Platypygus Loew
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.204417 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6185223 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1D3287FB-FFF8-3926-FF3C-ACE2999F166B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Platypygus Loew |
| status |
|
Genus Platypygus Loew
Platypygus Loew, 1844: 127 . Type species: Platypygus chrysanthemi Loew, 1844 , by monotypy.
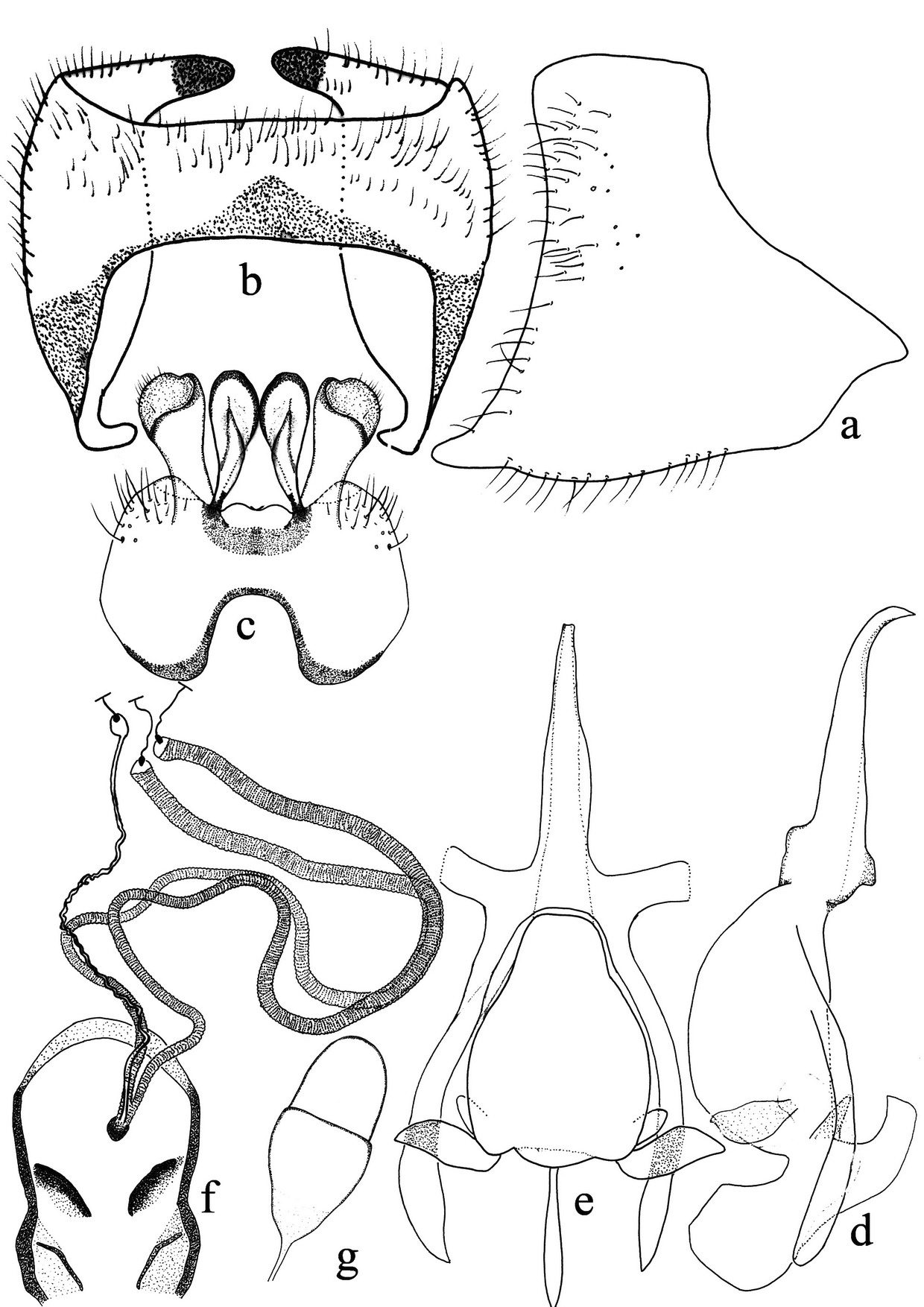
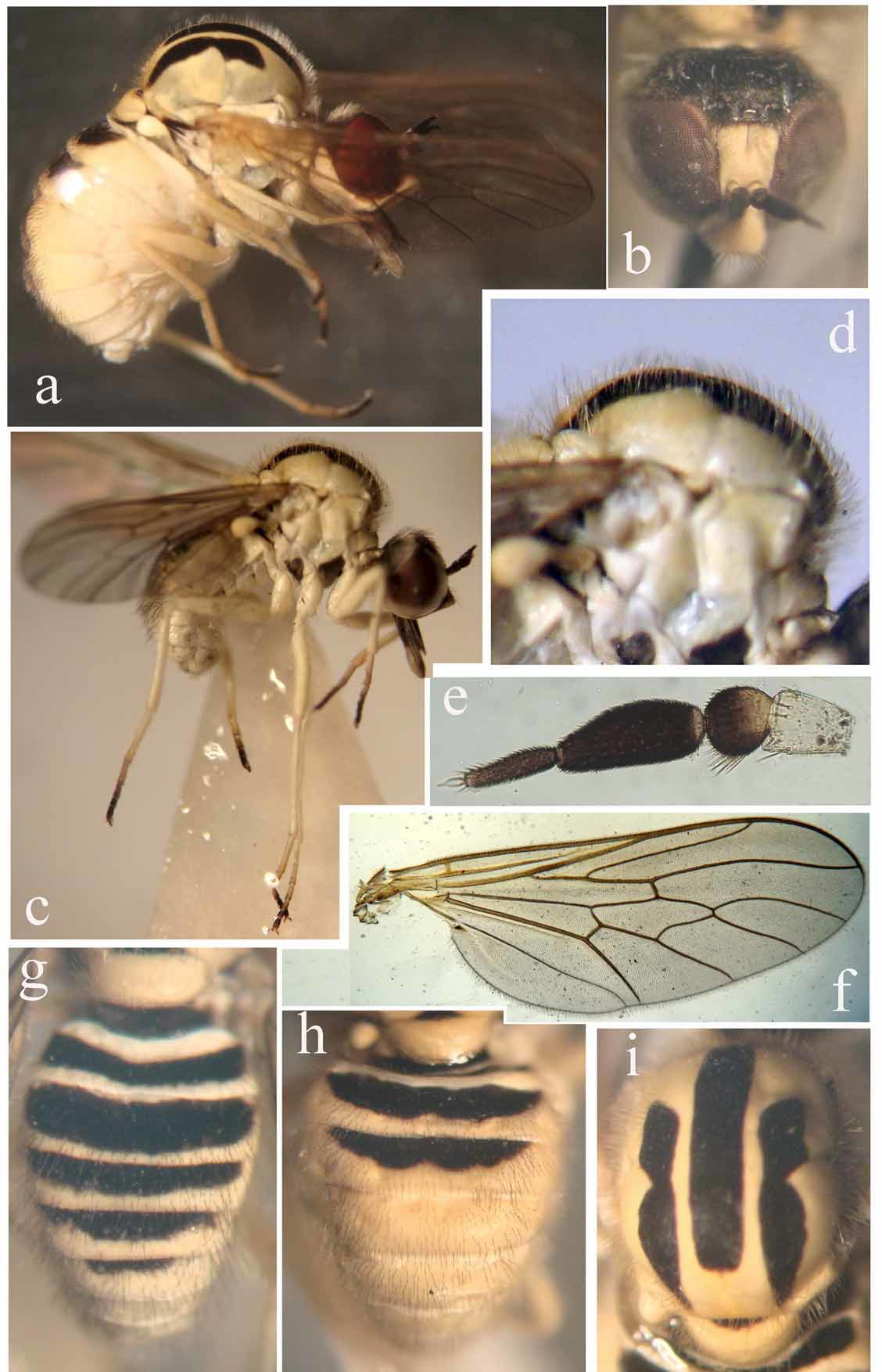
Platypygus is distinguished from other genera of Platypyginae by the combination of following characters: postgena not developed as an acute process; mesonotum highly arched; discal cell closed and presence of vein R2+3 at the middle of veins R4+5 and R1 (i.e., its apex is equidistant between the end of both veins).
Key 1 to species of the genera Platypygus and Cyrtisiopsis known from Iran
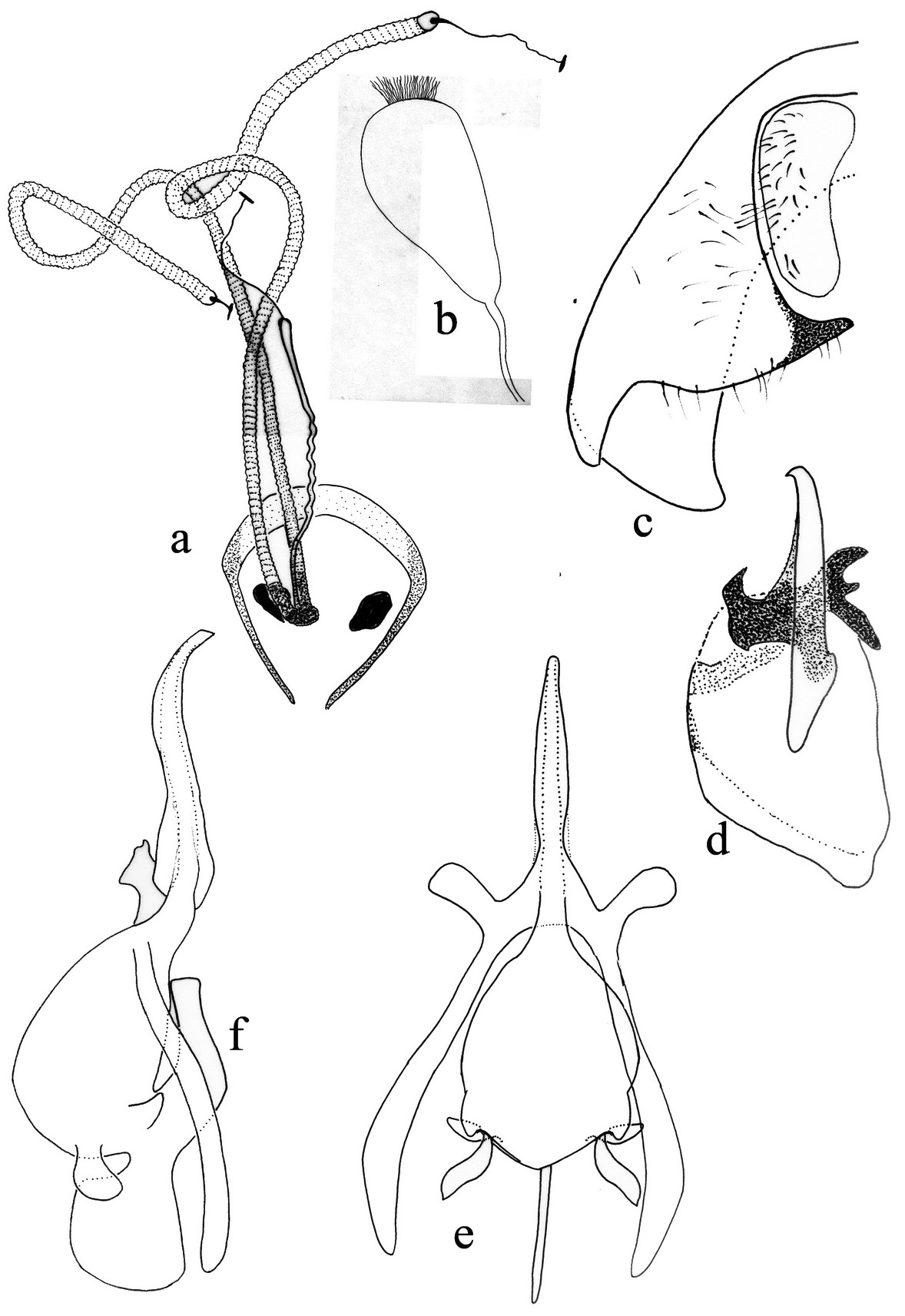
1. Postgena extending posterior as an acute process ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 a), br cell equal to bm cell ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 d)..................................................................................... Cyrtisiopsis maculiventris ( Loew, 1874) , comb. nov. - Postgena normal, at most with minute blunt process (e.g. Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1. P a, b); br cell longer than bm cell ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1. P j, 3d, 6f)..........
1. Although the species P. lativentris and P. chrysanthemi do not occur in Iran, to show differences between them and the new Iranian species, we included both in the key.
........................................................................................( Platypygus )...2
2. Halteres with a black spot on dorsal surface.............................................. P. lativentris Loew, 1873
- Halteres completely yellow, without any black mark.......................................................... 3
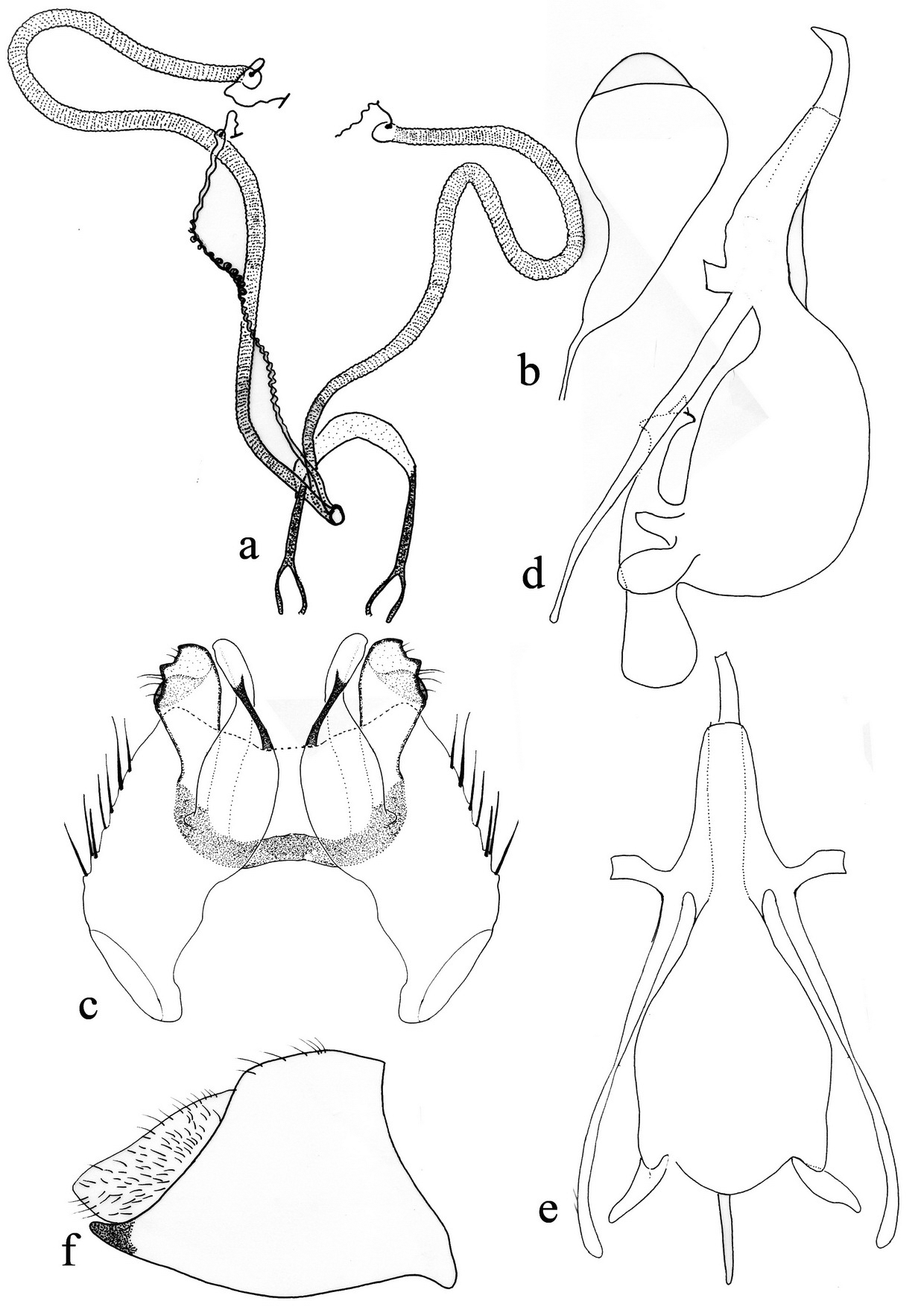
3. Mesonotum completely bare ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3. P. k u f); antennae completely black; female genitalia with furca without sclerotized plates next to genital orifice ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 a)....................................................... P. kurdorum Paramonov, 1929 2
- Mesonotum hairy; antennal scape yellow or black; female genitalia with furca with two sclerotized plates next to genital orifice................................................................................................. 4
4. Hairs on mesonotum completely black, frons yellow with a black, Y-shaped mark medially.... P. chrysanthemi Loew, 1844
- Hairs on mesonotum completely yellow, frons yellow, at most with a narrow black line medially...................... 5
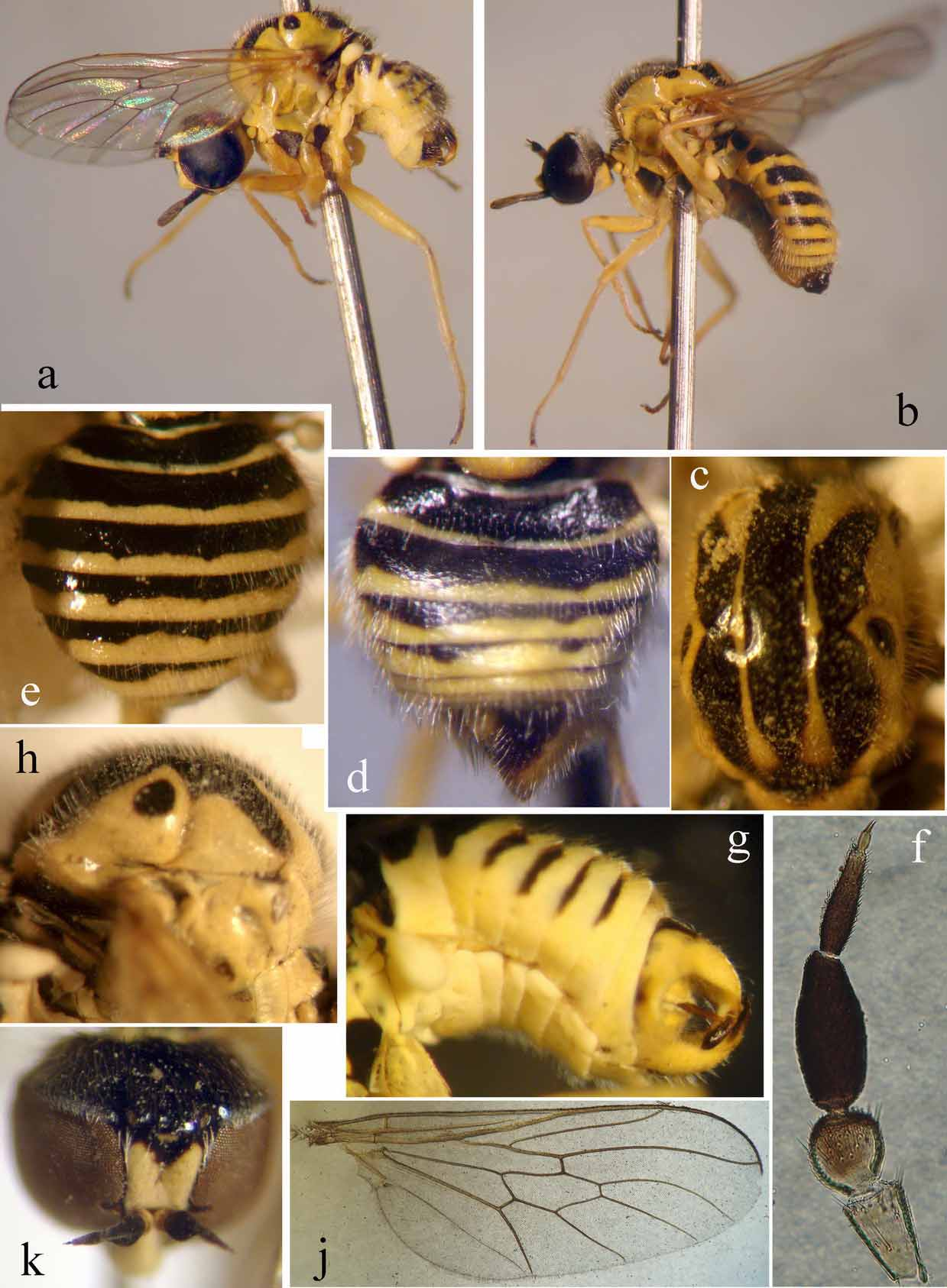
5. Mesonotum with two black spots next to transverse suture; black median stripe on mesonotum mostly reaching to scutellum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1. P c); abdominal tergites with fine and long pale hairs; male genitalia huge and well exposed ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1. P g); spermathecal reservoirs acorn-shaped, with an obvious cap ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 g)......................... P. titanomedea Gharali & Evenhuis , sp. nov.
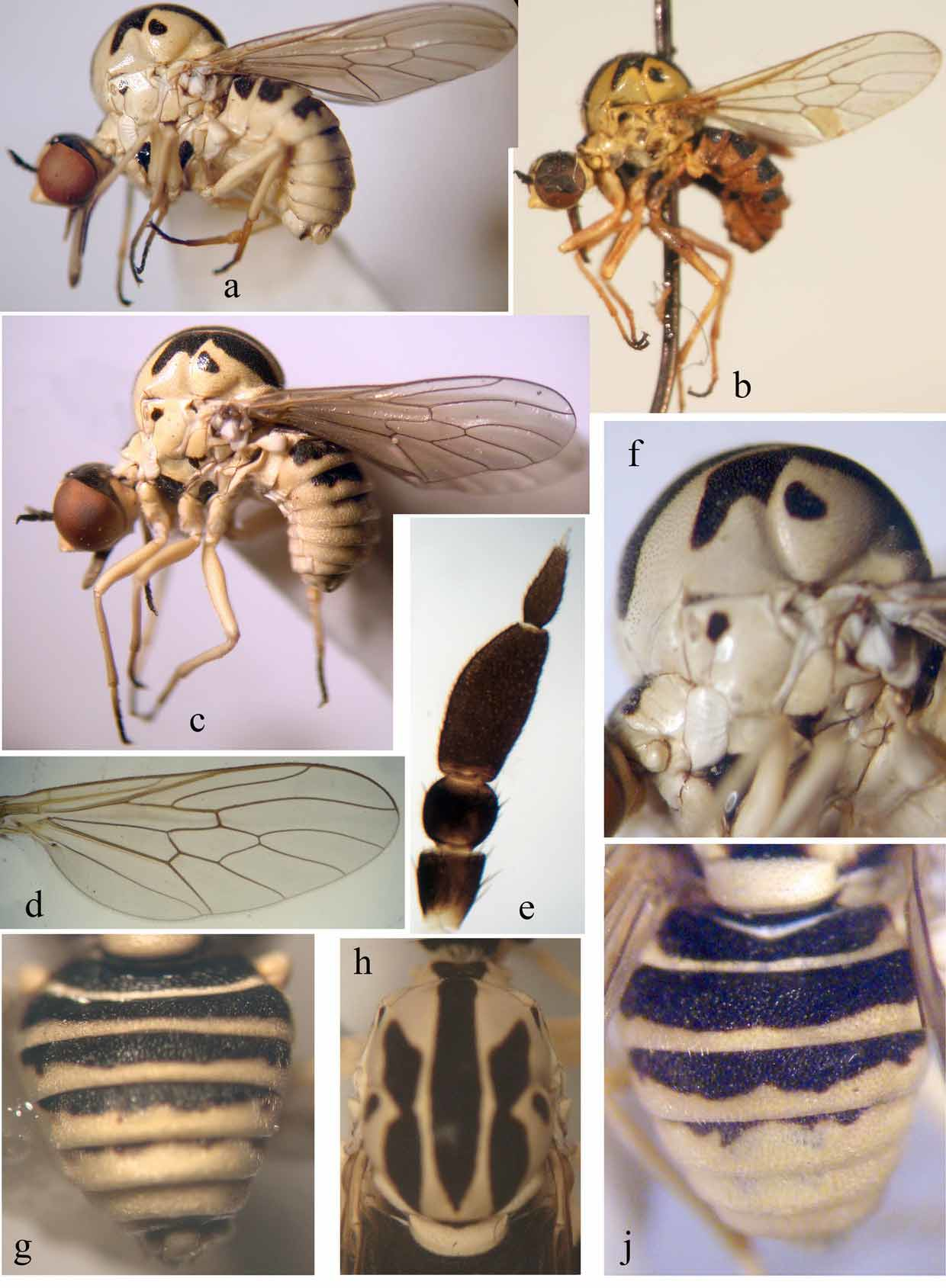
- Mesonotum without black spots ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. P d); black median stripe on mesonotum ending much before scutellum with straight posterior margin ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. P i); scape yellow; abdominal tergites with short, dense and black bristly hairs on disc ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6. P g, h); male genitalia very small ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. P c); spermathecal reservoirs oboval, without cap ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 b)........... P. melinoproctus Loew, 1873
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Platypyginae |
Platypygus Loew
| Gharali, Babak, Evenhuis, Neal, Kamali, Karim & Talebi, Ali Asghar 2011 |
Platypygus
| Loew 1844: 127 |