Roussoella japanensis Kaz. Tanaka, J.K. Liu & K.D. Hyde, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.181.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5150552 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/223F0302-FF90-9933-DAE3-32BBFDFFFD00 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Roussoella japanensis Kaz. Tanaka, J.K. Liu & K.D. Hyde |
| status |
sp. nov. |
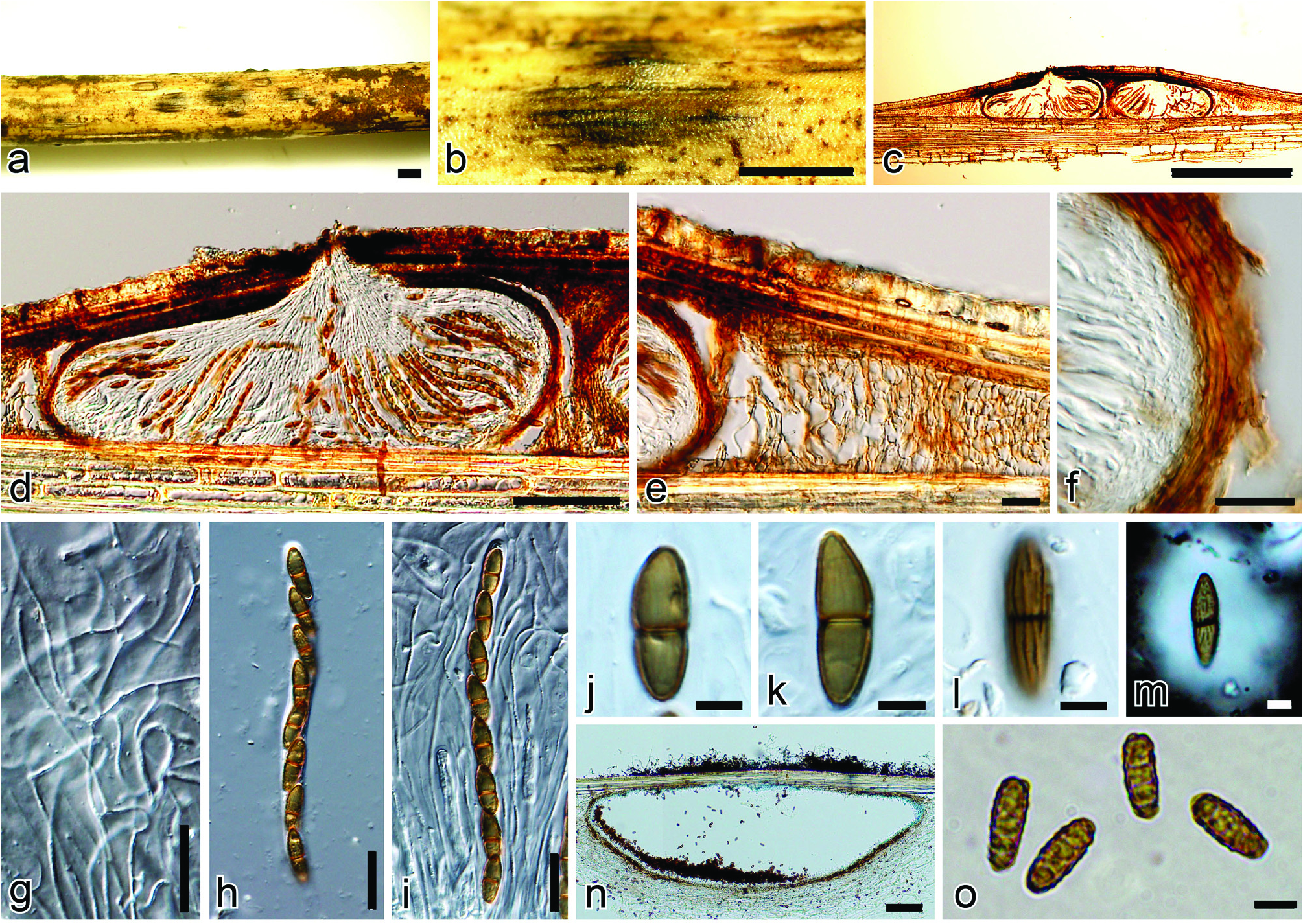
Roussoella japanensis Kaz. Tanaka, J.K. Liu & K.D. Hyde View in CoL , sp. nov. FIG. 7 View FIGURE
Index Fungorum : IF550663
Etymology. Named after the country from where this fungus was collected, Japan.
Saprobic on decaying bamboo culms. Ascostromata 0.5–2 mm diam., immersed under a clypeus, raised, visible, black, dome-shape areas on host surface, uni-biloculate. Locules 190–210 µm high, 500–560 µm diam, depressed globose with a flattened base, single or 2–3 grouped, ostiolate. Beak short papillate, 38–50 µm high, 50–85 µm wide. Peridium 10–15 µm thick at sides, composed of 3–5 layers of polygonal flattened cells (3.5–12.5 × 1.5–2.5 µm), surrounded by wedge-shaped stromatic region (450–800 µm wide at sides) composed of rectangular to polygonal cells (3.5–15 × 4–10 µm). Hamathecium comprising 1–1.5 µm wide, numerous, anastomosing, cellular pseudoparaphyses, branching, rough-walled, and embedded in a gelatinous matrix. Asci 107–132 × 8–9.5 µm, 8-spored, bitunicate, cylindrical, short pedicellate (10–13 µm). Ascospores 16–22 × 5.5–7 µm (x = 19 × 6.5 µm, n = 50), uniseriate, fusiform to ellipsoidal, with a median septum, 2-celled, brown, covered with longitudinal striations and surrounded by an entire sheath of 0.5–4 µm wide. Conidiomata in culture, 300–550 µm high, 900–2000 µm diam, depressed globose, single to grouped, immersed. Peridium 7–12.5 µm wide. Conidiophores absent. Conidiogenous cells phialidic, ampulliform. Conidia 9.5–13 × 4–5 µm, oblong-ellipsoidal, yellowish brown, warty.
Specimen examined. JAPAN, Kanagawa, Yokohama, Nakaku, Sankei-garden , on twigs of Sasa veitchii var. veitchii ; 9 Mar 2004; K . Tanaka & Y . Harada, KT 1651 (holotype HHUF 29217 About HHUF , ex-type living culture JCM 13126 = MAFF 239636 View Materials ) .
Notes: Although Roussoella japanensis produced an asexual morph similar to that of R. hysterioides , the asci and ascospores are considerably smaller than those of R. hysterioides (asci 107–132 × 8–9.5 µm vs. 140–210 × 8–11 µm; ascospores 16–22 × 5.5–7 µm vs. 18–34 × 6–8 µm). Tanaka et al. (2009) identified two Roussoella specimens ( HHUF 26988 and KT 1651) as R. hysterioides , but sequence similarity between these fungi is very low (ca. 90.6%) in their ITS regions (Tanaka, unpublished data).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.