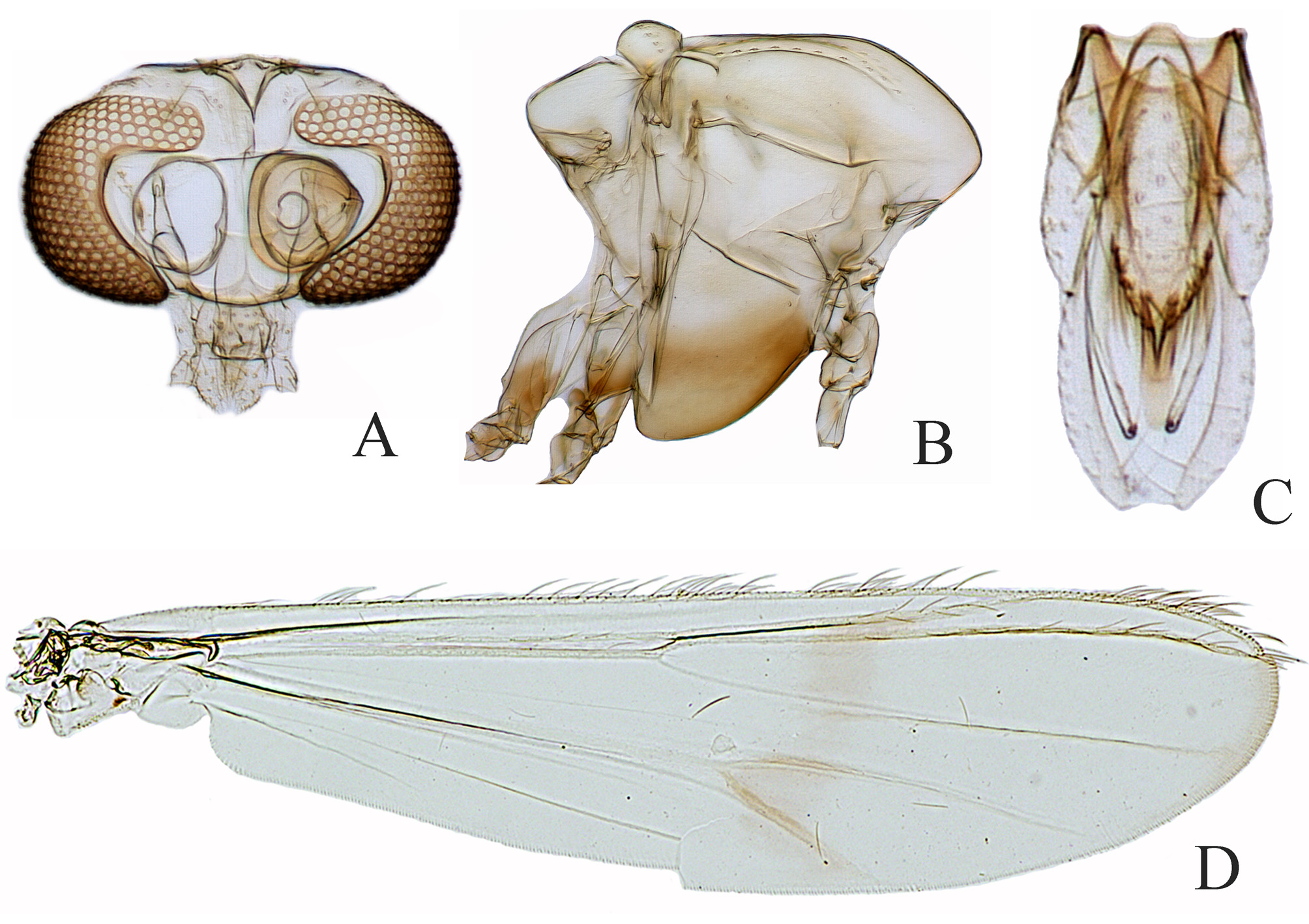
Head ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 A). AR 1.49. Thirteenth flagellomerum 680 µm long. Temporal setae 13. Clypeus with 14 setae. Tentorium, stipes and cibarial pump as in Figure 21 View FIGURE 21 A. Tentorium 150 µm long, 40 µm wide at sieve pore, 18 µm wide at posterior tentorial pit. Stipes 114 µm long, 5 µm wide. Palpomere lengths (1–2 in µm): 34; 38.
Thorax ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 B). Acrostichals 16, in two rows; dorsocentrals 13, in a single row; prealars 5–6, in an irregular single row. Scutellum with 15 setae, in two rows. Anterior edge of scutum slightly rounded in lateral aspect.
Wing ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 C). VR 1.19. Brachiolum with 2 setae. R with 28 setae; R1 with 27 setae; R4+5 with about 45 setae; M with 1 setae at apex; RM with 1 setae; remaining veins bare . Squama with 5 setae.
Legs. Scale of front tibia 36 µm long, with 3 strong setae; spurs of middle tibia 37 µm and 38 µm long; spurs of hind tibia 28 µm and 37 µm long. Apex of fore tibia 47 µm wide, of mid tibia 48 µm wide, of hind tibia 52 µm wide. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 7.
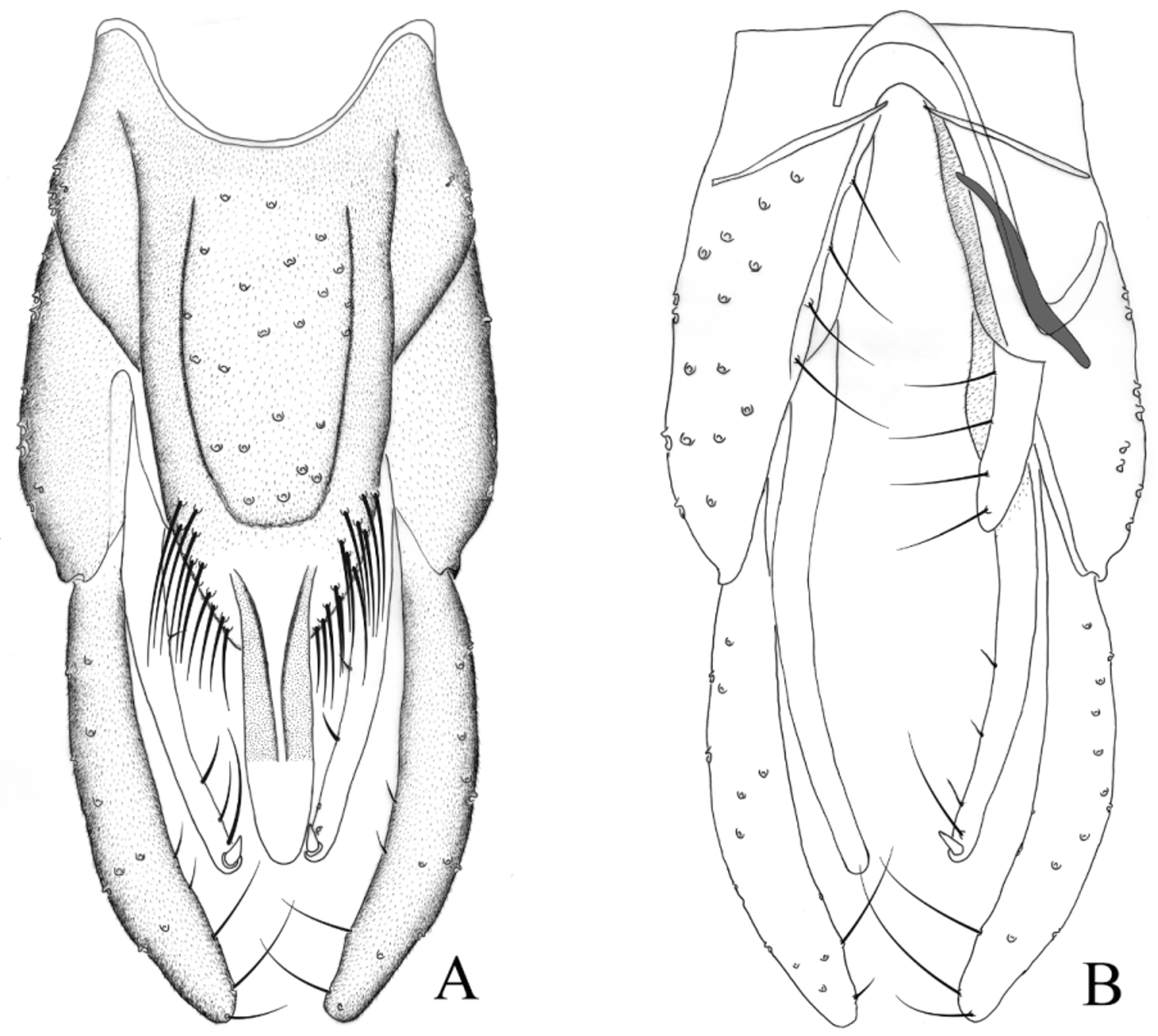
Hypopygium (Figs, 12C, 13A, 13B). Anal point broad, originating subapically on T IX, with dorsal crests converging posteriorly; 71 µm long, 20 µm wide at base. Tergite IX narrow, elongated, with 25 strong dorsal setae; caudal apex slightly wedge-shaped in dorsal aspect, with posteroventral rows of stout setae. Laterosternite IX with 4 setae. Phallapodeme 58 µm long; transverse sternapodeme rounded, 20 µm long. Gonocoxite 130 µm long; inferior volsella 140 µm long, with 5 setae, apical setae stout; superior volsella subcylindrical, not extending beyond apex of gonocoxite, 47 µm long, with 4 setae distributed along entire length. Gonostylus slightly curved, 125 µm long, with two subapical long setae on inner margin. HR 1.04. HV 2.70.
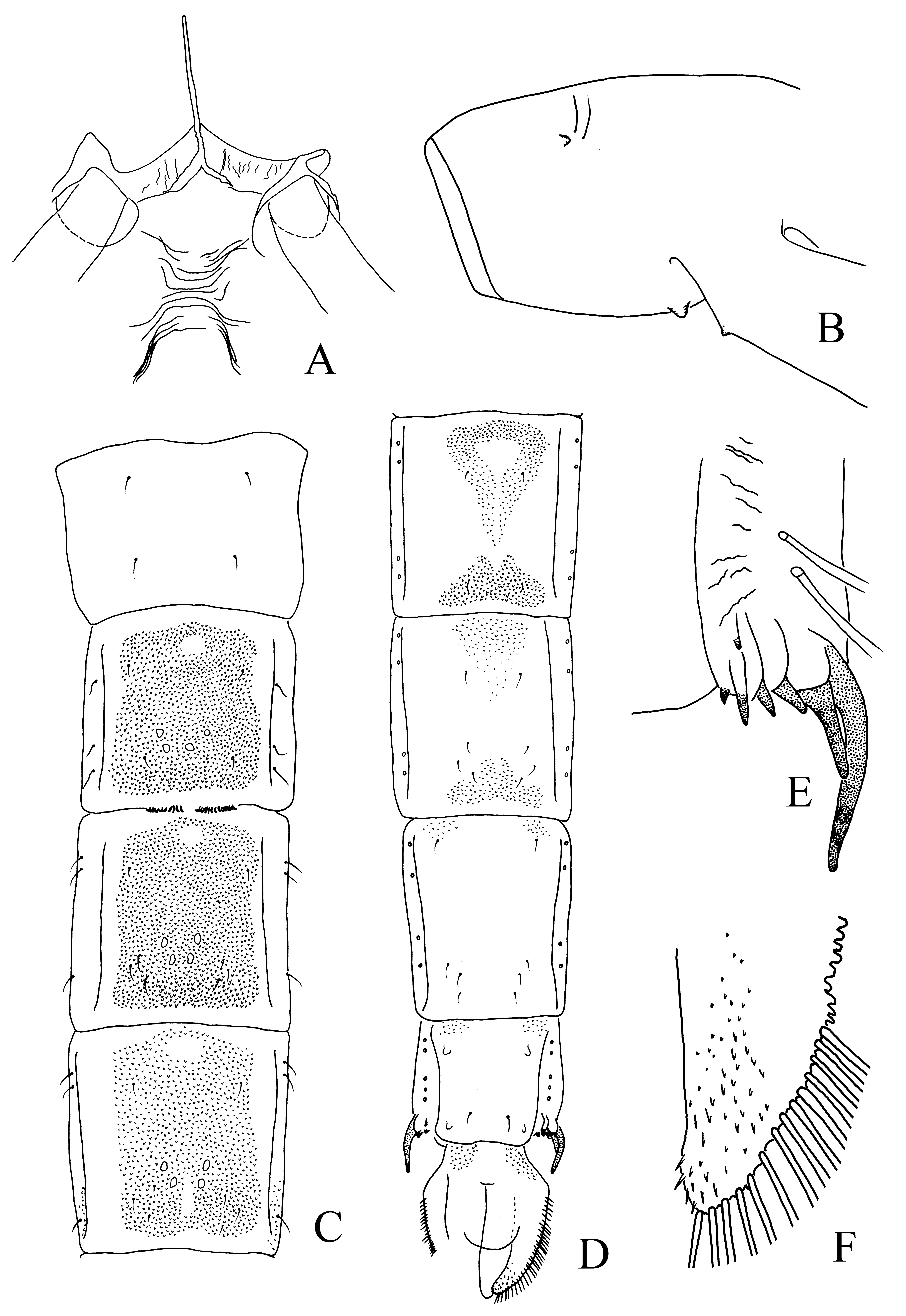
Pupa (n = 1). Total length 4.09 mm. General coloration pale to very light brown; spur on T VIII light brown.
Cephalothorax ( Figs. 14 View FIGURE 14 A, 14B). Frontal apotome elongated ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 A); frontal warts absent. Precorneal setae 133 µm long. Dorsocentrals (Dc) 75 µm long. Distance between Dc1 and Dc2 5 µm; between Dc2 and Dc3 215 µm; between Dc3 and Dc4 3 µm. Median suture slightly rugose. A ventral tubercle close to wing sheath base and a laterodorsal tubercle anterior to Dc1 present ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 B).
Abdomen ( Figs. 14 View FIGURE 14 C, 14D). T I bare ; T II with large field of shagreen, with spines arranged in groups of 2–4 near the anterior margin of segment; T III–IV with two field of shagreen, an anterior smaller and a posterior larger, separated by a bare area; T IV with a somewhat elliptical bare area near posterior margin, paratergites with posterior fine shagreen; T V with three fields of shagreen separated by bare areas; T VI with an anterior small field of very fine shagreen; T VII without shagreen; T VIII with shagreen restricted to small areas near anterolateral margin; anal segment with anterior pair of shagreen patches. Conjunctive IV/V with shagreen. T II with posterior row of small sized hooklets not extending to lateral margin of tergite, not divided medially; pedes spurii B absent. Abdominal setation: S I without L setae; S II–V with 3 L setae; S VI with 3 LS setae; S VII with 4 LS setae; S VIII with 5 LS setae. Spur on S VIII ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 E) with 2–3 teeth yellowish brown, with a more elongated lateral tooth, 70 µm long ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 E). Genital sac 180 µm long, overreaching the posterior margin of the anal lobe by 35 µm; anal lobe with fringe of about 17–19 filaments, without spicules.
Female and larva unknown.
Systematic remarks. The male imago of S. gracilis sp. nov. keys to couplet 12 with S. fittkaui and S. albidorsalis in Borkent (1984) . However, the new species has a light median band in the wing and the ventral portion of preepisterno is brown, contrasting with S. albidorsalis , which does not have a medial band in the wing and the preepisterno is completely pale. S. gracilis sp. nov. is distinguishable from S. fittkaui by the coloration pattern of legs, which in the new species is poorly defined and restricted to apex of fore tibia and base of mid and hind femur, whereas in S. fittkaui it is more conspicuous and preset in all tibias and femurs. In addition, S. fittkaui has some brown pigmentation in lateral margin of lateral vitta and posterior portion of postnotum, which is absent in S. gracilis sp. nov. The pupa of S. gracilis sp. nov. is similar to those of S. albidorsalis by sharing the frontal apotome elongated and absence of shagreen in T VII, but can be recognized by having a continuous posterior row of small hooklets on TII, contrasting with S. albidorsalis in which the row of hooklets is divided medially into two groups.
Notes on biology of the species. The adult was reared from larva which had been mining leaves in a fast flowing, black-water stream. In the laboratory the mined leave was kept at regulated temperature of about 20 °C. The adult of S. gracilis sp. n. emerged one week after the leave had been collected.
| INPA |
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazonia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.