Malacomys edwardsi, Rochebrune, 1885
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6887260 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6816062 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1E30E275-3497-FF26-E19E-25B97F8F800B |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Malacomys edwardsi |
| status |
|
Edwards’s Swamp Rat
French: Malacomys d'Edwards / German: Edwards-Grofsohr-Sumpfratte / Spanish: Rata de ciénaga de Edwards
Other common names: Edwards's Malacomys
Taxonomy. Malacomys edwards i Rochebrune, 1885 , “Mellacorée.” Clarified by I. L. Rautenbach and D. A. Schlitter in 1978 as “Melikhoure River, Guinea.”
Previously listed as a subspecies of M. longipes . A recent molecular work confirmed the validity of this species and its geographical distribution. Monotypic.
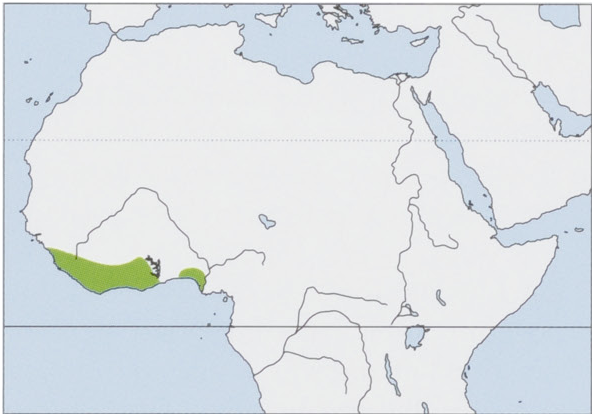
Distribution. Upper Guinea Forest of W Africa, from Guinea E to SW Nigeria, W of the Niger River. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 126-160 mm, tail 155-180 mm, ear 24-28 mm, hindfoot 31-37 mm; weight 46-80 g. Edwards’s Swamp Rat is a medium-sized, slenderbuilt rodent with long hindfeet, large ears, a very long tail and soft, dense, velvety fur. Fur of adults is rusty brown to warm brown above and whitish gray below, notably on the throat, chest and chin. In juveniles and subadults the fur is smoky gray. Tail is very long (c.130% of head-body length), thin, naked, dark above and pale below. Muzzle is elongated with long vibrissae; eyes are large; ears are elongated, naked and darkly pigmented, as well as mobile. Forefeet and hindfeet whitish and very long, with three central toes. Females have two pairs of nipples. Chromosomal complement is 2n = 48, FN = 52.
Habitat. Primary and secondary rainforests, and cacao plantations and farms on the edge of rainforests, especially on damp soils.
Food and Feeding. Edwards’s Swamp Rat is omnivorous. In Ghana and Nigeria, diet comprises vegetable matter and invertebrates, including earthworms, slugs, grasshoppers, butterfly caterpillars, and adult beetles.
Breeding. In Nigeria, breeding occurs in the dry season and early wet season (November to July). Females have 2-3 embryos.
Activity patterns. Edwards’s Swamp Rats are nocturnal and terrestrial, and can swim.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Edwards’s Swamp Rat constructs saucer-shaped nests from forest leaves,situated under logs or buttress roots oftrees.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red Last.
Bibliography. Bohoussou et al. (2015), Cole (1975), Happold (1977 2013a), Monadjem et al. (2015), Rautenbach & Schlitter (1978), Rosevear (1969), Van der Straeten & Verheyen (1979b).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.