Chrysis bhavanae Bingham, 1903
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4929.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1290857D-36E6-47DE-81C7-70CBD7C0AE01 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4676766 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A96A8877-B423-FF8D-64CD-F581FAA78F34 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chrysis bhavanae Bingham, 1903 |
| status |
|
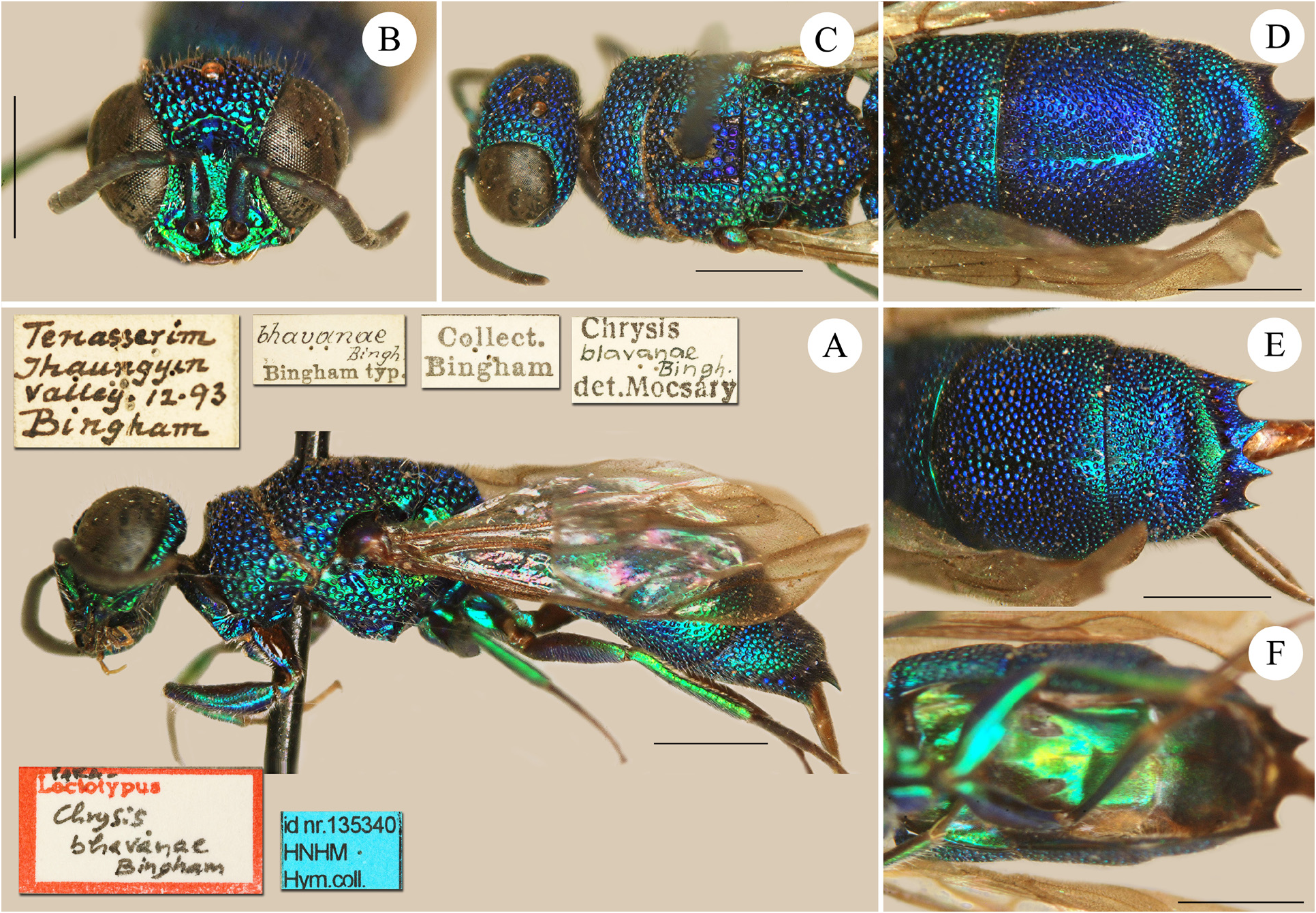
Chrysis bhavanae Bingham, 1903
( Figs 25 View FIGURE 25 A–25F)
Chrysis bhavanae Bingham, 1903: 472 . Lectotype ♀ designated by Bohart in Kimsey & Bohart 1991: 389; Myanmar: Tenas- serim (HNHM) (examined). Kimsey & Bohart 1991: 389 (cat., ignita group).
Chrysis bhavanne (!): Jonathan et al. 1977: 87 (cat., India: Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana).
Material examined. 1♀; India: Tamil Nadu, Nalgiri Hills, Kallar , 1500 ft, 3.vii.1954, leg. Nathan, GBIF_ Chr 00033252 ( MNLU) . 1♀: Devala, Nalgiri Hills, without further data ( NHMW) , 1♀, Mysore State, Shimoga Dist., Agumbe Ghat , 2000 ft, 05.1995, leg. T. Nathan ( GLAC) .
Redescription. Female. Body length 7.0 mm. Forewing length 4.2 mm. OOL 1.7 × MOD; POL 1.5 × MOD; MS 0.6 × MOD; relative length of P:F1:F2:F3 = 1.0:1.2:1.0:0.8.
Head. Frons with large (up to 0.5 × MOD) and contiguous punctures; vertex with double punctation and smaller punctures, with tiny dots on intervals; ocellar triangle and occiput with smaller punctures; transverse frontal carina distinctly angled, short, ending less than 1.0 × MOD from eye’s inner margin; scapal basin transversally microstriate; subantennal space about 1.0 × MOD; apical margin of clypeus incurved and thickened; genal carina sharp to mandibular insertion; distinct subgenal carina.
Mesosoma. Medial pronotal line [= pronotal groove] shallow, barely visible, and differently coloured, darker blue, reaching almost the posterior margin of pronotum; pronotum with even punctation, with tiny dots on interspaces, 0.1–1.0 × PD apart; mesoscutum with larger punctures, with abundant tiny dots on interspaces; notauli as lines of small, deep and rounded foveae, dark blue contrasting with colour of mesoscutum; parapsidal signum [= parapsidal line] fully developed and visible; mesoscutellum postero-medially with larger and contiguous punctures; metanotum with large, irregular foveate punctures without interspaces; metapectal-propodeal disc unmodified; posterior propodeal projections [= propodeal teeth] subparallel; mesopleuron with posterior oblique sulcus [= scrobal sulcus], formed by foveate punctures, transversally confluent with other punctures of pleuron; with tiny dots on interspaces. Spurs of mesotibia distinctly unequal in length; mesotarsomere I as long as II–IV together, V as long as II. Wings with nervures unmodified.
Metasoma. Tergum I and tergum II with similar punctation, punctures decreasing in diameter to apical margin and double on lateral margins; tergum III denser, with double punctures, with deeper tiny dots on interspaces, somewhere corrugated; pits of pit row deep, distinctly larger than other punctures on tergum; ovipositor broad; apical margin with four short, triangular teeth. Metasomal terga without median longitudinal carina. Black spots on sternum II narrow and elongate, placed at side of sternum, 2.5 × MOD distant from each other.
Colouration. Body metallic green to light blue, darker blue on median area of mesoscutum, medially on mesoscutellum, and at base of terga II and III. Tegula brown in the holotype and metallic light blue in the paratype; scape, pedicel and flagellomere I blue, other flagellomeres black. Wings clear, with brownish veins.
Vestiture. Head with brownish, erect, and short setae, about 1.0 × MOD long, white to silvery on scapal basin, whitish and short on meso- and metasoma; on meso- and metatibiae whitish, erect and longer (about 1.5 × MOD).
Male. Unknown.
Distribution. India ( Uttar Pradesh; Punjab; Haryana; Mysore; Tamil Nadu). Oriental: Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines ( Kimsey & Bohart 1991).
Remarks. Chrysis bhavanae Bingham was included in the Ch. ignita group by Kimsey & Bohart (1991). We tentatively include it in the Chrysis maculicornis species group for the noticeably short malar space, the subgenal carina and the narrow and elongate black spots on the sternum II; however, its placement in this group is doubtful without examination of the male. It resembles Chrysis gracilenta Mocsáry, 1889 , in the ignita group, for its general habitus; however, the shape of head and the black spots on sternum II are diagnostic and do not match the diagnostic features of this group. Chrysis bhavanae is separated from Ch. gracilenta , by shorter malar spaces; shorter distance between inner margin of eyes; shorter flagellomere I [l/w = 2 in Ch. bhavanae (width taken at base of F1) vs. l/w = 3]; transverse frontal carina arcuate (vs. medially straight and downcurved toward eye); black spots on sternum II small (vs. large, oval and covering half sternum), punctation on tergum II even (vs. double and more spaced).
| NHMW |
Naturhistorisches Museum, Wien |
| GLAC |
Glacier National Park, Glacier Collection |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Chrysidinae |
|
Tribe |
Chrysidini |
|
Genus |
Chrysis bhavanae Bingham, 1903
| Rosa, Paolo, Aswathi, Pokkattu Gopi & Bijoy, Chenthamarakshan 2021 |
Chrysis bhavanne
| Jonathan, J. K. & Roy, S. B. & Dhar, M. 1977: 87 |
Chrysis bhavanae
| Kimsey, L. S. & Bohart, R. M. 1991: 389 |
| Kimsey, L. S. & Bohart, R. M. 1991: 389 |
| Bingham, C. T. 1903: 472 |