Nausithoe eumedusoides ( Werner, 1974 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5336.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:98F89833-1EBB-41A6-B943-2091F2296D40 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8268468 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C908878A-FFAE-E133-FF12-F9E8FC60EC62 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Nausithoe eumedusoides ( Werner, 1974 ) |
| status |
|
Nausithoe eumedusoides ( Werner, 1974) View in CoL
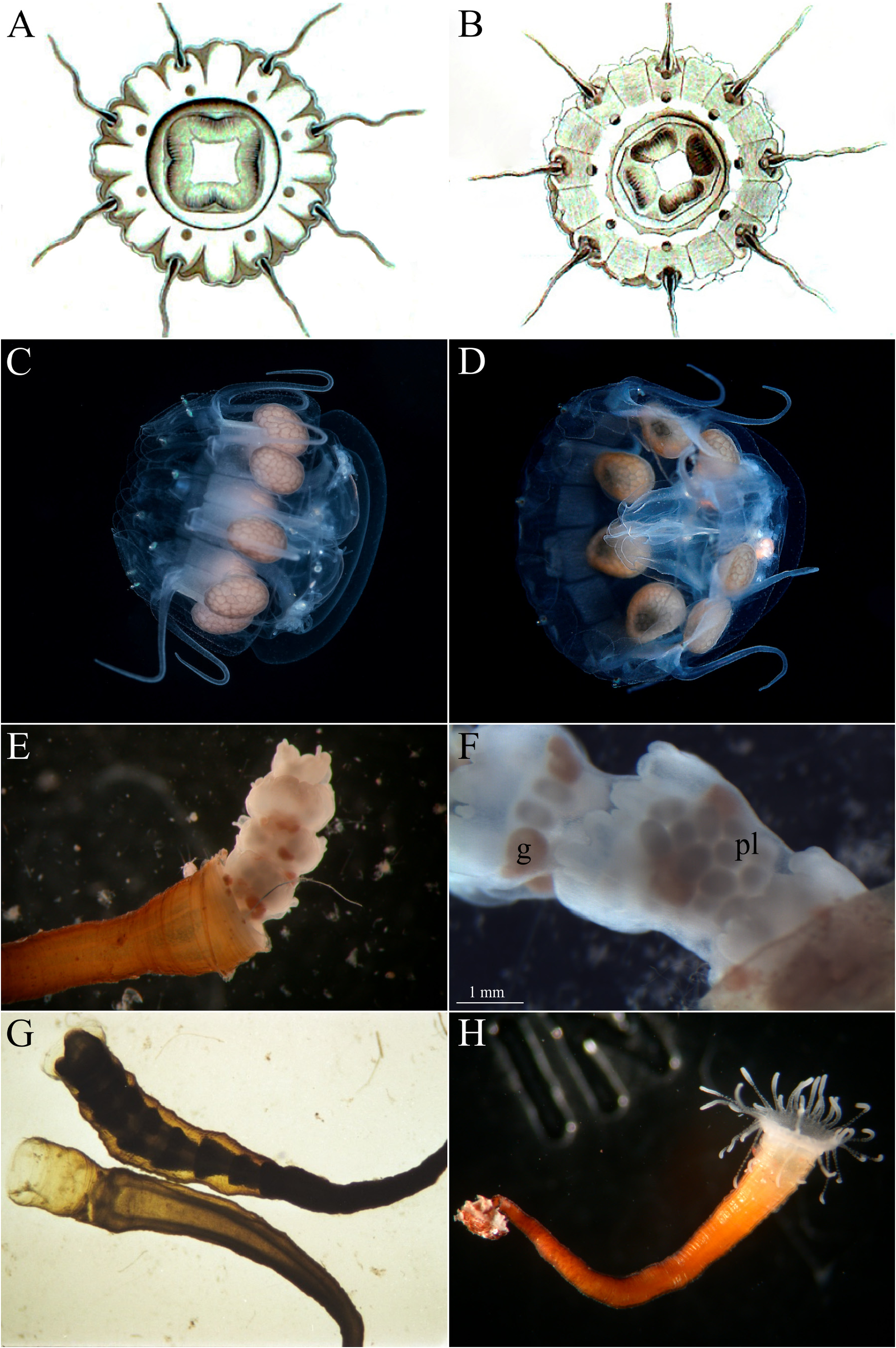
( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 : E–H)
Stephanoscyphus eumedusoides Werner, 1974: 439–461 View in CoL , figs 1–5.
Nausithoe eumedusoides View in CoL — Jarms, 1990: 11.
Holotype ZMH C9797 View Materials .
Material examined: Living polyps kept in laboratory cultures (from submarine caves in Mljet, Croatia, 2002; 26m depth; H. Zibrowius col.).
Diagnosis: medusoid—tetrameric form with no manubrium, can be hermaphroditic; polyp—solitary with single cusp closer to the base.
Description: Based on Werner (1970) and original description. Medusoid 1–1.5 mm in umbrella width and 1–1.2 mm in height; quasi-tetrameric; lack of manubrium; rhopalia with minimally developed sense organ; absence of coronal groove until the final moments of strobilation; no gastric filaments; reduced umbrella musculature with 4 thin longitudinal muscle strands; beating flagella on the epidermis; four gonads in total (eight merged in pairs), bean-shaped or oblong, with yellow to brown pigmentation; can be hermaphroditic (with even the production of both eggs and sperm cells at the same time in the same gonad) or single sexed. Polyp solitary; 22.2 mm in total length; 1–2 single cusp closer to the base (arranged vertically one above the other); produces 4–5 medusoids per strobilation.
Type locality: Submarine caves near Marseille, France.
Distribution: Marine caves probably of all Mediterranean (2–50 m depth).
Remarks: Only N. eumedusoides and N. racemosa have a medusoid described in their life cycle, but the polyps are extremely different from each other. N. eumedusoides is a solitary species while N. racemosa is colonial (and with significant soft body differences, e.g., oral disc, symbiosis with algae).
| ZMH |
Zoologisches Museum Hamburg |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Nausithoe eumedusoides ( Werner, 1974 )
| Molinari, Clarissa G., Collins, Allen G. & Morandini, André C. 2023 |
Nausithoe eumedusoides
| Jarms, G. 1990: 11 |
Stephanoscyphus eumedusoides
| Werner, B. 1974: 461 |