Arotes moiwanus ( Matsumura, 1912 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3893.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:02AC06D3-58F9-442F-B4E3-8D00F49DCE5F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5667141 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/897C87FC-FFA7-427A-969B-FB98C7E96346 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Arotes moiwanus ( Matsumura, 1912 ) |
| status |
|
Arotes moiwanus ( Matsumura, 1912)
( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 5 View FIGURES 4 – 6 , 8 View FIGURES 7 – 9 , 11 View FIGURES 10 – 12 , 13–16 View FIGURES 13 – 16 , 19–21 View FIGURE 19 – 21. A )
Phaenolobus (Acoenitus) moiwanus Matsumura, 1912: 123 . [Type locality: Japan, Hokkaido, Sapporo]
Arotes moiwanus var. alboannulatus Uchida, 1928: 34 . [Type locality: Japan, Hokkaido] Synonymized with the variety moiwanus by Townes et al. (1965)
Arotes albicinctus View in CoL var. moiwanus: Uchida, 1953: 128 View in CoL ; Iwata, 1960: 150.
Arotes albicinctus View in CoL f. moiwanus: Iwata, 1958: 68 .
Arotes albicinctus moiwanus: Konishi & Yamamoto, 2000: 749 View in CoL .
Arotes moiwanus: Castillo et al., 2011: 85 -86.
Female (n=18). Body length: 13.5–18.0 mm.
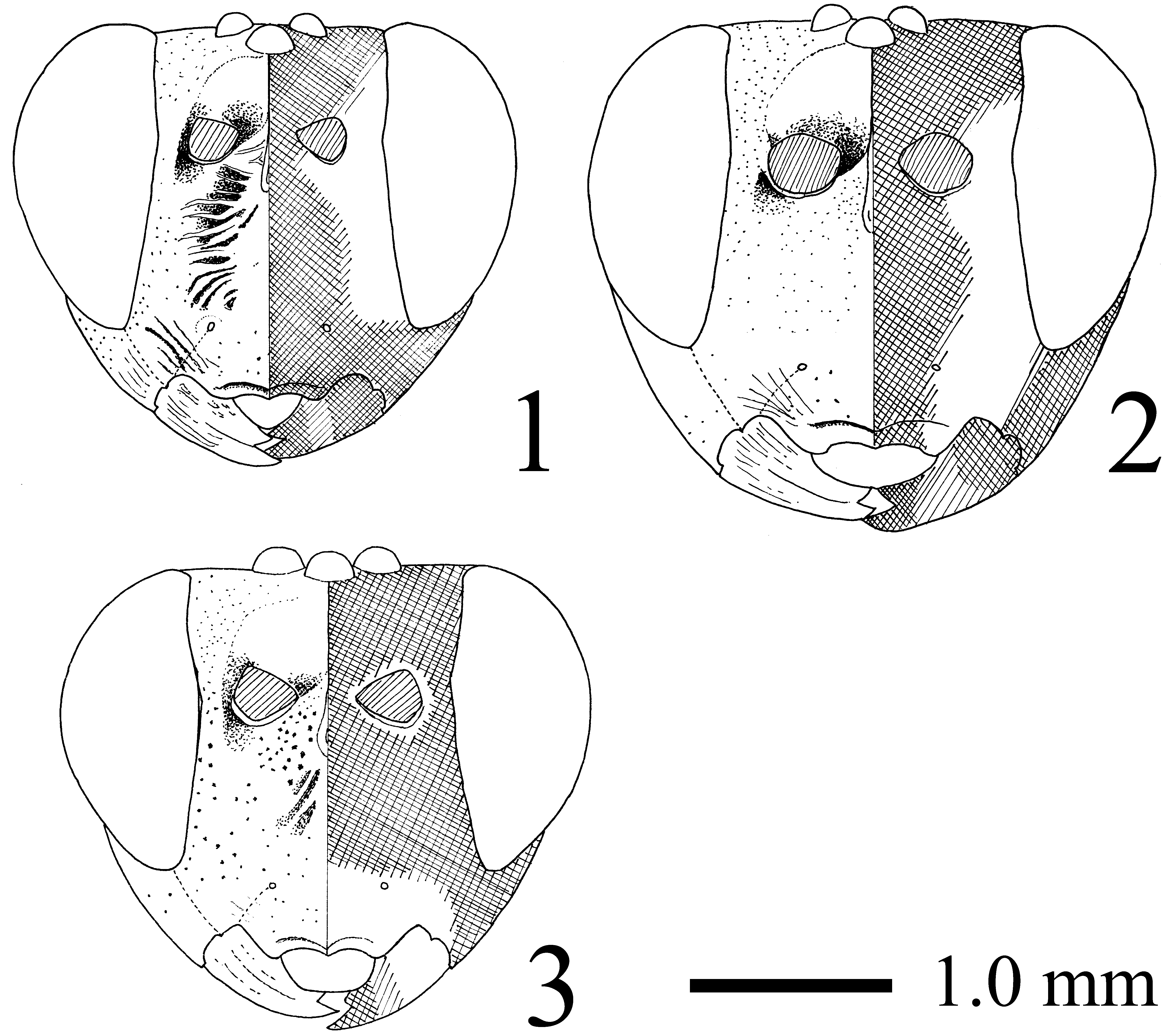
Head. Clypeus 0.6–0.7 times as long as wide. Face 0.6–0.7 times as long as wide, strongly punctate and weakly convex. MSL 0.9 times as long as BWM. Lower tooth of mandible longer than upper tooth. OOL/OD=1.6–1.8. POL/OD= 1.2–1.4. Antenna with 35–38 flagellomeres; first flagellomere 1.2–1.4 times as long as second flagellomere.
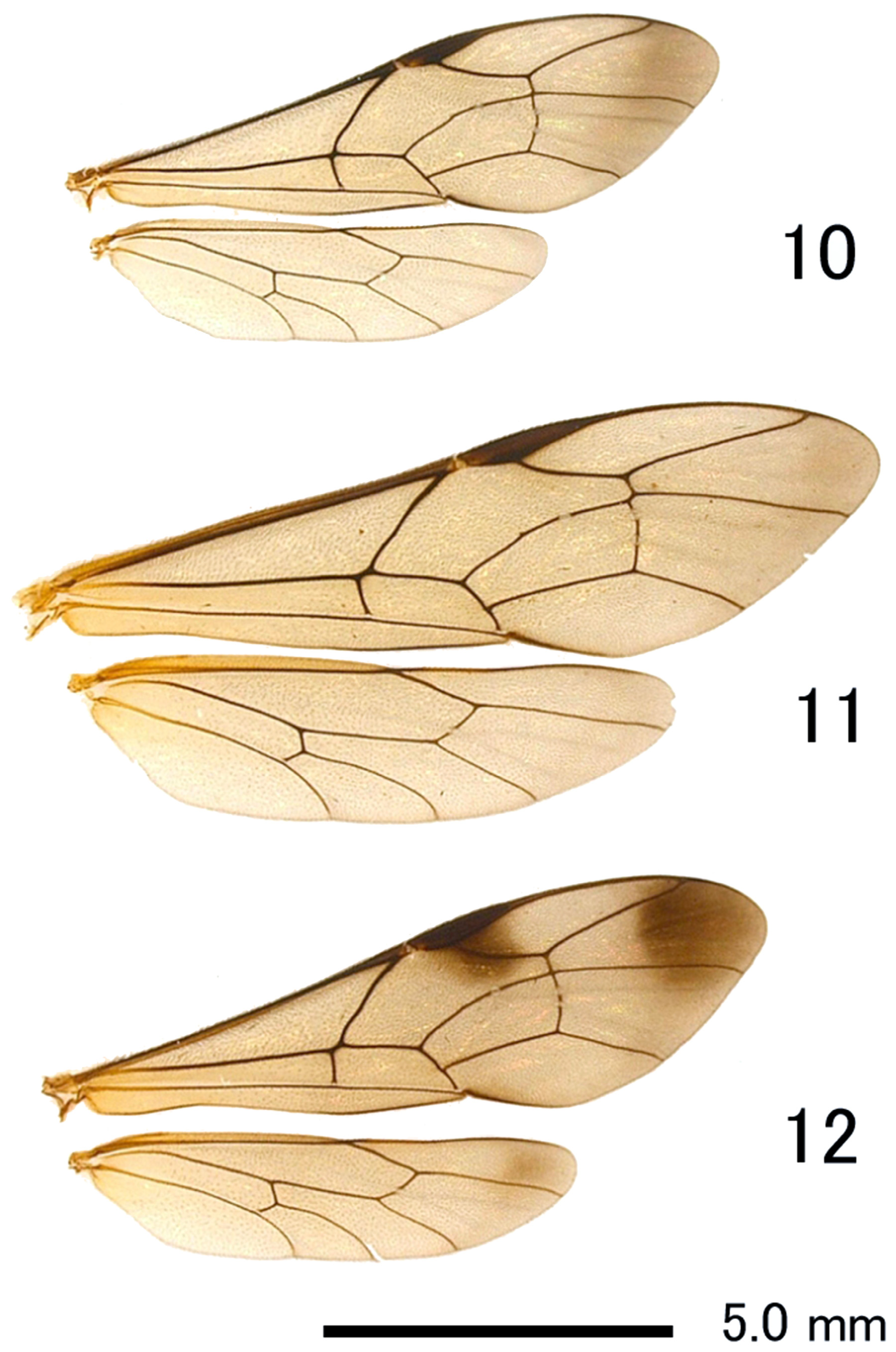
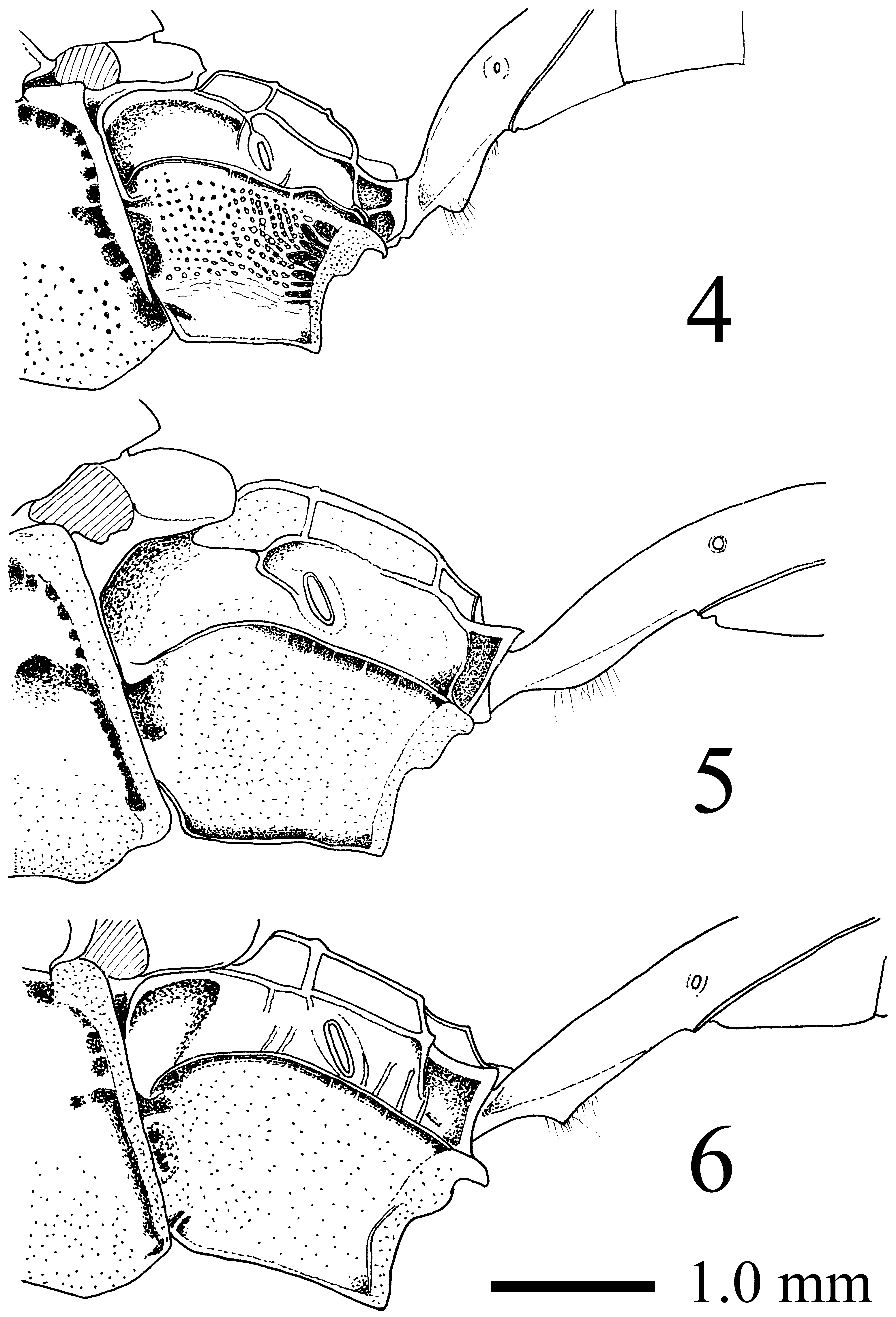
Mesosoma. Lateral area of pronotum densely punctate and longitudinally striate. Lateral part of collar densely punctate. Subalar prominence sparsely punctate. Metapleuron extensively punctate ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 4 – 6 ). Fore wing: length 11.5–15.5 mm, with vein rs-m cross-vein distad of vein 2 m-cu ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 10 – 12 ). Hind femur 3.4–3.7 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view, with distinct convexity ventrally ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 7 – 9 ). Hind tibia 10.8–12.8 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. Hind first tarsomere 2.4–2.7 times as long as second hind tarsomere and 3.2–3.8 times as long as longer hind tibial spur.
Metasoma. T1 2.6–3.2 times as long as maximum width, 2.2–2.3 times as long as T2. T2 0.7–0.8 times as long as maximum width. T1and T2 sparsely punctate. Other tergites densely punctate. Ovipositor sheath 2.4–2.5 times as long as hind tibia.
Coloration. Body black. Antennal flagellum usually without a white band (color form A), but occasionally with a white band in Hokkaido (color form B) ( Figs 19, 20 View FIGURE 19 – 21. A ). Inner margin of eye, tegula, hind corner of pronotum, mesopleuron in part, scutellum, postscutellum, propodeum, apices of T1 and T2 light yellow. Front and middle leg, trochanter, trochantellus, apex of hind tarsus tinged with yellowish brown. Fore wing lacking dark marks ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 10 – 12 ).
Male (n=6; genitalia, n=3). Similar to female. Frons sometimes with strong oblique striations extending from medial ocellus toward eye and densely punctate near antenna ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 19 – 21. A ). MSL 0.8 times as long as BWM. OOL/ OD= 1.4–1.7 OD. POL/OD= 1.1–1.3. Antenna with 39–42 flagellomeres; first flagellomere 1.1–1.2 times as long as second flagellomere. Hind femur 3.2–3.6 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. Hind first tarsomere 2.1–2.6 times as long as second hind tarsomere and 2.8–3.6 times as long as longer hind tibial spur. Face and clypeus light yellow.
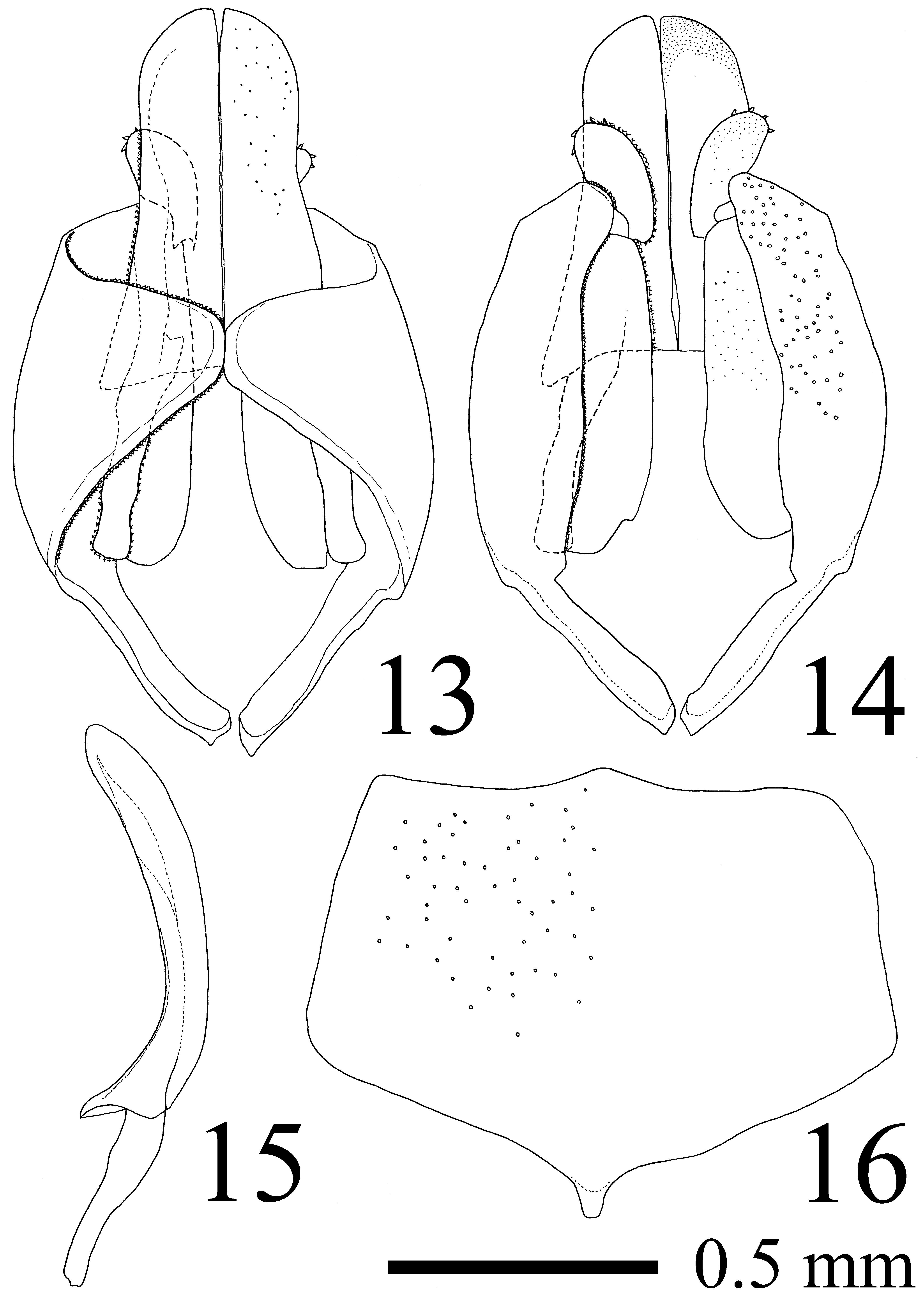
Subgenital plate pentagonal with basal angle obtuse ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 13 – 16 ), its length ca. 0.7 times as long as aedeagus. Paramere short, basal part strongly projected toward the base of subgenital plate ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 13 – 16 ). Aedeagus gently curved, its penis valve ca. 2.0 times as long as basal apodeme ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 13 – 16 ).
Specimens examined. Color form A: Japan: 1F (holotype of Phaenolobus moiwanus ), Mt. Moiwasan, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaido, 18. June 1904, Ishida (SEHU); 1M, Jozan-kei, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaido, 1. July 1912, S. Mastumura (SEHU); 1F, Maruyama, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaido, 29. July 2009, K. Watanabe (KPMNH) [AmHk]; 1F, Hinoemata-mura, Fukushima Pref. 19. July-1. August 2004, H. Makihara (MsT) (KPMNH); 1F, Mt. Hotaka-san, Katashina-mura, Gumma Pref., 1. August, T. Ishizaki (KPMNH); 1F, Mt. Hotaka-san, Katashina-mura, Gunma Pref., 1. August 2007; 1F, same locality, 2. August 2007, K. Watanabe (KPMNH) [AmHn1]; 1F, Kinunuma, Kuriyama-mura, Tochigi Pref., 19. July-1. August 2004, H. Makihara (Malaise Trap) (KPMNH); 1F, Mt. Hakkaisan, Outaki-mura, Nagano Pref., 8. August 2010, K. Watanabe (KPMNH); 1F, Mt. Hakkaisan, Outaki-mura, Nagano Pref., 2. August 2012, M. Ito (NSMT); 1F, Masutomi, Hokuto-shi, Yamanashi Pref., 7. August 2007, K. Watanabe (KPMNH); 1M, Hikawa-rindo, Yamanashi Pref., 16. June 2007, H. Katahira (KPMNH); 1F, Daibosatsutoge, Yamanashi Pref., 3. August 2010, T. Maeda (KPMNH); 1F, Gozaishi Spa., Nirasaki-shi, Yamanashi Pref., 8–17. July 2005, K. Hosoda (Malaise Trap) (OMNH); 1M, Kaminegori, Obama City, Fukui Pref., 8. June 2013, M. Adachi (NSMT) [AmHn2]; 1F, Noka-dani, Ooi Town, Fukui Pref., 9. June 2013, S. Fujie (SEHU) [AmHn3]; 1F, Biwako Balley, Otsu-shi, Shiga Pref., 29. June 2011, M. Ito (SEHU); 1M, Seizui, Togouchi-cho, Hiroshima Pref., 16. May 1997, A. Shimizu (KPMNH); 1M, Tsuchigoya, Omogo-mura, Ehime Pref., 12. July 1998, R. Matsumoto (OMNH); 2M, Mt. Ibukiyama, Saijo-shi, Ehime Pref., 23. June 2004, R. Matsumoto (OMNH).
Color form B: Japan: 1F (lectotype of Arotes moiwanus var. alboannulatus ), T. Uchida (SEHU); 1F, Mt. Daisetsu-zan, Hokkaido, 4–10. August 1926, S. Matsumura (SEHU); 1F, Mt. Teine-kanayama, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaido, 18. July 2012, M. Ito (OMNH) [Ama1]; 1F, Kannonzawa, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaido, 20. August 2007, T. Yoshida (KPMNH) [Ama2]; 1F, Yuni-cho, Sorachi, Hokkaido, 2–12. July 2007, N. Kuhara (MsT) (NIAES).
Distribution. Japan (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu) and Taiwan.
Remarks. We found no other morphological differences between the color form A (including the type of A. moiwanus ) and the color form B (including the type of A. m. var. alboannulatus ). As shown by Castillo et al. (2011), this species can be distinguished from A. albicinctus by the following character states of females: frons with weak striations or striations absent between medial ocellus and eye (densely and coarsely punctate in A. albicinctus ); orbit with moderately fine, sparse punctures near antenna (strong oblique striations in A. albicinctus ); yellow marking on scutellum (black in A. albicinctus ). But males of both species cannot be distinguished from each other except for the following body coloration: scutellum, propodeum and mesopleuron each with a light yellow (black in A. albicinctus ). It can also be distinguished from two Japanese congeners, A. japonicus and A. sugiharai , by the fore wing lacking dark markings and the long ovipositor sheath, 2.4–2.5 times as long as the hind tibia (1.9–2.0 times in other species).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Arotes moiwanus ( Matsumura, 1912 )
| Ito, Masato, Watanabe, Kyohei & Maeto, Kaoru 2014 |
Arotes moiwanus: Castillo et al., 2011 : 85
| Castillo 2011: 85 |
Arotes albicinctus moiwanus:
| Konishi 2000: 749 |
Arotes albicinctus
| Iwata 1958: 68 |
Arotes albicinctus
| Iwata 1960: 150 |
| Uchida 1953: 128 |
Arotes moiwanus
| Uchida 1928: 34 |
Phaenolobus (Acoenitus) moiwanus
| Matsumura 1912: 123 |