Episoriculus soluensis (Gruber, 1969)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6870843 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6869924 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3D474A54-A010-877C-FAF5-AD3D184DF494 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Episoriculus soluensis |
| status |
|
Nepalese Brown-toothed Shrew
French: Musaraigne du Solu / German: Nepal-Braunzahnspitzmaus / Spanish: Musarana de dientes marrones de Nepal
Other common names: Solu Long-tailed Shrew
Taxonomy. Soriculus caudatus soluensis Gruber, 1969 ,
Ringmo , Solukhumbu District, Nepal, 2700 m.
Episoriculus soluensis used to be included in E. caudatus View in CoL as a synonym. It was recognized as a full species based on its distinct karyotype. Monotypic.
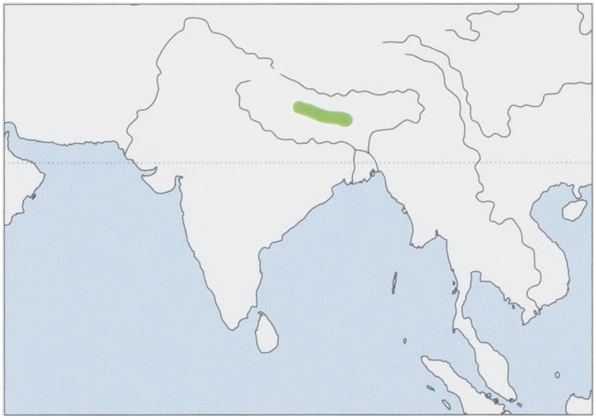
Distribution. Known from Nepal and NE India (Sikkim). Distributional limits remain unclarified because it recently has been elevated to full species. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 62-66 mm, tail 49-56 mm, hindfoot 11-8-12-7 mm. No specific data are available for body weight. Condylo-incisive lengths are 18-4 mm, and mandible length is 11-11-6 mm. Dorsum of the Nepalese Brown-toothed Shrew is dark brown, and venter is yellowish brown. Tail length is shorter than head-body length. Braincase is very dome-shaped and high. Coronoid process of ascending ramus is moderately developed. Talon (posterior cusp) of upper incisor and first upper unicuspid are low and similar in height. Tips of teeth are pigmented light brown or red. It has four upper unicuspids. Chromosomal complement has 2n = 74 and FN = 126.
Habitat. Mountain habitats.
Food and Feeding. The Nepalese Brown-toothed Shrew is insectivorous.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. No information.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The IUCN Red List. Population trend and distributional boundary of the Nepalese Brown-toothed Shrew are unclear and require additional research.
Bibliography. Hoffmann (1985), Jenkins (2013), Motokawa & Lin Liangkong (2005), Motokawa et al. (2008).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Episoriculus soluensis
| Russell A. Mittermeier & Don E. Wilson 2018 |
Soriculus caudatus soluensis
| Gruber 1969 |