Hemienchytraeus quadratus, Dózsa-Farkas, Klára & Hong, Yong, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.194222 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5669747 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/65774246-B86F-9D19-FF5B-3356FA96282A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hemienchytraeus quadratus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Hemienchytraeus quadratus View in CoL sp. n.
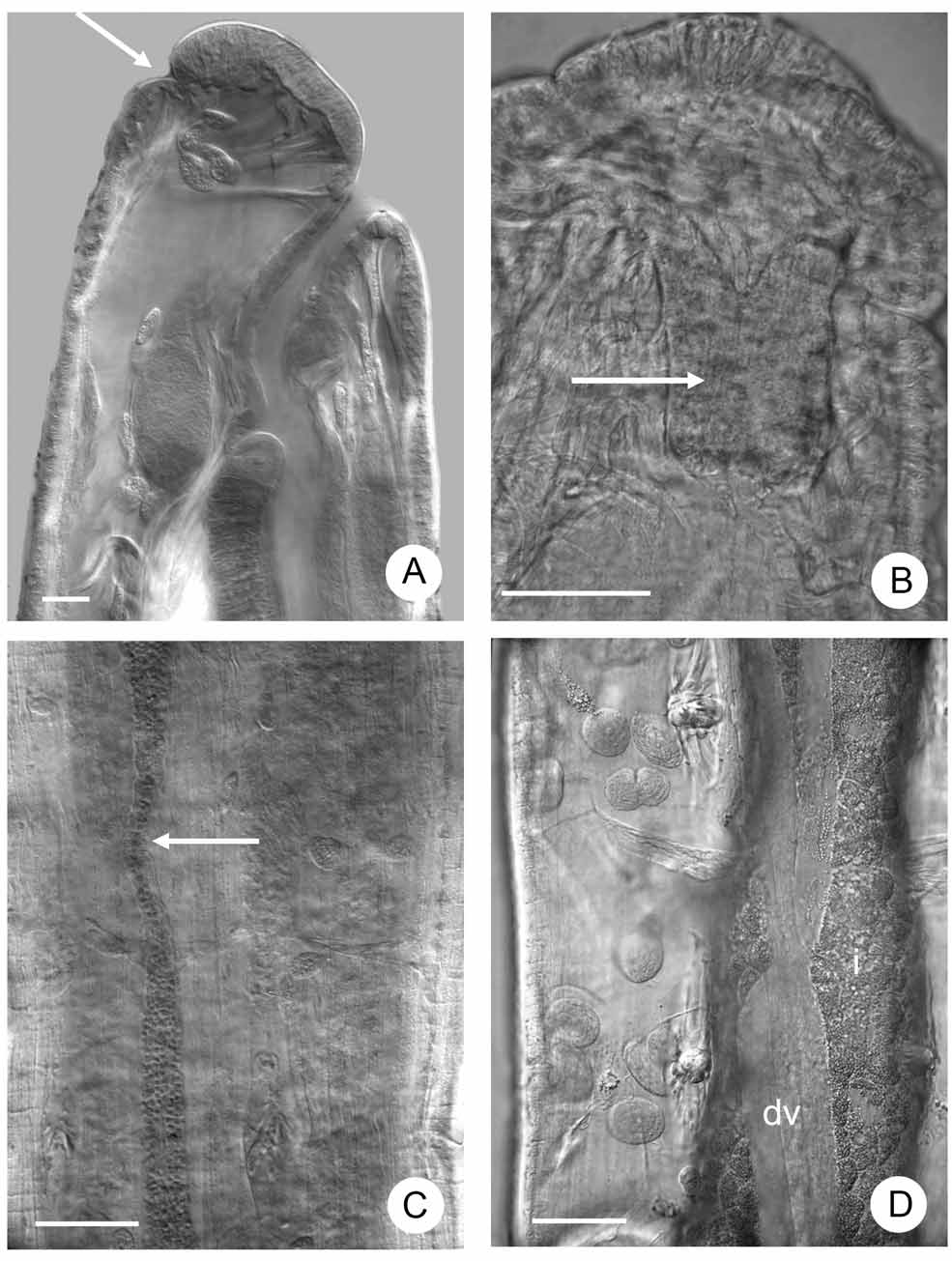
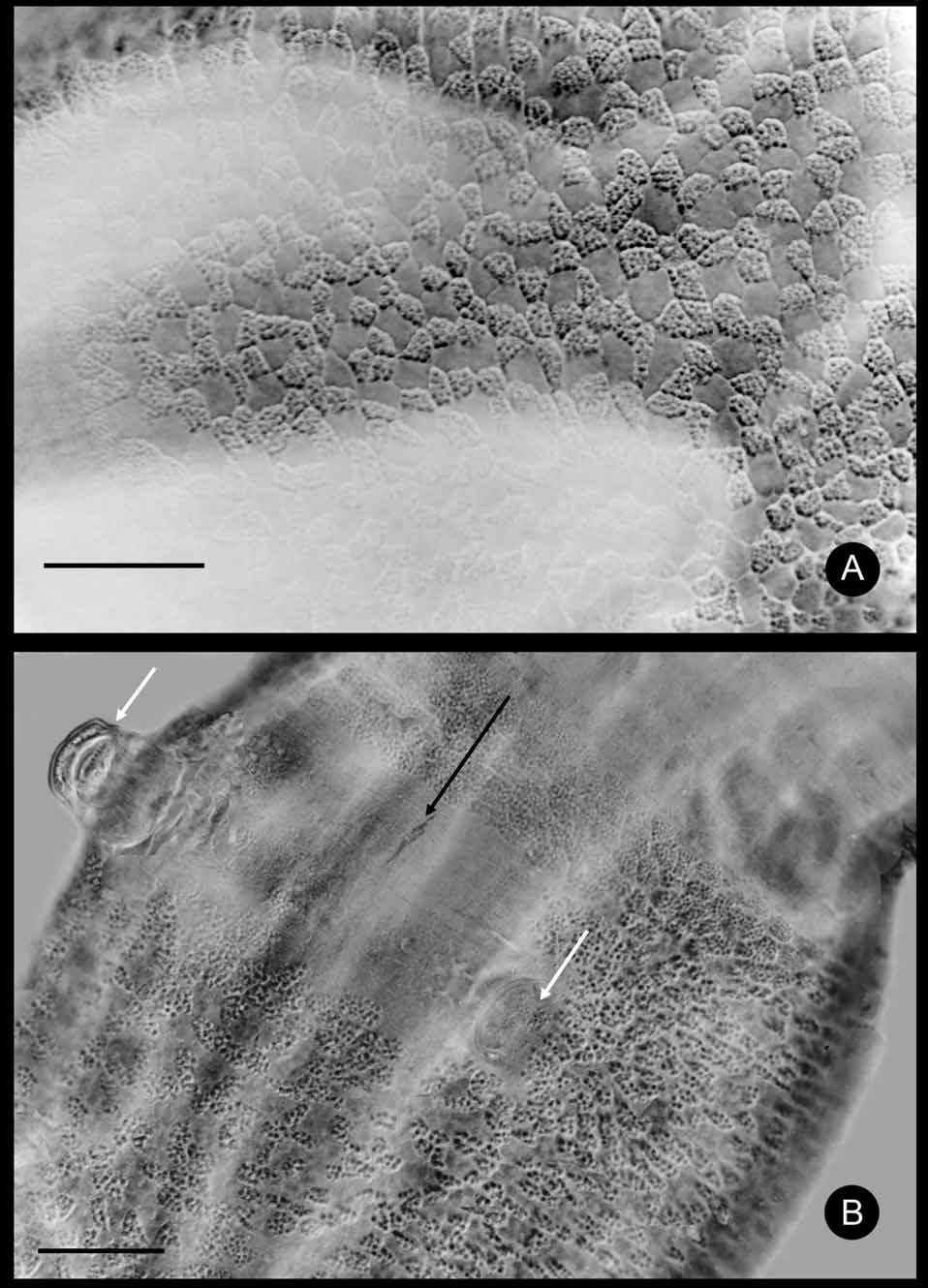
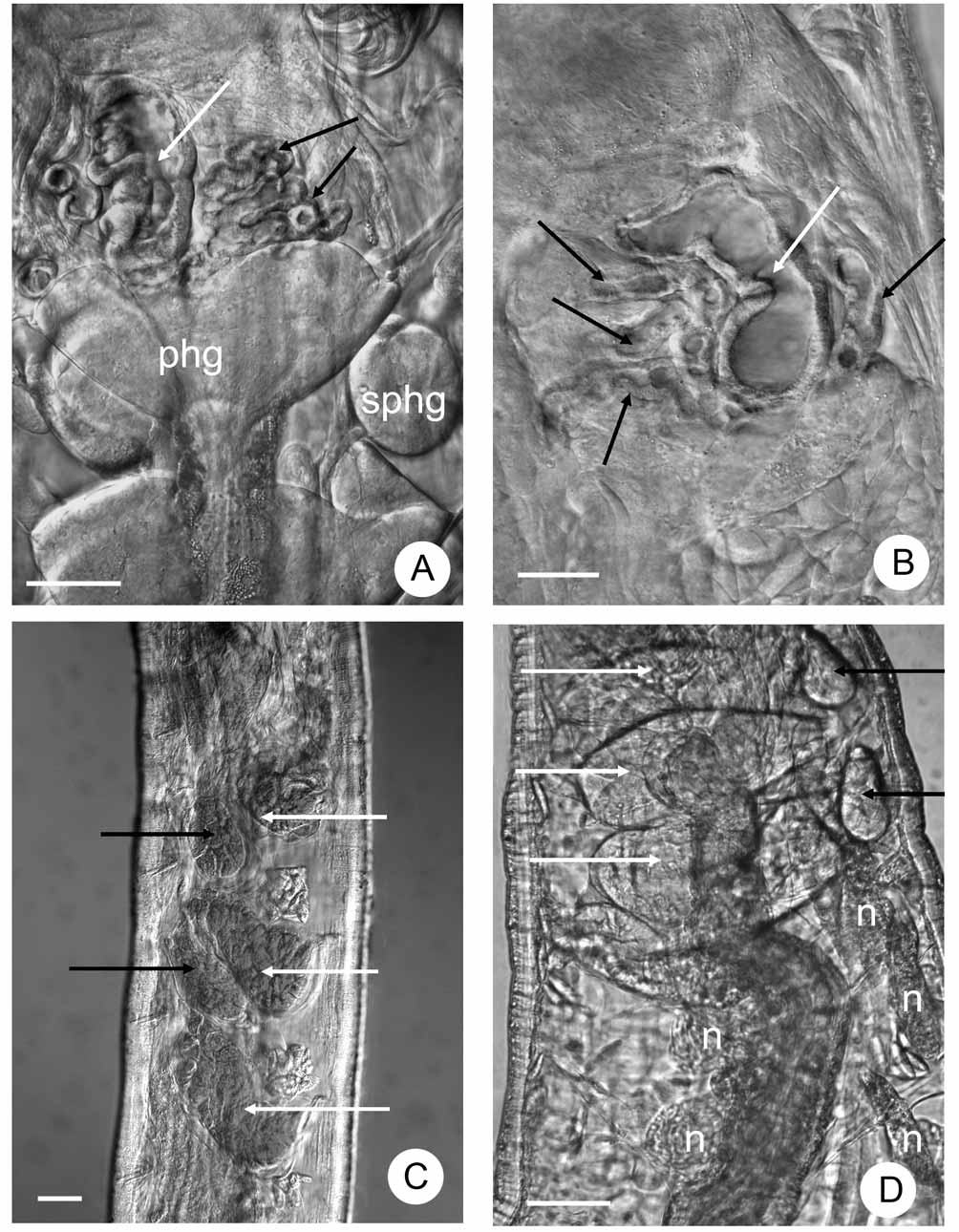
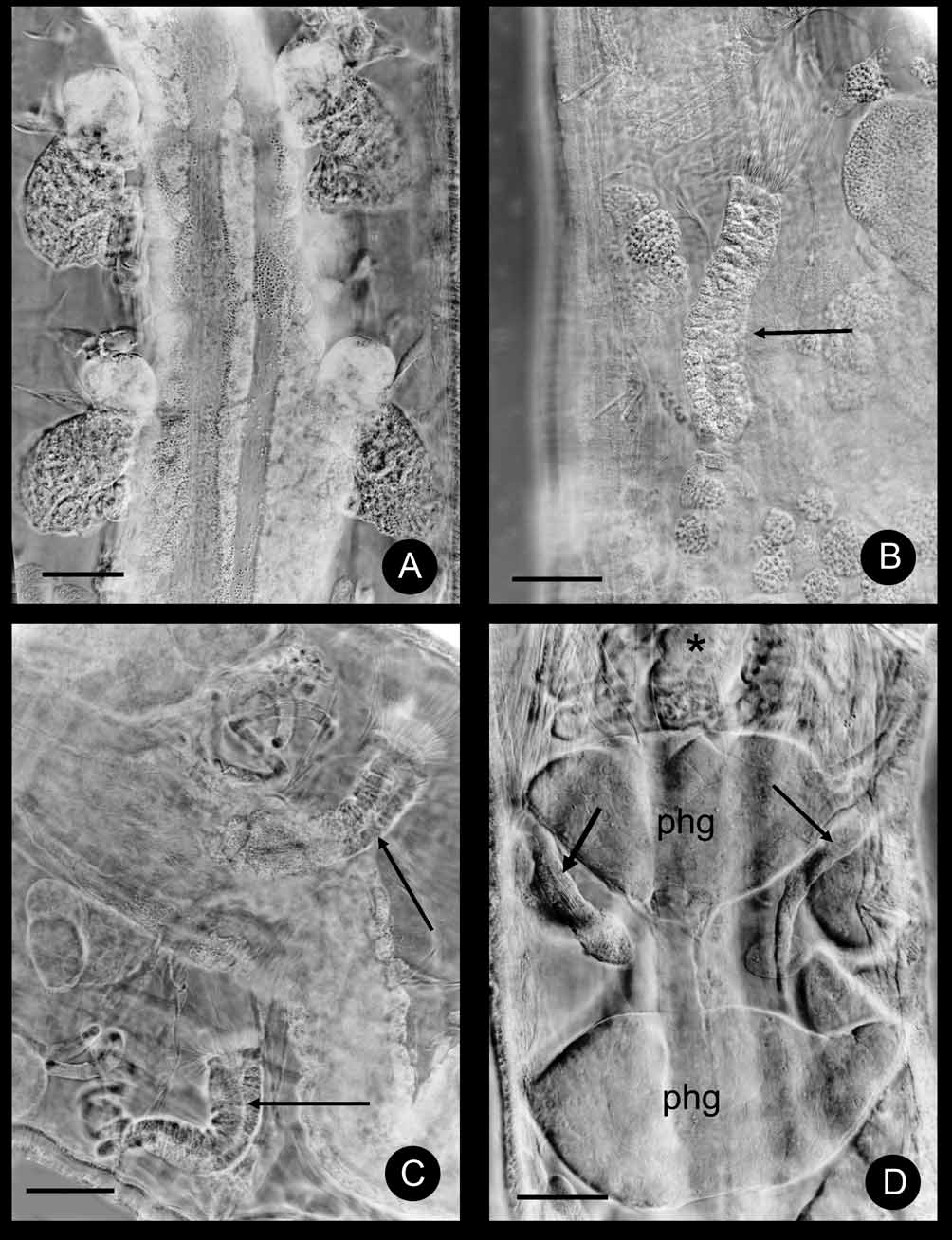
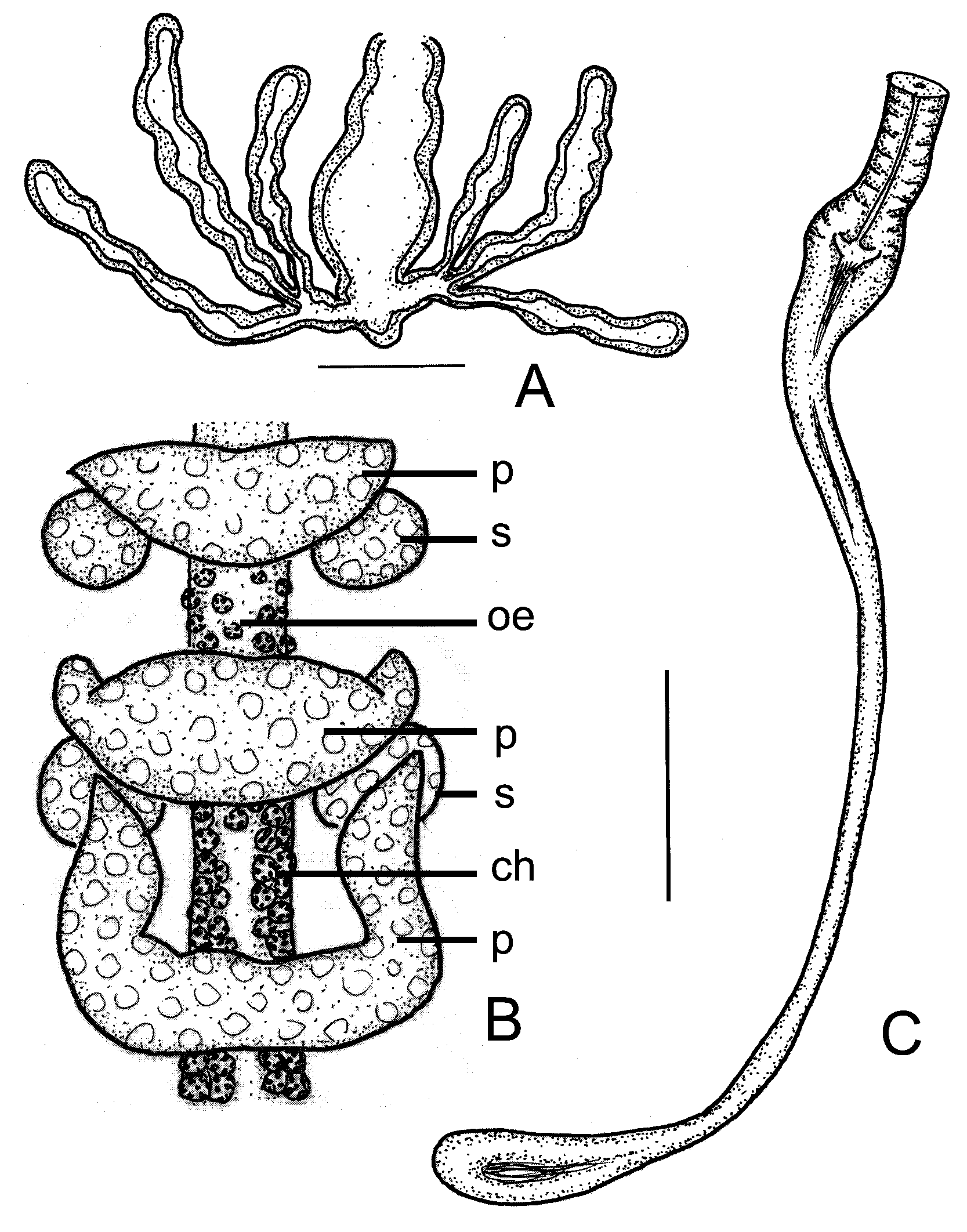
( Fig. 13–17 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURE 14 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 )
Type material. Holotype: Clitellate (NIBRIV 0 0 0 0 138929): Type locality: Korea, soil and litter layers in mountain forest nearby experimental farm, College of Agriculture & Life Science, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju-si, Jeollabuk-do, (N 35˚50΄50.2ʺ, E 127˚08΄0 1.8ʺ), (Site C), coll. 3 September 2007. stained with borax-carmine, whole-mounted on slide (No. 185). Deposited in the National Institute of Biological Resources, Korea.
Paratypes: Clitellate (NIBRIV 0 0 0 0 138930 and NIBRIV 0 0 0 0 138931) two specimens on two slides (No. 129, 183), stained with borax-carmine, collected 0 3. 0 9. 2007, locality is the same as the locality of the holotype
P. 87. 1-5 five specimens on five slides (No. 128, 135, 184, 237, 238), stained with borax-carmine coll. 0 3. 0 9. 2007; P. 87. 6 one specimen on slide (No.208), stained with borax-carmine coll. 0 6. 10. 2008. Locality of all six specimens is the same as the locality of the holotype.
Etymology: the species name refers to the characteristic gland-free square area of the clitellum, derived from the Latin quadratus = square
Description. Holotype 5.2 mm long, 214 µm wide at VIII and 271 µm at the clitellum (fixed), segments 32. Body length of paratypes 4.5–9.6 mm, width 260–300 µm at VIII and 320–400 µm at the clitellum (in vivo), length of fixed specimens 3.6–6.6 mm, width 110–285 µm at VIII, 133–360 µm at the clitellum, segments (25)–28–34. Chaetae 2 per bundle, absent in XII (in two specimens one or two chaetal bundles had three chaetae in terminal segments, slightly sigmoid without nodulus, pointed distally, blunt proximally. Chaetae in preclitellar bundles 25–35x 2.5–3 µm, ventrally slightly longer and gradually increasing in size posteriad, in terminal segments up to 45– 50 x3.7–4 µm. Head pore on the prostomium, dorsal, subterminal ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 A), dorsal pores absent. Epidermal gland cells clearly visible in three transverse rows per segments. Clitellum in XII extending over a little more than one segment, girdle shaped, hyalocytes and granulocytes net-like dorsally ( Fig.14 View FIGURE 14 A); diameter of hyalocytes 12–16 µm, granulocytes 12.5 x7–8 µm (fixed). Ventrally, between and in front of the male pores, there is a ca. 175 x70 µm area, where the glands are absent, anterior to this only granulocytes more or less in transverse rows, and posterior granulocytes in two rows followed by reticulated granulocytes and hyalocytes. ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 B). Body wall ca. 17–20 µm, cuticle 1–1.5 µm thick (fixed). Anterior septa are thicker than postclitellar septa. Brain ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 B) about twice as long as wide, deeply incised anteriorly and posteriorly. Post-pharyngeal bulbs conspicuous. Ventral nerve cord perikarya fewer in the region of the septa but continuous ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 C).
Unpaired root of the oesophageal appendage (peptonephridia) 45 µm wide and ca. 90 µm long (in vivo), with wide cavity. Two primary branches very short, 11-15 µm long and divide into three thin-walled branches, 75–100 µm long by 12–13 µm wide, with wide lumen. ( Fig.15 View FIGURE 15 A, B, 17A). All three pairs of pharyngeal glands ( Fig.15 View FIGURE 15 C, D, 17B) united dorsally, with wide connection and without ventral lobes in IV, with small ventral lobes in V, and with narrower connection but with large ventral lobes in VI. Two pairs of welldeveloped secondary glands in V, VI. Chloragocytes from V, flat (diameter 10 µm in vivo) light yellow. Dorsal vessel from XII–XIII, blood colorless. Inflated ventral gut epithelium from ½XIX to XX or XX–XXI. Three or two pairs of preclitellar nephridia from 6/7 to 8/9 ( Fig.15 View FIGURE 15 D, 16A). In preclitellar segments efferent duct arising medially, in posterior segments sub-terminally; no terminal vesicle. Lengths of preclitellar nephridia 110–133 µm (fixed), those in terminal segments of a similar size or a little larger (140–170 µm long). Length ratio anteseptal:postseptal in anterior segments 1:1.3–2, in the terminal segments 1:1. Anteseptal with brownish granules ( Fig 16 View FIGURE 16 A). Coelomocytes ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 D) light yellow oval with clearly visible nucleus and finely granular matrix, 25–42x 20–25 µm in vivo), 17–20x 7–12 µm (fixed).
Seminal vesicle absent. Sperm funnels ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 B, C) cylindrical tapering distad, about ½ as long as body diameter, 3–4 times as long as wide (100–120 µm long, in vivo). Collar as wide as the funnel body, spermatozoa ca. 55–60 µm, the head 11 µm (fixed). Sperm ducts not long more or less coiled in XII, diameter 10 µm (fixed). Male copulatory organs oval ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 B) with developed musculature (diameter 40x 33 µm), male glandular body globular, diameter ca. 37–38 µm (fixed). No accessory copulatory glands.
Spermathecae ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 C) free, not attached to oesophagus. Ectal ducts short muscular ca. 30–37 µm long and 13–18 µm wide (fixed), swelling to form thick-walled ectal dilations (diameter 20–23 µm) ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 D) most often containing sperm, continuing as 200 µm long tubes distally tapered (12–10–8 µm) and terminating in reclinate ampullae (diameter 13–16 µm, fix) in VII (in the fixed specimens they are often in VI). The ampullae thin walled. Ampullae and ducts also contain sperm. One mature egg at a time.
Distribution and habitat: Only known from type locality (Soil and litter layers in mountain forest nearby experimental farm, College of Agricultur & Life Science, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju-si (site C).
Diagnosis. The new species can be recognized by the following combination of characters: (1) the size of worms (4.5–9.6 mm, width 260–300 µm in vivo, segment number 28–34); (2) all pairs of pharyngeal glands united dorsally, large ventral lobes only in VI, secondary glands in V and VI; (3) two or three pairs of preclitellar nephridia; (4) nephridia in the terminal segments are as long as or a little larger than preclitellar nephridia; (5) the unpaired trunk of oesophageal appendages has a wide lumen, primary branches are very short, divided into three secondary branches on each side, which are long and thin-walled with wide lumen; (6) oval yellowish faintly granular coelomocytes with well visible nucleus; (7) clitellum is girdle-shaped, ventrally with a characteristic square area devoid of any glands; (8) dorsal vessel from XII–XIII; (9) seminal vesicle is absent; (10) sperm funnels are cylindrical, approximately 3–4 times as long as wide, collar is as wide as the funnel body itself; (11) spermathecae are free, extending into VII, ectal ducts are short, ectal dilations are thick-walled, the connecting tubes are tapered distally, the ampullae thin-walled. Dilations, ampullae and ducts can contain sperm equally.
Differential diagnosis. Among the previously described in which the oesophageal appendage have more than two secondary branches, the spermathecae extends as far as VII and the ental ampullae of spermathecae are not dilated considerable, four species [ H. patricii Schmelz and Römbke, 2005 , H. stephensoni (Cognetti, 1927) , H. mauriliae Righi, 1981 and H. brachythecus Xie, Wang and Liang, 1999 ] are similar to the new species. The main differences are as follows:
H. quadratus resembles H. patrici in size, segments number, numbers of preclitellar nephridia, the formation of the pharyngeal glands and spermathecae but differs as the terminal chaetae are more than twice as large as preclitellar chaetae in H. patrici (70–80 compared to 25-30 µm) ( Schmelz & Römbke 2005), whereas they are only moderately larger in the new species (45–55 compared to 25–35 µm). In both species the primary branches of the oesophageal glands are short but in H. patricii there are 4-5 secondary branches with different thickness and length, forming a cauliflower-like mass, in H. quadratus there are just three uniform, slender secondary branches. Moreover, in H. patricii the dorsal vessel is from XIII–XIV, the sperm funnels are longer than the worm’s diameter, 6–8 times as long as wide and the clitellum saddle-shaped while in H. quadratus the dorsal vessel is from XII–XIII, the sperm funnels are half as long as the diameter of worms, only 3–5 times as long as wide and the clitellum is girdle-shaped with a square verntral area free of glands.
The segment number and the size of H. stephensoni are similar to the new species, and both have oesophageal appendage with three secondary branches but in H. stephensoni the trunk of the oesophageal appendage and the primary branches are equal long and the secondary branches are 3–4 times as long as wide and compact, in contrast with H. quadratus , which have very short primary branches and the secondary branches are ca. 8 times as long as wide and have wide lumen. Additionally, in H. stephensoni the terminal chaetae are 70–83 µm long, the third pair of pharyngeal glands is free and there are four pairs of preclitellar nephridia, but in H. quadratus these chaetae are only 45–55 µm long, there is a wide connection between all pharyngeal glands and there are two–three pairs of nephridia preclitellarly. Also in H. stephensoni the dorsal vessel origin is in XIII–XIV, even if the clitellum is girdle-shaped ventrally there are only granulocytes, the collar of the sperm funnel is narrower, the ectal ducts of spermathecae are longer and the ampullae reach segment VIII (Cognetti 1927, Schmelz & Collado 2007).
Because Schmelz and Collado (2007) provided substantial evidence that the worms from China described as H. stephensoni by Xie et al. (1999) are not identical with H. stephensoni Cognetti, I feel it is necessary to make a comparison between this Chinese and the new species. Differences: in the Chinese species the clitellum is longer (XII-1 /2XIII) (about the ventral site no information), the secondary pharyngeal glands are absent, there are more preclitellar nephridia (5 pairs), the sperm funnels are shorter (3 times longer than wide) and the collar is narrower than the funnel itself. The oesophageal appendages are similar to H. stephensoni (after the revision of Schmelz & Collado 2007).
The size of H. maurilae is unknown, because it was described on the basis of only one specimen and the end of worm was absent ( Righi 1981), but it differs from H. quadratus because it has 5 pairs of preclitellar nephridia and the sperm funnels are twice as long as the body diameter.
Finally H. brachythecus ( Xie et al. 1999) View in CoL from China differs from the new species by the spermathecae, which are found only in V, and have 5 pairs of preclitellar nephridia.
Table 2 View TABLE 2 is provide a summary of the differences among the three new species.
We are grateful to the two reviewers: Kathryn Coates and Jiři Schlaghamerskỹ for their constructive help. This research was financed by the Hungarian National Scientific Research Foundation (OTKA 49635). Some research equipments (microscope and digital camera) were also provided by the OTKA - Foundation (M 27225 and M 045482).
This work was also supported by a grant from Rural Development Administration, Korea (2006).
TABLE 2. Characters distinguishing the three new Hemienchytraeus spp.
| Chaetal length in preclitellar segments in terminal segments | 35–38 μm 63–71 μm | 28–35 μm 50 μm | 25–35 μm 45–50 μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. secondary branches of oesophageal appendages | 5–6 each side (compact with few small canals) | 2 each side (long, compact) | 3 each side (long with wide lumen) |
| Dorsal vessel | XIII–XIV | XII–XIII | XII–XIII |
| Secondary pharyngeal glands | 3 pairs in V well developed in VI, VII rudimentary | 2 pairs in V, VI | 2 pairs in V, VI |
| Preclitellar nephridia | 5 pairs | 3 pairs | 2–3 pairs |
| Clitellum mid-ventrally | only granulocytes | only granulocytes | characteristic square devoid of any glands |
| Seminal vesicle | large | absent | absent |
| Sperm funnel length | about equal body diameter | 1/4 as long as body diameter | ½ as long as body diameter |
| length: width collar | 5–6: 1 wider than funnel body | 2–3: 1 slightly wider than the funnel body | 3–4: 1 as wide as the funnel body |
| Spermathecae extending | into VIII–X | into VI–VII | into VI–VII |
| Acknowledgement |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hemienchytraeus quadratus
| Dózsa-Farkas, Klára & Hong, Yong 2010 |
H. brachythecus (
| Xie et al. 1999 |