Chironomus detriticola, Correia, Leny Célia Da Silva & Trivinho-Strixino, Susana, 2007
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.177153 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6251258 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B84253-FFE6-0C66-FF26-4D25FB4F9E1C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chironomus detriticola |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chironomus detriticola View in CoL sp. n.
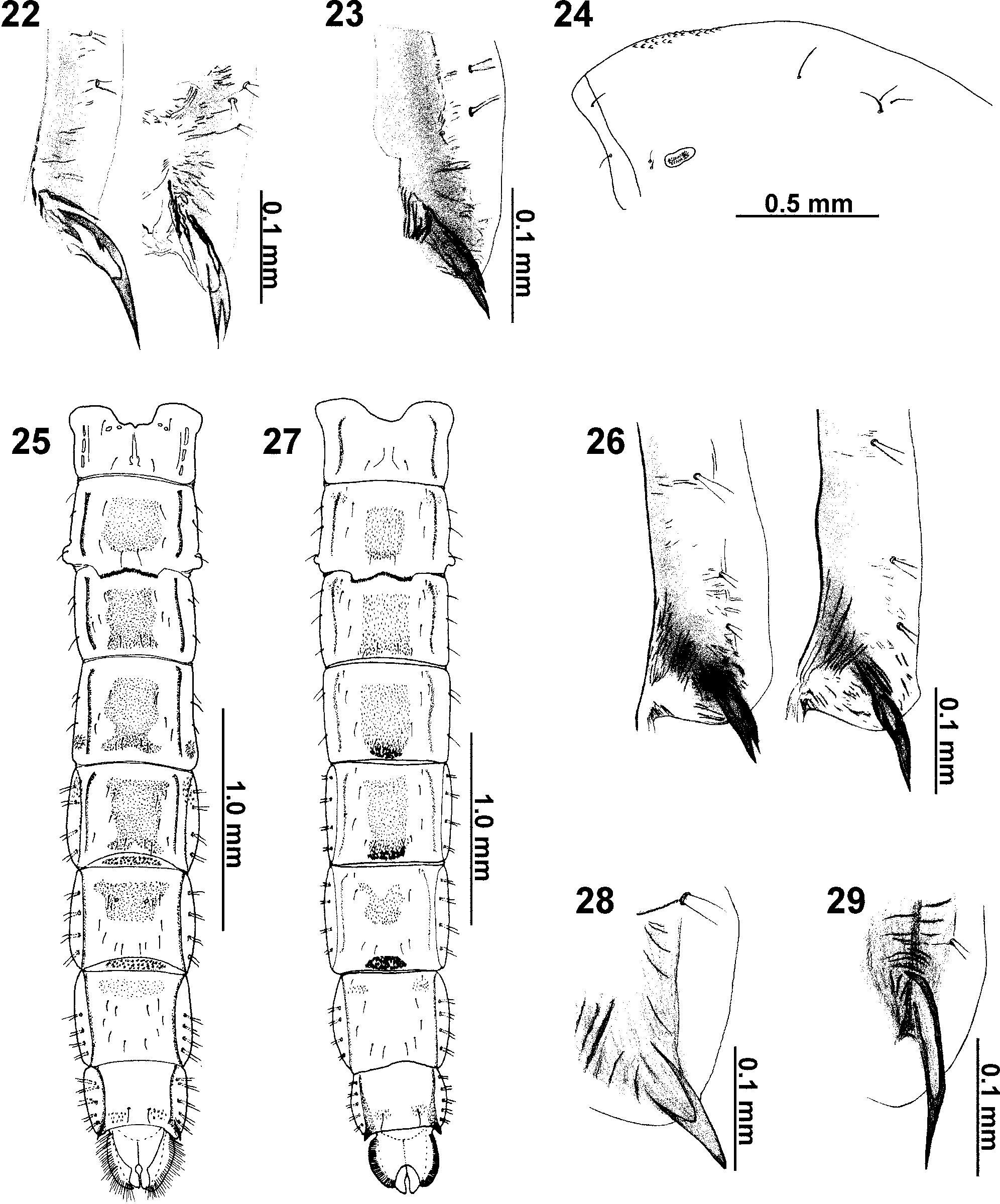
( Figs. 3, 7 View FIGURES 1 – 11 , 12, 13 View FIGURES 12 – 21 , 22 View FIGURES 22 – 29 , 30–35 View FIGURES 30 – 58 )
Type material: Holotype male with pupal and larval exuviae. BRAZIL: São Paulo, São Carlos, UFSCar campus, Fazzari Stream, in temporary pools, 29.iii.2001, L. Correia ( LEA). Paratypes: 1 male with pupal and larval exuviae, 1 male with pupal exuviae, 4 larvae, as holotype; 1 male with pupal and larval exuviae, São Paulo, São Carlos, UFSCar campus, Espraiado Stream, in pools, 5.iv.2001, L. Correia ( LEA, MZUSP).
Etymology. From Latin, detritus and cola, meaning detritus dweller; referring to the habitat of the larvae.
Diagnostic characters. The male can be distinguished from other Neotropical Chironomus species by having yellowish brown legs with tarsi, tibia and distal third of femur dark brown; and by the elongated, hooked superior volsella. The pupa is indistinguishable from most described Neotropical species. The larva can be distinguished from other Neotropical species by the following combination of characters: abdomen with comparatively long lateral and ventral tubules, postmentum and frontoclypeus without pigmentation, antennal blade not surpassing segment three, mandible with two inner teeth, and mentum with trifid median tooth that appears as three equally sized teeth.
Male (n = 4)
Length [4.3] 4.3–5.5, 5.0 mm. Coloration: head yellowish brown, flagellum and maxillary palp pale brown. Thorax yellowish brown with brown mesonotal stripes and posteromedian region darkened (as in Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ). Sternum yellowish brown; scutellum yellowish; postnotum brownish, darkened in posterior portion. Abdomen ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ) pale brown, tergites I–V with median dark brown markings. Legs ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ) yellowish brown with distal third of femur, tibia, and tarsi dark brown.
Head. Flagellum [920] 920–988, 961 µm long; AR = [2.66] 2.66–2.74, 2.70. Palpomere 2–5 lengths (in µm): [49] 37–49, 43; [148] 139–148, 143; [201] 198–201, 199; [287] 241–288, 272. Frontal tubercles about 12 µm long, 2 times as long as wide. Dorsal and ventral interocular distance [74] 74–167, 105 µm and [148] 148–185, 161 µm, respectively. Temporal setae [23] 23–33, 26. Clypeus with [19] 17–23, 20 setae.
Thorax. Acrostichals [11] 11–13, 12, biserial, beginning near antepronotum; dorsocentrals [9] 8–9, 9, partly biserial; prealars [4] 4–5, 4; supraalar [1] 1. Scutellum with [10] 10–14, 12 uniserial, transversally arranged setae. Scutal tubercle low.
Wing. Length [2.05] 2.05–2.18, 2.11 mm. Membrane transparent, without setae; most veins pale brown; RM brown, darker than FCu. Brachiolum with [2] 2 setae; R with [28] 28–31, 29 setae; R1 with [24] 23–27, 25 setae; R4+5 with [30] 29–33, 31 setae in distal 2/3. Squama with [9] 9–10, 10 setae. R2+3 ends halfway between R1 and R4+5. VR = [1.03] 1.03–1.05, 1.04.
Legs. Mid- and hind ta1 with [8] 8–9, 8 and [8] 8–10, 9 sensilla chaetica, respectively. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 1.
Hypopygium ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ). Anal tergal bands fully enclosing [10] 10–13, 12 strong setae. Anal point narrow basally, apex curving ventrad. Superior volsella ( Figs. 12, 13 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ), narrow, elongate, strongly curved; basal lobe with [5] 5–6, 6 long setae. Inferior volsella weakly clubbed, not extending beyond mid-point of gonostylus.
Gonostylus elongate, [148] 148–163, 156 µm long; distal part slender with [6] 5–6, 5 inner marginal setae. Pupa (n = 4)
Length of abdomen [4.6] 4.5–4.9, 4.7 mm. Exuviae pale brown.
Cephalothorax. Cephalic tubercles conical; frontal setae [49] 18–49, 34 µm long. Thorax granulose in anteromedian dorsal region; scutal tubercle present; lateral antepronotals 2, precorneals 2, dorsocentrals 4.
Abdomen. Tergite VI with fine shagreenation more numerous near posterior margin, T VII with fine shagreenation near anterior margin, T VIII with pair of posteromedian patches of fine shagreen, T V–VI with posterolateral point patches. Conjunctives IV/V and V/VI with fine shagreenation. Hook row continuous, occupying 2/3 width of segment II. Pedes spurii B present on segment II. Pedes spurii A present on segment IV. Spur on segment VIII with 1–2 apical teeth ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 22 – 29 ). Segments I–IV with 0, 3, 3, 3 L setae, respectively; segments V–VIII all with 4 taeniae. Anal lobe with 1 stout dorsal seta and about [107] 107–122, 116 taeniate fringe setae.
4th instar larva (n = 7)
Total length 8.0-12.0, 9.4 mm. Coloration: body red; head yellowish, postmentum and frontoclypeus without dark areas.
Head. Ventral head length [261] 261–276, 269 µm; head width [441] 441–491, 469 µm. Antenna ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), [171] 171–199, 190 µm long; AR = [1.35] 1.35–1.89, 1.64; ring organ near base; antennal blade not surpassing segment three. Pecten epipharyngis ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), simple, consisting of about 17 subequal teeth. Premandible ( Fig. 32 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), bifid with well-developed brush. SI ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), plumose. Mandible ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), with yellowish brown dorsal tooth, apical and two inner teeth blackish, inner margin with 2 spines. Mentum ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 30 – 58 ), with deeply incised trifid median tooth and 6 pairs of blackish, lateral teeth. Ventromental plates separated by about 1/4 width of mentum, anterior margin smooth.
Abdomen. Anal tubules with median constriction; lateral tubules about 1/3 as long as 8th abdominal segment; with 2 pairs of ventral tubules, 1.1–1.5, 1.3 mm long.
Remarks. The most similar Neotropical males are C. strenzkei Fittkau , C. latistylus Reiss , C. joni Sublette et Sasa , and C. wuelkeri Sublette et Sasa. C. detriticola can be separated from all these species on the leg coloration. Further, the shape of superior volsella separates C. detriticola from C. latistylus , which has a less elongated and hooked volsella; and from C. strenzkei , which has a straighter volsella with blunt tip. In C. joni the anal point in dorsal view is widest basally; and in C. latistylus the gonostylus is wider, with rounded distal margin. The coloration of the abdominal tergites of C. detriticola differs from C. latistylus ; the wing lacks extensive dark markings, which is present in C. strenzkei ; and the wing is shorter than in C. joni and C. wuelkeri . The pupa of C. detriticola is indistinguishable from most described pupae of Neotropical Chironomus species, except C. stigmaterus Say , which has strong shagreenation on tergites IV–VI. In the larva, C. latistylus is the most similar Neotropical species. However, the two species can be separated on the length of the antennal blade, which is surpassing third segment in C. latistylus .
Ecology. Larvae of Chironomus detriticola were collected from coarse detritus substrate formed by decomposing leaves, fruits, and brush woods in small marginal pools of the Fazzari Stream, where it coexisted with larvae of C. reissi (see Correia et al. 2005), and in a pool in the Espraiado Stream. Both are first order streams, and tributaries to the Monjolinho River, which again is a tributary to the Jacaré-Guaçu River. They are located in protected areas with exuberant riparian vegetation on the UFSCar campus in São Carlos. The environmental characteristics of both habitats are shallow pools (Fazzari Stream, depth = 15 cm; Espraiado Stream, depth = 50 cm), with low levels of dissolved oxygen (Fazzari Stream = 0.7 mg /l; Espraiado Stream = 4.32 mg /l), and acid water (Fazzari Stream pool, pH = 4.8; Espraiado Stream, pH = 5.5).
| MZUSP |
Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Chironominae |
|
Genus |