Tettigometra (Tettigometra) ziaratensis Kamran et Zhang, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4816.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E28CA9F4-231F-4EFC-B460-4298E766D736 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F7211D-FFC4-1D16-FF3E-A553FE08FD78 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tettigometra (Tettigometra) ziaratensis Kamran et Zhang |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tettigometra (Tettigometra) ziaratensis Kamran et Zhang sp. nov.
( Figs 1–11 View FIGURES 1–5 View FIGURES 6–11 )
Diagnosis. Tettigometra ziaratensis sp. nov. is similar to T. pseudovitellina in general appearance but can be differentiated by the round posterior corner of subocular plate (sharp in T. pseudovitellina ) and dorsal aedeagal tooth which is pointed and slightly elevated (quadrangular with straight dorsal margin in T. pseudovitellina ). This new species is also similar to T. sulphurea but can be separated from the latter by the aedeagal tooth (pointed and more elevated in T. sulphurea ).
Description. Length of male (from apex of head to tip of forewing) N=3: 4.2–4.3mm; female, N=2: 4.5–4.6mm
Coloration. General body color yellow. Vertex yellow, anterior margin with light thin brown stripe. Frons, gena and clypeus yellow, gena slightly lighter laterally. Rostrum light brown; medial groove brown, apical segment black. Eyes brown with white verticale. Pronotum and mesonotum yellow, posterior margin of pronotum brown. Tegula concolorous with thorax; tegmina yellow (brownish in Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–5 as the picture was taken on slide microscope for higher magnification of wing venation), hind wings hyaline. Abdominal tergites, sternites and male genitalia yellow. Legs yellow, tibial and tarsal spines black tipped.
In dorsal view, head wider than long, vertex shorter than width between eyes; medially longer than pronotum, anteriorly convex smoothly arcuate towards eyes; posterior margin slightly curved behind eyes ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1–5 ). In ventral view, frons wider than long widest portion between eyes; anterior margin smoothly arched, medially convex, lateral margins concave at antennae and narrower at clypeus, uniform yellow pits scattered on the surface ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–5 ). Rostrum long, reaching hind coxae. Subocular callus well developed beyond eyes and on posterolateral margins ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–5 ); in lateral view, posterolateral corner of subocular callus round, no incison between subocular callus and pronotum, no notch at the anterolateral margin of eyes and vertex almost continuous ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–5 ). In dorsal view, pronotum wider than long and much wider than mid length of vertex, vertex and pronotum gradually elevated posteriorly in lateral view, vertex and thorax irregularly pitted ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–5 ). Scutellum slightly convex anteriorly, length of scutellum nearly equal to combined length of vertex and pronotum ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–5 ). Tegmina pitted; tectiform with nearly straight commissural, wing venation as in Figure 5 View FIGURES 1–5 . Hind wing well developed bilobed. Metatibial apical spines arranged in two rows; 6 spines in first, 3 spines in second row, tarsomere I with 8 spines arranged in single row. Metatibia tarsal formula 6+3/8/2.
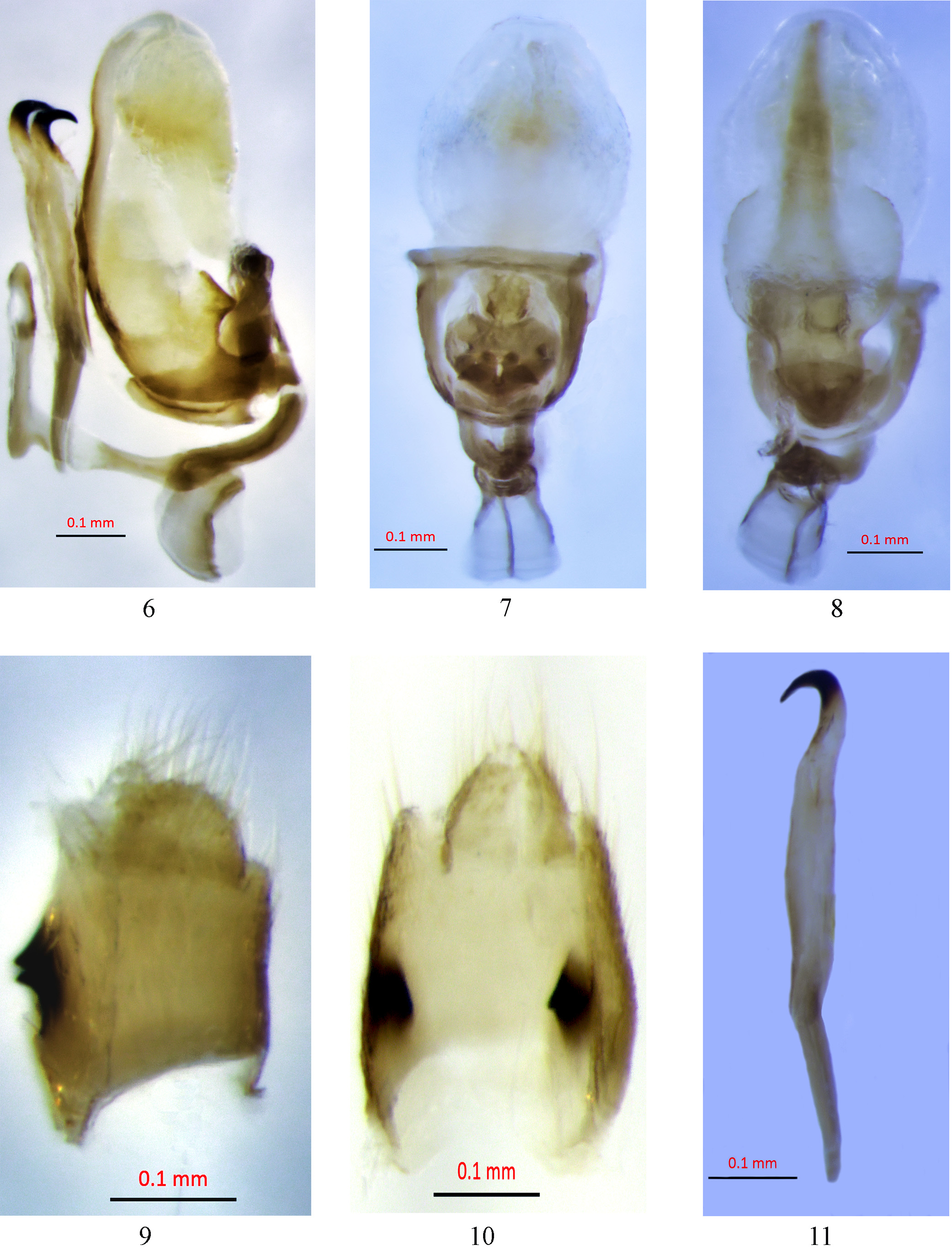
Male terminalia. In lateral view, anal segment quadrangular; epiproct located apically, laterally with black tooth at middle ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 6–11 ). Genital styles paired and symmetrical much longer than wide ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–11 ); apically hook shaped, dorsal margins straight, slightly wider medially, narrow in basal 1/3 ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 6–11 ). Corpus connectivi slightly longer than brachi connectivi ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–11 ). Tectiform structure (tectiductus) well developed; concave medially ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–11 ). Periandrium stirrup-shaped ( Figs 7, 8 View FIGURES 6–11 ) surrounding aedeagus ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–11 ). Aedeagus in basal half bears a distinct pointed tooth, slightly elevated, laterally curved; apical half long, bearing membranous endosoma sac ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–11 ).
Female genitalia. Much reduced and of typical Tettigometrini type.
Type materials. Holotype: ♂ Ziarat , Baluchistan, Pakistan, 30°22'58.54"N, 67°43'27.63"E, 2400 m, 14-viii- 2019, coll. Kamran Sohail. GoogleMaps Paratypes: 2♂♂, 2♀♀, same data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The new species epithet is named for the type locality ‘Ziarat’.
Distribution. This new species was collected in Ziarat, located in northern part of Balochistan Province, Pakistan near the Afghanistan border. This new species was collected at the higher altitude of 2400 m. The area has a very diverse habitat and the type locality is an understudied habitat for fulgoroids as many other planthopper species have been collected.
Host plants. Unknown.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |