Molossus fentoni, Loureiro, B.K.Lim & Engstrom, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6418279 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6567987 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/194287C9-FFBA-BA16-B182-F66DBBF2F921 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Molossus fentoni |
| status |
|
Fenton’s Masuft Bat
French: Molosse de Fenton / German: Fenton-Samtfledermaus / Spanish: Moloso de Fenton
Other common names: Fenton's Free-tailed Bat
Taxonomy. Molossus fenton: Loureiro, B. K. Lim & Engstrom, 2018 ,
Bototo Wau near the village of Parabara, Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo, Guyana (2.18201°, -59.33706°, elevation 245 m).
Molossus fenton : was recently recognized as distinct from M. molossus from Guyana and Ecuador based on morphological and molecular differences. Monotypic.
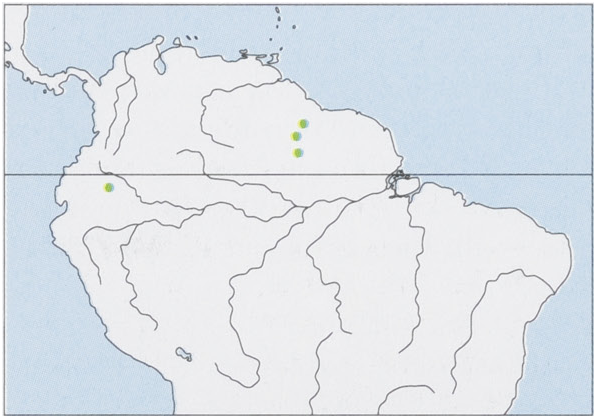
Distribution. Known from a fewlocalities in NE Ecuador and Guyana, but some Pallas’s Mastiff Bats ( M. molossus ) in the intervening Amazon Basin might have been misidentified. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 55-62 mm, tail 30-37 mm, ear 12-14 mm, hindfoot 8-11 mm, forearm 34-36 mm; weight 7-14 g. Fenton’s Mastiff Bat overlaps in size with the Coiban Mastiff Bat ( M. coibensis ) but is smaller than all other species of Molossus . Dorsal pelage of Fenton's Mastiff Bat is dark to medium brown, with pale brown band at base that covers one-quarter to one-half the hair length. Ventral hairs are markedly bicolored, with dark brown tips and pale yellow bases. Dorsal hairs between shoulders are long (4:3-4-6 mm). Ears are rounded and arise from same point on forehead. Tragus is small, and antitragus is constricted at its base. Face is dark brown to black. Upper lip and snout are smooth and lack any medial ridge. Wings and uropatagium are dark brown. Skull has elongated braincase, triangular occipital region, and infraorbital foramen opening laterally in frontal view. Basioccipital pits are moderately deep. I* is thin and long, with paralleltips.
Habitat. Savannas at interface with gallery forests (holotype caught in triple-high net set of ¢. 8 m height).
Food and Feeding. Fenton’s Mastiff Batis an aerial insectivore.
Breeding. Two pregnant Fenton 's Mastiff Bats were caught in early March, a non-pregnant female was lactating in mid-November, and another non-pregnant female was caught in mid- may. mid-May.
Activity patterns. No infonnation.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The I UCN Red List.
Bibliography Lım, B K & Engstrom (2001). Lım, B K er al (2016), Loureiro, Lım a Engstrom (2018)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Molossus fentoni
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Molossus fenton:
| Loureiro, B. K. Lim & Engstrom 2018 |