Bregmaceros anchovia Ho, Endo & Lee, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4801.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:67D938A6-BB3F-4E60-926F-FEBEF7D7797D |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FC00BDC3-4CD2-452A-94C6-40EFB7A4287E |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:FC00BDC3-4CD2-452A-94C6-40EFB7A4287E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bregmaceros anchovia Ho, Endo & Lee |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bregmaceros anchovia Ho, Endo & Lee , sp. nov.
(New common name: False anchovy codlet; new Japanese name: Hitosuji-saiuo)
Figs. 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ; Table 1
http://zoobank.org/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:FC00BDC3-4CD2-452A-94C6-40EFB7A4287E
Bregmaceros nectabanus View in CoL (not of Whitley): Gloerfelt-Tarp & Kailola, 1984: 83, 311 ( Indonesia; based on NTM S. 10824-005).
Holotype. BSKU 74079 View Materials (43.7 mm SL), ca. 33°28' N, 133°30' E, Tosa Bay , off Haruno (Haruno fishing port), Kochi City, Kochi, Shikoku Island, Japan, by-catch of floating trawl net for young sardines, coll. by E. Katayama and W. Hiramatsu, 18 Dec. 2004. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. Seventy specimens, 35.0– 81.5 mm SL. Japan : BSKU 4652 View Materials (1, 71.5), Tosa Bay, off Susaki, Kochi, Shikoku Island , 2 Jun. 1955 ; BSKU 43422 View Materials (1, 51.2), off Kagoshima, 30°50.5' N, 132°32.4' E, 115–118 m, 1 Nov. 1986 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 50708 View Materials (1, 68.3), Tosa Bay, off Haruno, Kochi, 35 m, coll. by Kochi Prefectural Fisheries Experiment Station , 27 Mar. 2012 ; BSKU 73826 View Materials (1, 49.5), Tosa Bay, Mimase fish market, Kochi, 5 Dec. 1998 ; BSKU 108708 View Materials (1, 49.6) , BSKU 108709 View Materials (1, 56.4) , BSKU 108710 View Materials (1, 49.7), 33°26' N, 133°32' E, Tosa Bay, off Haruno, Kochi, 45 m, coll. by Kochi Prefectural Fisheries Experiment Station , 27 Mar. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 108717 View Materials (1, 57.7) , BSKU 108718 View Materials (1, 58.4), Tosa Bay, off Haruno, Kochi City, 33°27.7' N, 133°31.7' E– 33°28' N, 133°32.5' E, 25 m, coll. by Kochi Prefectural Fisheries Experiment Station , 27 Mar. 2012 GoogleMaps ; KAUM–I.806 (1, 73.0), Uchinoura Bay, Kimotsuki, Ka- goshima, Pacific coast, 31°17' N, 131°05' E, 40 m, set net, coll. by M. Yamada (from Kagoshima City Aquarium ), 6 Apr. 2006 GoogleMaps ; KAUM–I.07465 (1, 46.9), off Chiringa-shima Island, Ibusuki, Kagoshima, 31°16.4' N, 130°40.2' E, 25 m, set net, coll. by Orita Fishery , 9 Dec. 2007 GoogleMaps ; KAUM–I.14737 (1, 58.9), 31°16.4' N, 130°40.2' E, off Chiringa-shi- ma Island, Ibusuki , Kagoshima, 25 m, set net, coll. by M. Meguro and M. Yamashita, 25 Feb. 2009 GoogleMaps ; KAUM–I.27767 (1, 67.2), off Kasasa, Minami-satsuma, Kagoshima, East China Sea , 31°25' N, 130°11' E, gill net, coll. by M. Itou, 15 May 2010 GoogleMaps ; NSMT-P 132876 (9, 38.5–44.9), out of BSKU 125154 View Materials . Taiwan : NMMB-P25588 (10, 51.7–69.8) (measured & counted) ; NMMB-P25589 (10, stained, 67.3–81.5) (measured & counted) ; NMMB-P25590 (1, 71.9) ; NMMB-P25591 (3, 68.5–76.1) ; NMMB-P25593 (20, C&S, 35.0–63.1) (counted); all collected from off Ke-tzu- liao, Kaohsiung, southwestern Taiwan, northern South China Sea , bottom trawl, 30–50 m, 5 Dec. 2016 . Indonesia: NTM S.10824-005 (1, 73.5), Semarang harbor, Sumatra, Indonesia, 65 m, 3 May 1983 . Australia: CSIRO H 4138- 04 View Materials (1, 66.0), FRV Soela, 19°04' N, 118°50' E, north of Port Hedland , Western Australia, 82 m, benthic trawl, 16 Feb 1983 GoogleMaps ; CSIRO H 4195-04 View Materials (1, 57.0), 19°04' N, 118°50' E, northeast Port Hedland , Western Australia, 30 Oct 1983 GoogleMaps , 81 m, benthic trawl; NMV A 29686 View Materials -002 View Materials (1, 53.5), Imperieuse L23 transect, 18° 25' 31" S, 120° 05' 55" E, 103–105 m, beam trawl, 19 Jun 2015 GoogleMaps .
Non-types. Japan: BSKU 17049 View Materials (1), 5°13.5'– 5°13.7' N, 107°0.8'– 107°1.1' E, South China Sea , 60 m, 10 Jul. 1972 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 41125 View Materials (1), off Cape Ashizuri, ca. 250 m, Mimase fish market, Kochi City , Kochi, 22 Mar. 1985 ; BSKU 41997 View Materials (1), 3 Jul. 1985 ; BSKU 72772 View Materials (1), Tosa Bay, off Saga, Kuroshio Town , Kochi, 21 Nov. 2003 ; BSKU 102870 View Materials (1), Tosa Bay , R / V Kotaka-maru, St. 1-1, 120 m, 11 Dec. 2008 ; BSKU 110294 View Materials (1), Japan Sea, off Mishima, Yamaguchi Pref., 85–86 m , R / V Tansei-maru (KT-98-17, St.13-512), 29 Sep. 1998 ; BSKU 125151 View Materials (10) , BSKU 125152 View Materials (102), Tosa Bay , 33°09.3' N, 133°19. 9' E– 33°07.8' N, 133°23.8' E, mid-water trawl, 20–40 m (103–125 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , T3-1 , 28 Nov. 2000 ; BSKU 125153 View Materials (14) , BSKU 125154 View Materials (249), Tosa Bay , 33° 08.9' N, 133°21.6' E– 33°07.1' N, 133°25.4' E (time: 19:47–20:58), mid-water trawl, 25–45 m (117–141 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , T3-2 , 28 Nov. 2000 ; BSKU 125284 View Materials (4), 33°15.9' N, 133°33.6' E– 33°16.2' N, 133°35.6' E (time: 18:53–19:55), surface to mid-water trawl (128–130 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , MT3 , 24 Nov. 1999 ; BSKU 125286 View Materials (1), Tosa Bay , 33°09.3' N, 133°19.9' E– 33°07.8' N, 133°23.8' E (time: 17:35–18:37), midwater trawl, 20–40 m (103–125 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , T3-1 , 28 Nov. 2000 ; BSKU 125300 View Materials (2), Tosa Bay , 33°00.3' N, 133°14.6' E– 32°57.9' N, 133°17.7' E (time: 19:10–20:20), midwater trawl 10–68 m, (124–148 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , T3-4 , 30 Nov. 2000 ; BSKU 125301 View Materials (9), Tosa Bay , 33°08.9' N, 133°21.6' E– 33°07.1' N, 133°25.4' E (time: 19:47–20:58), mid-water trawl 25–45 m (117–141 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru , T3-2 , 28 Nov. 2000 ; BSKU 125302 View Materials (2), Tosa Bay , 33°20.6' N, 133°46.6' E– 33°20.5' N, 133°48.1' E (time: 18:46–19:39), mid-water trawl, 60–127 m (141–145 m at bottom) GoogleMaps , R / V Tenyo-maru, MT-2, 23 Nov. 1999 ; KAUM-I.77876 (1, 64.9), 31°17.3' N, 131°6.6' E, Uchinoura Bay, Kimotsuki, Kimotsuki-gun , Kagoshima, Pacific coast, 40 m, 19 May 2015 GoogleMaps , set net. Taiwan: KAUM–I.114136 (1, 37.6), KAUM–I.114138 (1, 38.5), KAUM–I.114268 (1, 37.0), KAUM–I.114270 (1, 38.7), KAUM–I.114271 (1, 36.4), off Dong-gang, Pingtung County, Taiwan , 8 Mar. 2018 , midwater trawl; NMMB- P25588 (12 of 22), Ke-tzu-liao, 5 Dec. 2015 ; NMMB-P25593 (1, 49.5), Dong-gang , 20 Jan. 2017 ; NMMB-P25595 (34, C&S), Ke-tzu-liao, 5 Dec. 2015 ; NMMB-P25766 (1, 58), Dong-gang , 2017 ; NMMB-P25592 (4, 63–69) (dissected), Ke-tzu-liao, 5 Dec. 2015 . Indonesia: NTM S.10740-005 (1, 68.6), south of Lombok, Indonesia , Jul. 1981 ; NTM S.11914-001 (1), south of Lombok, Indonesia , Jul. 1981 ; NTM S.11915-001 (1, 74.5), Postillon Island, Indonesia. Jul. 1981 . Australia: CSIRO H 2182-02 View Materials (1, 32.0), FRV Soela, 19°05.1' S, 118°53.4' E, north of Port Hedland , Western Australia, 15 Feb 1983 GoogleMaps , 83 m, epibenthic sled; CSIRO H 2253-05 View Materials (3, 27.0–46.0), FRV Soela, 19°05' S, 118°57' E, northeast of Port Hedland , Western Australia, 82 m, benthic trawl, 28 Apr 1983 GoogleMaps . CSIRO H 2806-03 View Materials (2, 13.0–38.0), FRV Soela, 19°3.4' S, 119°2.4' E, North West Shelf, northeast of Port Hedland , Western Australia, 82 m, epibenthic sled, 28 Apr. 1983 GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. A species of Bregmaceros with a pointed snout extending beyond jaws, a stripe of black dots above anal-fin base, a vertical black band on caudal-fin base, and the following combination of characters: ventral surface of head and abdomen devoid of melanophores; ventral portion of abdominal vertebrae with a pointed parapophysis and a blunt ventral post-zygapophysis; peritoneum, pyloric caeca, and intestine pale; dorsal-fin rays 46–52 (usually 47–50); anal-fin rays 47–55 (usually 48–52); pectoral-fin rays 15–17 (usually 16); principal caudal-fin rays 12–14 (usually 13 with middle 11 branched); caudal vertebrae 35–39 (usually 36–37); total vertebrae 50–54 (usually 51–52).
Description. Meristic characters and body proportions of the holotype and selected paratypes are presented in Table 1.
Body moderately elongate, slightly compressed. Snout more pointed than rounded, its tip protruding beyond the jaws. Mouth oblique and slightly subterminal. Upper jaw ending posteriorly below area between center of eye and posterior margin of pupil. Interorbital space smoothly convex. Eye partially covered over its dorsal margin with adipose eyelid. Two nostrils just anterior to eye. Premaxilla with band of two or three rows of conical teeth, all slightly curved inward, those on outer row largest. Dentary teeth biserial, conical, those on inner row larger than those on outer row. Small conical teeth in a V-shaped cluster on vomer anteriorly. First gill arch with multiple rows of small teeth on both limbs.
Pectoral fin inserted at middle of body axis, distal margin pointed, lower 3–6 rays branched. Caudal fin emar- ginate, principal rays usually 13 (12–14), middle 11 (10–12) rays branched, 7 rays supported by caudal plate (sensu Masuda et al., 1986). Pelvic fin insertion at throat, tip of longest ray reaching to between middle portion of anterior lobe and origin of posterior lobe of anal fin; outer 3 rays greatly elongate, finely segmented, unbranched; inner rays short with multiple branches.
First dorsal fin with a single slender occipital ray, its tip reaching to just before origin of second dorsal fin. Origin of second dorsal fin above first or second anal-fin ray. Second dorsal and anal fins with long bases, nearly identical in profile. Both divided confluently into three portions: anterior lobe high, triangular; middle portion low, consisting of rudimentary rays; posterior lobe of moderate height. A rather deep groove bordered by a pair of longitudinal dermal ridges (=lateral line), housing occipital ray, with irregularly shaped scales along groove from middle or posterior fourth of groove to origin of second dorsal fin. A pair of rather wide dermal flaps bordering a groove along ventral contour from insertion of pelvic fin to posterior end of anterior lobe of anal fin; the groove scaleless, internally flat, except a short ridge along middle of groove just after insertion of pelvic fin and before anus.
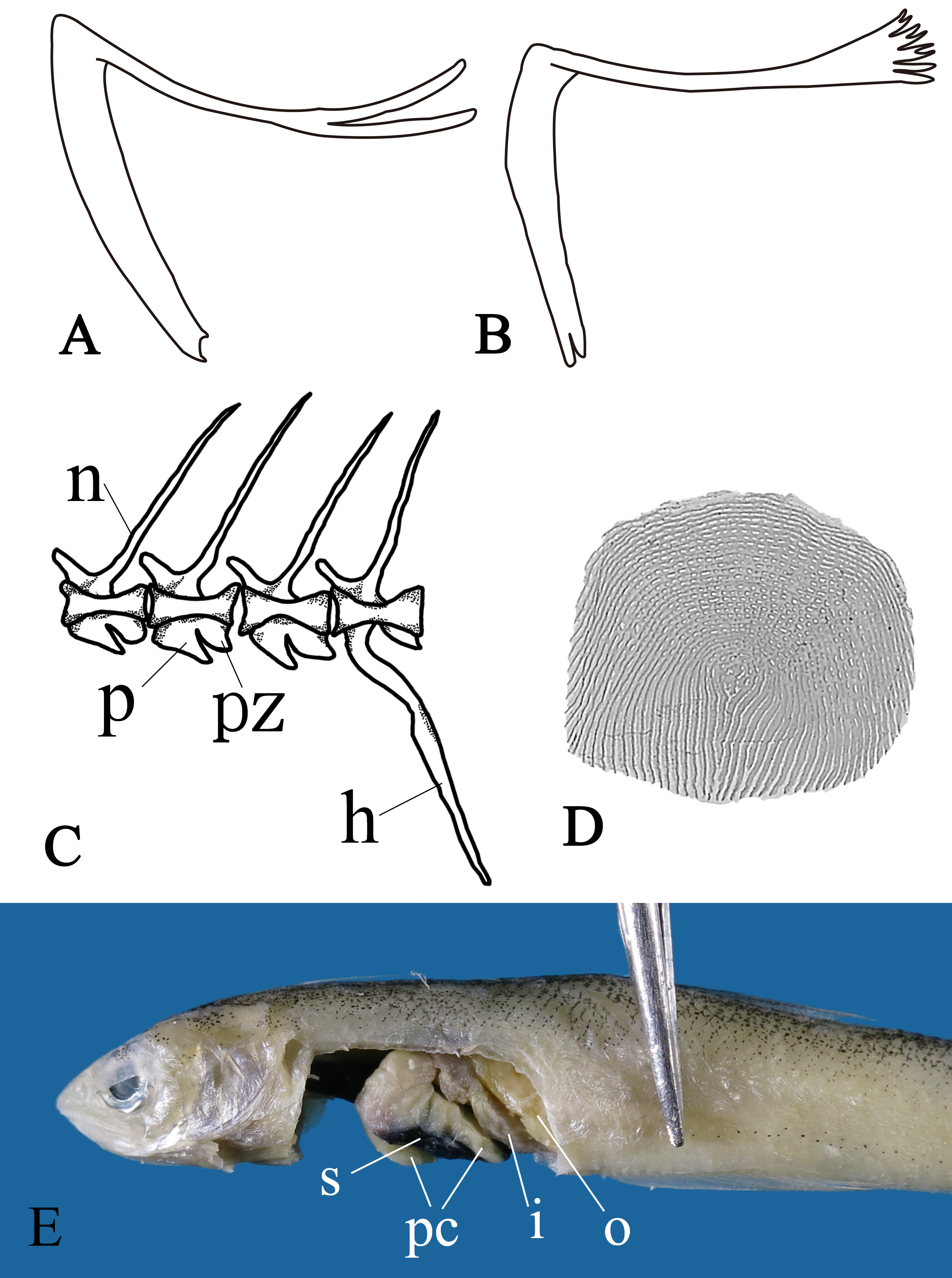
Opercle slender, smoothly convex along anterior margin, tapering to a blunt point dorsally, a simple or slightly forked point ventrally, and a slender, simple (in younger specimens), bifurcate or multi-branched (in larger specimens; Figs. 3A, B View FIGURE 3 ; especially visible when stained), nearly horizontally directed shaft projecting from dorsoposte- rior margin; length of upper arm to lower arm of opercle 85.8% (84.5–89.0%). Axillary flap attached to shoulder girdle, lower half covered by pectoral fin; slender and tapering to a sharp point dorsally and attached to back of pectoral fin ventrally with a nearly round projection on its lower half.
Ventral surface of abdominal vertebrae with a pointed parapophysis anteriorly and a blunt ventral post-zygopophysis posteriorly, both divided by a deep notch ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ).
Scales on middle of body nearly circular, small, cycloid, deciduous, with circuli concentric around focus on exposed part, longitudinally straight and truncated at anterior border on covered part ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ). Small, round cycloid scales on isthmus; scales absent from cheek. Lateral line beginning at about midpoint between dorsal edge of gill cover and insertion of occipital ray, running along dorsum from above posterior margin of gill cover to about middle of posterior lobe of second dorsal fin, and declining diagonally, ending shortly behind declination point.
SL (mm) 43.7 43.7–71.5 (n=8) 66.1–81.5 (n=12)
%SL Mean (Range) SD Mean (Range) SD Head length (HL) 17.0 17.7 (16.7–18.6) 0.7 18.8 (17.5–20.2) 0.8 Upper fork of opercle 4.3 4.2 (3.6–4.7) 0.4 4.6 (4.0–4.9) 0.3 Lower fork of opercle 4.0 3.8 (3.2–4.2) 0.4 4.3 (3.8–4.7) 0.3 Body depth 13.2 13.4 (12.5–14.3) 0.5 15 (13.3–16.9) 1.0 Predorsal length 39.6 40.7 (39.6–43.6) 1.3 42.9 (40.7–44.9) 1.0 Preanal length 37.5 41.2 (37.5–42.9) 1.8 43.8 (41.2–45.5) 1.0 Pectoral fin 8.7 9.8 (8.5–10.9) 0.9 11.3 (10.2–11.9) 0.5 Caudal depth 5.8 5.2 (4.7–5.8) 0.4 5.3 (5.0–5.6) 0.2 Eye diameter 4.8 4.6 (4.0–5.2) 0.4 5.4 (4.7–6.1) 0.4 Interorbital width 3.7 3.2 (2.7–3.8) 0.4 3.7 (3.3–4.0) 0.2 Snout length 5.4 4.9 (4.2–5.4) 0.4 4.6 (4.3–5.0) 0.2 Upper-jaw length 8.4 8.2 (7.8–8.7) 0.3 9.0 (8.3–9.9) 0.4 %HL
Eye diameter 28.1 25.8 (22.1–28.1) 2.0 28.6 (26.3–30.9) 1.7 Interorbital width 21.9 18.1 (15.6–21.9) 2.1 19.8 (17.5–21.3) 1.2 Snout length 31.4 27.6 (25.0–31.4) 2.2 24.6 (22.7–27.7) 1.4 Upper-jaw length 49.5 46.6 (43.1–49.5) 2.1 47.7 (45.5–49.6) 1.2 Meristics n=8 n=33
Dorsal-fin rays 49 47–51 46–52
Anal-fin rays 50 48–52 47–55
Pectoral-fin rays 16 15–17 15–17
Principal caudal-fin rays 13 13 12–14
Total caudal-fin rays 26 26–29 27–31
Prehaemal vertebrae 15 15 15
Caudal vertebrae 37 36–39 35–38
Total vertebrae 52 51–54 50–53
Longitudinal scales rows 77 75–78 74–79
Coloration. When fresh, body unevenly covered by melanophores, dense melanophores on dorsum and posterior fourth of the body; lower parts of body pale. A horizontal band of large black dots on dorsal fourth of body, originating from above pectoral fin to posterior end of second dorsal fin. Ventral half of body largely devoid of pigment, except for band of one to four irregular rows of scattered black dots above anal-fin base, originating from slightly in front of origin of anal fin to end of fin base.
Posterior half of dorsal surface of head densely covered by melanophores, gradually becoming less dense from above eyes to tip of snout anteriorly; V-shaped black mark on snout in dorsal view; lateral surface of head, including both jaws, gill cover, isthmus, and branchiostegal membranes, devoid of pigment. Dorsal margin of adipose eyelid and upper half of scapular covered by dense melanophores.
Second dorsal fin covered by scattered melanophores, denser on anterior than posterior lobe. Pectoral, pelvic, and anal fins devoid of melanophores, or only occasionally few scattered ones at anterior base of fins. Caudal fin with dense melanophores on base forming a vertical band, remaining section covered by scattered melanophores.
Dorsal groove with scattered melanophores; ridges on each side of groove densely covered with melanophores; longitudinal central ridge and lateral dermal flaps of ventral groove devoid of melanophores.
Stomach black; peritoneum, pyloric caeca, and intestines pale ( Fig. 3E View FIGURE 3 ).
Preserved specimens with body creamy white ground color and pigmentation pattern as described above.
Size. The largest specimen examined is 81.5 mm SL (NMMB-P25589, 1 of 10).
Etymology. The specific name anchovia , as a noun in apposition, a genus of anchovies (family Engraulidae ), refers to the outline of the fish which is very similar to anchovies.
Distribution. Known from Japan (off Kagoshima and Kochi), southwestern Taiwan (off Ke-tzu-liao and Donggang) and Indonesia (off Lombok and Postillon Islands), and Australia (North West Shelf). Bathymetric range 10– 120 m.
Remarks. Bregmaceros anchovia is no doubt the same as B. “ pseudonectabanus ” [an unavailable name] proposed by Torii (2003, unpublished thesis). The pointed snout and a stripe of black dots above the anal-fin base distinguish it from all other species in the family.
Bregmaceros anchovia is most similar to B. nectabanus , which also occurs in the western Pacific Ocean, but differs from B. nectabanus in having a pointed snout that projects well beyond the jaws (vs. snout rounded and barely projecting beyond jaws) and a stripe of dots above anal-fin base (vs. no such pigmentation in same area). The emarginate caudal fin and lack of scales on the cheek distinguish B. anchovia from B. lanceolatus and B. pseudolanceolatus , both of which possess a pointed (sometimes rounded) caudal fin and scales on the cheek.
Examination of the large number of specimens of B. anchovia showed that the upper arm of the opercle changes with growth in shape. In many smaller individuals (ca. <30 mm SL), the upper arm terminates in a single tapering point, whereas, in large individuals (ca.> 30 mm SL), it is bifurcated and divided into many small branches in some individuals (> 60 mm SL) ( Figs. 3A, 3B View FIGURE 3 ). This variation is rare in Bregmaceros , as we found the forked or simple conditions to be usually quite consistent. For example, in B. japonicus , the upper arm is always simple, whereas in B. lanceolatus , B. pseudolanceolatus , and B. nectabanus , the upper arm is always bifurcate to trifid in small individuals (ca. <40 mm SL), and gradually showsmore branches in larger individuals ( Torii et al, 2003a, b, c, 2004). Judging from the combination of other characters, such as meristics, pigmentation, and shape of snout, we are confident that all specimens of B. anchovia belong to a single species despite the variations of the upper opercular arm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Bregmaceros anchovia Ho, Endo & Lee
| Ho, Hsuan-Ching, Endo, Hiromitsu, Lee, Chia-Lien & Chu, Tah-Wei 2020 |
Bregmaceros nectabanus
| Gloerfelt-Tarp, T. & Kailola, P. J. 1984: 83 |