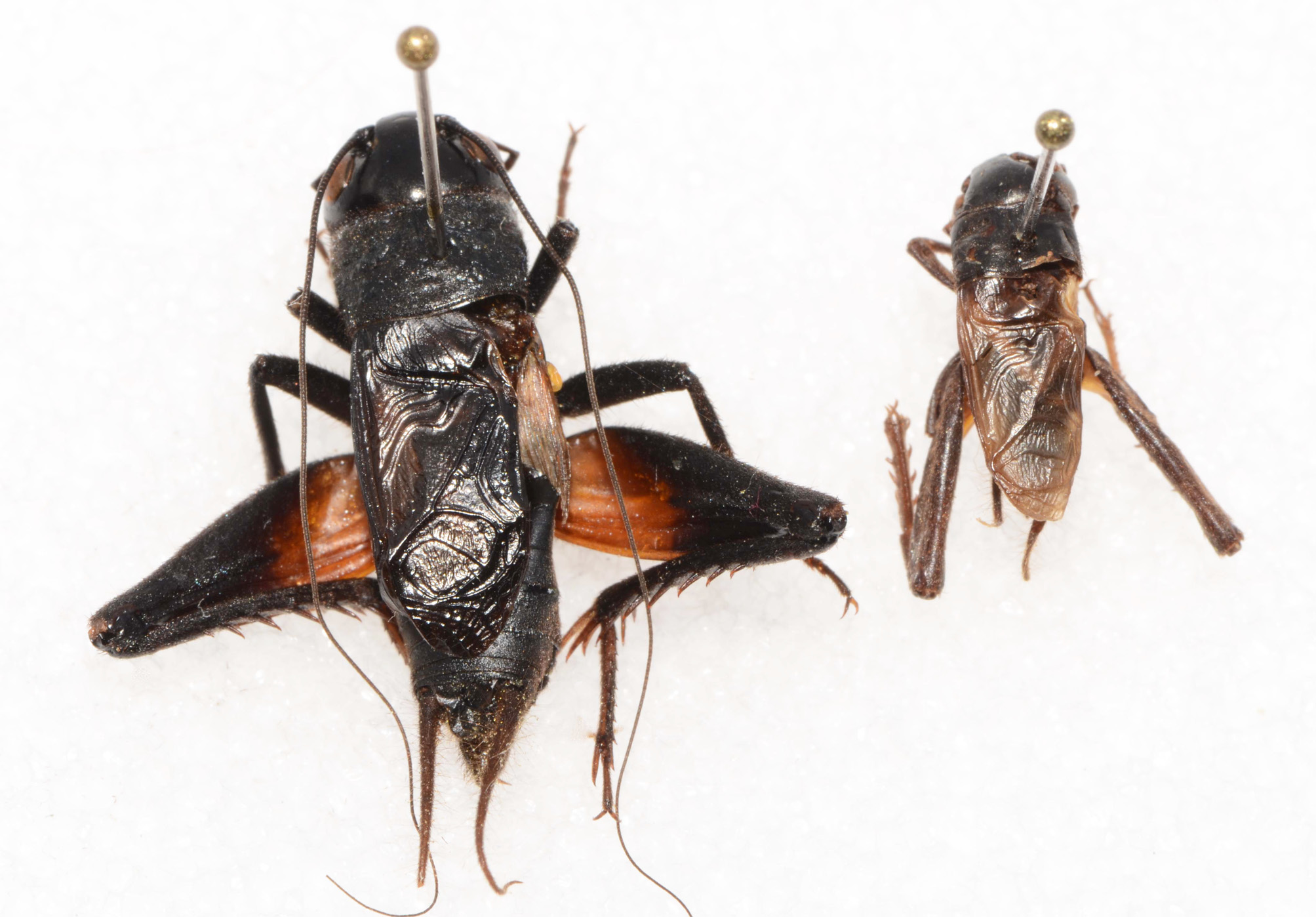
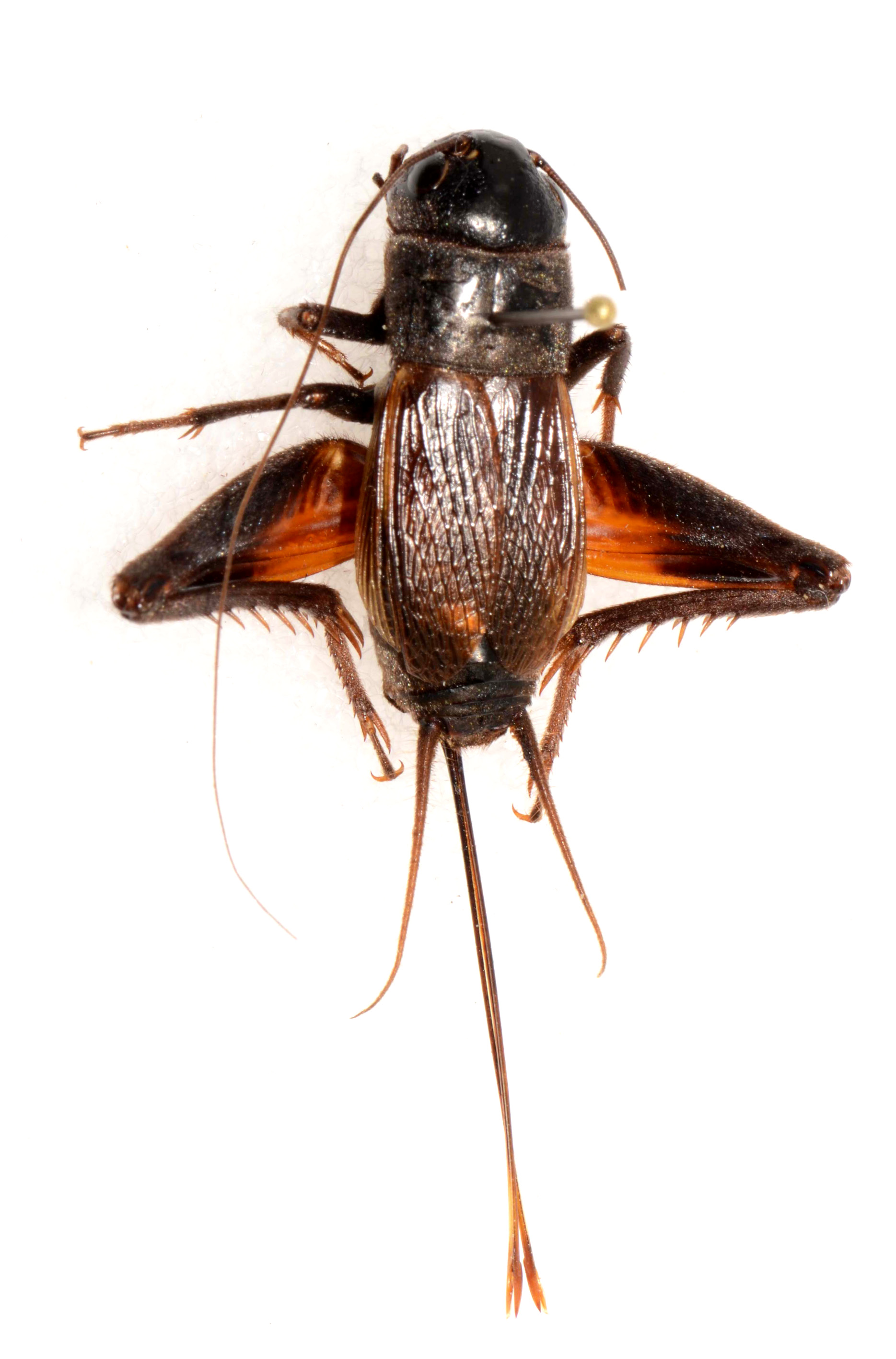
Gryllus pennsylvanicus Burmeister
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4705.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F534C43A-AB09-4CB3-9B08-FD5BDFD90298 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/182387A8-094E-FFA7-51F6-FF4B05CBFDA5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Gryllus pennsylvanicus Burmeister |
| status |
|
Gryllus pennsylvanicus Burmeister
Fall Field Cricket
Figs 28–37 View FIGURE 28 View FIGURE 29 View FIGURE 30 View FIGURE 31 View FIGURE 32 View FIGURE 33 View FIGURE 34 View FIGURE 35 View FIGURE 36 View FIGURE 37 , 45–50 View FIGURE 45 View FIGURE 46 View FIGURE 47 View FIGURE 48 View FIGURE 49 View FIGURE 50 , 52 View FIGURE , 53, 139, Table 1 View TABLE 1 , 2 View TABLE 2
1838 Gryllus pennsylvanicus Burmeister. Handb. Ent. , II, p,734. Lectotype male designated by Alexander, 1957, p. 586. “North America.” Burmeister’s original description (last paragraph under 13. Gr. Campestris) reads: “A similar species ( Gr. pennsylvanicus *) is found in North America; it is somewhat smaller, the tegmina shorter than the body, without yellow base, but with brown main longitudinal vein.” According to Michael Ohl (pers. comm. to DBW May, 2003) of the Museum of Natural History of Humboldt-University in Berlin (ZMB), entry #983 of the historic catalogue of the ZMB says (catalogue columns separated by slashes): “ Gryllus abbreviatus Serv. / 4 [specimens; subsequently corrected to 3]/ Pennsylvan. Zimmerm./ Types of Gryllus pennsylvanicus Burm. *” These 3 specimens are still in the collection and include the male lectotype labeled by R.D. Alexander and 2 females. Sigfrid Ingrisch (pers. comm. to DBW May, 2003) believes that although the “…original description reads only North America, …one might guess from the name [and the catalogue entry] that it was from Pennsylvania.” Lectotype male and labels illustrated on OSF website ( Cigliano et al. 2019).
1957 Acheta pennsylvanica . Alexander. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer. 50: 586.
1964 Gryllus pennsylvanicus . Randell. Can. Entomol. 96: 1592.
‘ G. eastern and western pennsylvanicus’, ‘G. hanksville’ and ‘G. near hanksville’ of DBW notebooks.
Distribution. Widespread across the US although absent from the Southwest and Southeast.
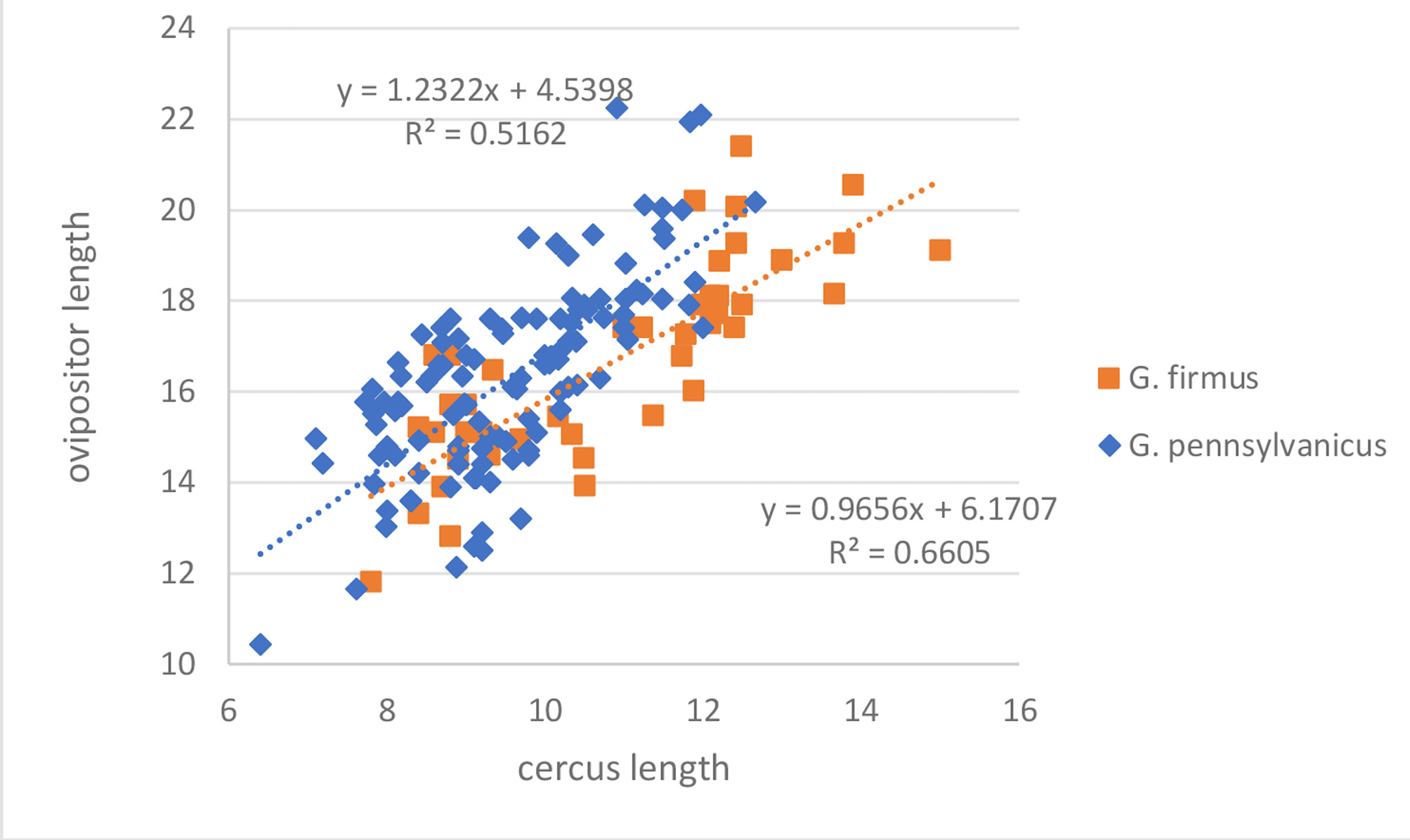
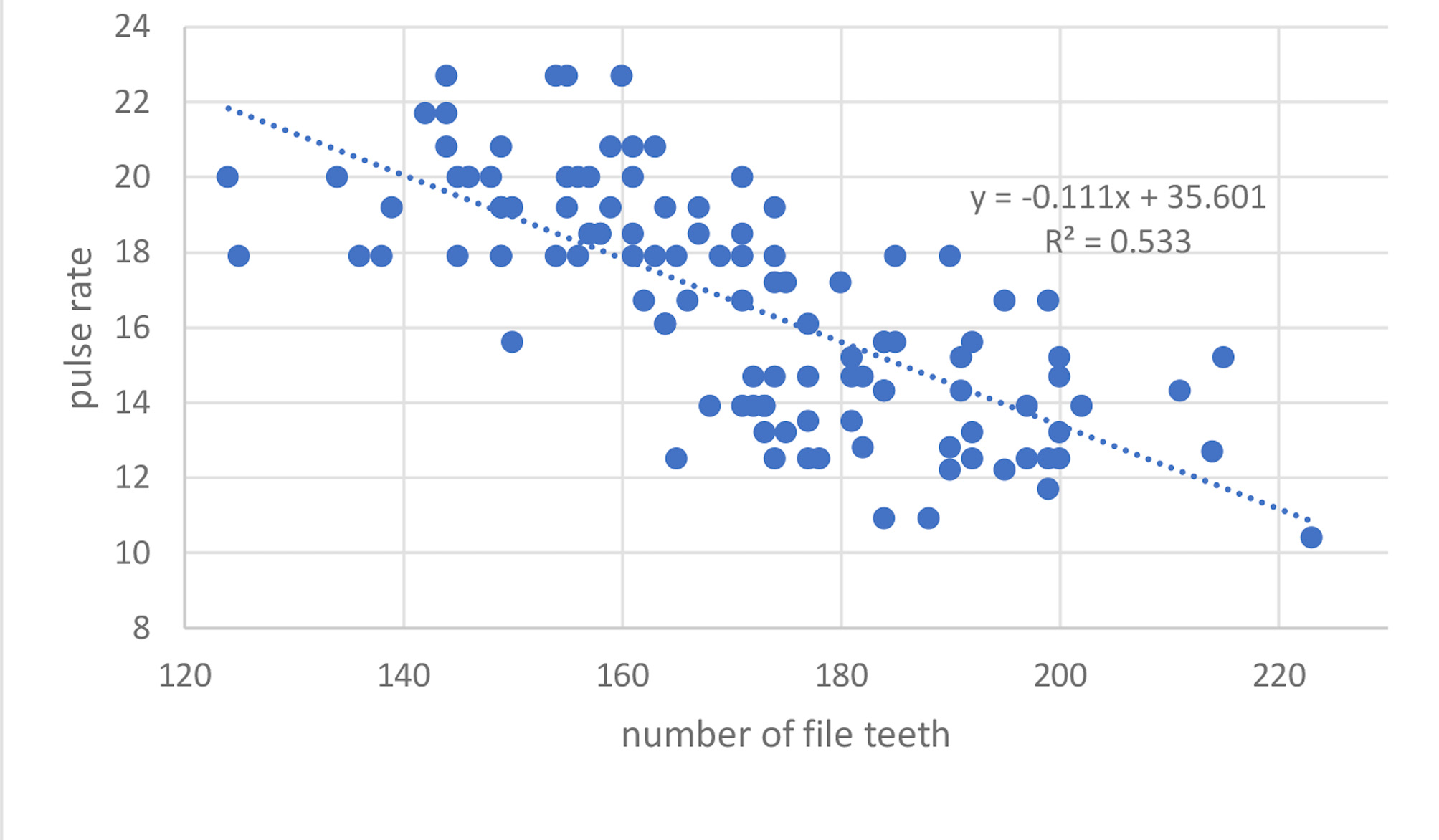
Recognition characters and song. We apply this name to any US Gryllus with the following constellation of characters: obligate (winter) egg diapause, one generation/year, adults first appearing mid to late summer (usually after August 1 st), slow chirping (2–3 c/s; Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 ; R04-110), 3–5 p/c, black crickets with short cerci, a relatively long ovipositor and generally not living on sandy substrates. Morphologically most similar to G. firmus and we discuss elsewhere (see Hybrid Zones, p. 61) the problems associated with separating the two species. Must also be separated from G. veletis which occasionally overlaps in distribution and time of occurrence. Where G. pennsylvanicus and G. veletis are synchronic in Nebraska, South Dakota, Oklahoma, Missouri, and Kansas, clear field differences (see Table 2 View TABLE 2 , p. 144) in pulse rate and tooth count, with G. pennsylvanicus having a lower pulse rate and higher tooth count, are apparent, although such song differences appear absent in Michigan ( Alexander & Meral 1967). Also, G. pennsylvanicus overwinters in an egg diapause while G. veletis overwinters as a late instar since the eggs have no diapause. In northwestern Oregon, G. pennsylvanicus can be distinguished from morphologically similar looking, black, short cerci, non-egg diapausing spring and early summer adult G. veletisoides compared to the late summer adults of G. pennsylvanicus with different DNA. We suspect that the 2 taxa may be synchronic in northwestern Oregon in late July–early August but have no collections to document.
Derivation of name. Apparently in reference to the type series being collected in Pennsylvania (see discussion above).
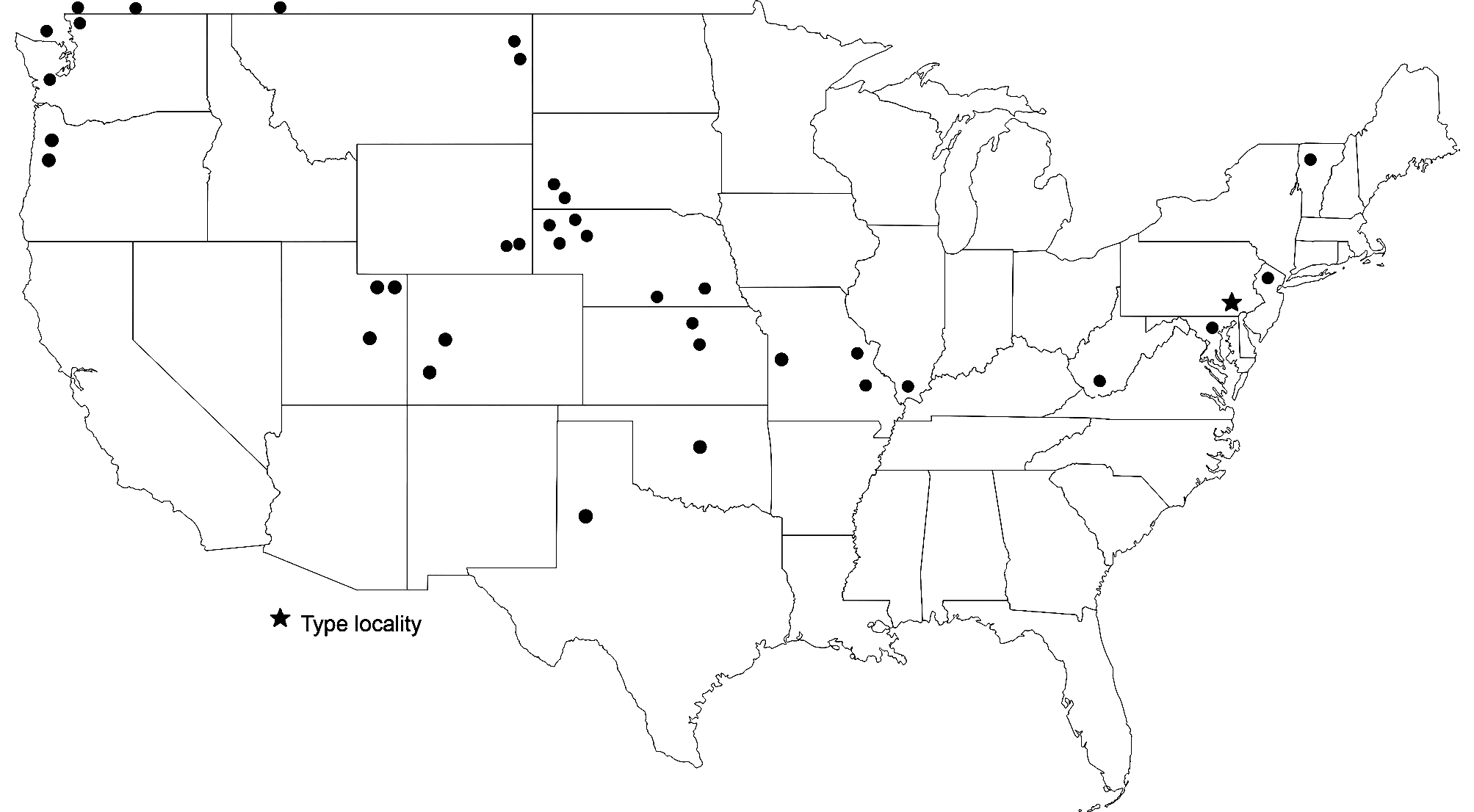
Geographic range. Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 . More eastern localities are presented in Walker (2019) and Capinera et al. (2004). An egg-diapausing cricket in Cuatrocienegas, Mexico may also be G. pennsylvanicus , and will be addressed in our Mexico Gryllus paper. California localities listed in Weissman et al. (1980) are actually G. saxatilis . We believe that a fall ( 18-ix-2013), long ovipositor ( 18.42 mm) adult female collected in the Texas Panhandle, in Lubbock (S13-80), is G. pennsylvanicus , despite no associated song, tooth count or egg diapause data, given the elevation of 990 m and 33° N latitude. This female (G2708) mapped in the multilocus tree (Gray et al. 2019) with other individuals of G. pennsylvanicus and G. firmus , without clearly resolving which. If indeed G. pennsylvanicus , this would represent the most southerly range limit (excepting the unconfirmed Cuatrociénegas samples).
Habitat. In towns in cracks, under objects, in grassy vegetated areas and also in clay badlands in Alberta, Canada (S05-72, 73) and Nebraska (S97-83).
Life cycle and seasonal occurrence. One generation/year. Obligate egg diapause present: Vancouver, Canada (S00-54), Scottsbluff, Nebraska (S99-144), Sidney, Montana (S97-95), Guernsey, Wyoming (S97-78, S99-138 & 99-139), Concordia, Kansas (S02-50), Corvallis, Oregon (S83-39), Hanksville, Utah (S04-128). Overwinter as eggs in diapause ( Rakshpal 1962) with first adults appearing in late July–early August. Field collections in early August typically yield a few adults with most of the population late instars. In early summer, it is not unusual to find adult G. veletis microsympatric with early-mid instar G. pennsylvanicus ; while in August, it is not unusual to find adult G. pennsylvanicus microsympatric with early to mid-instars of G. veletis .
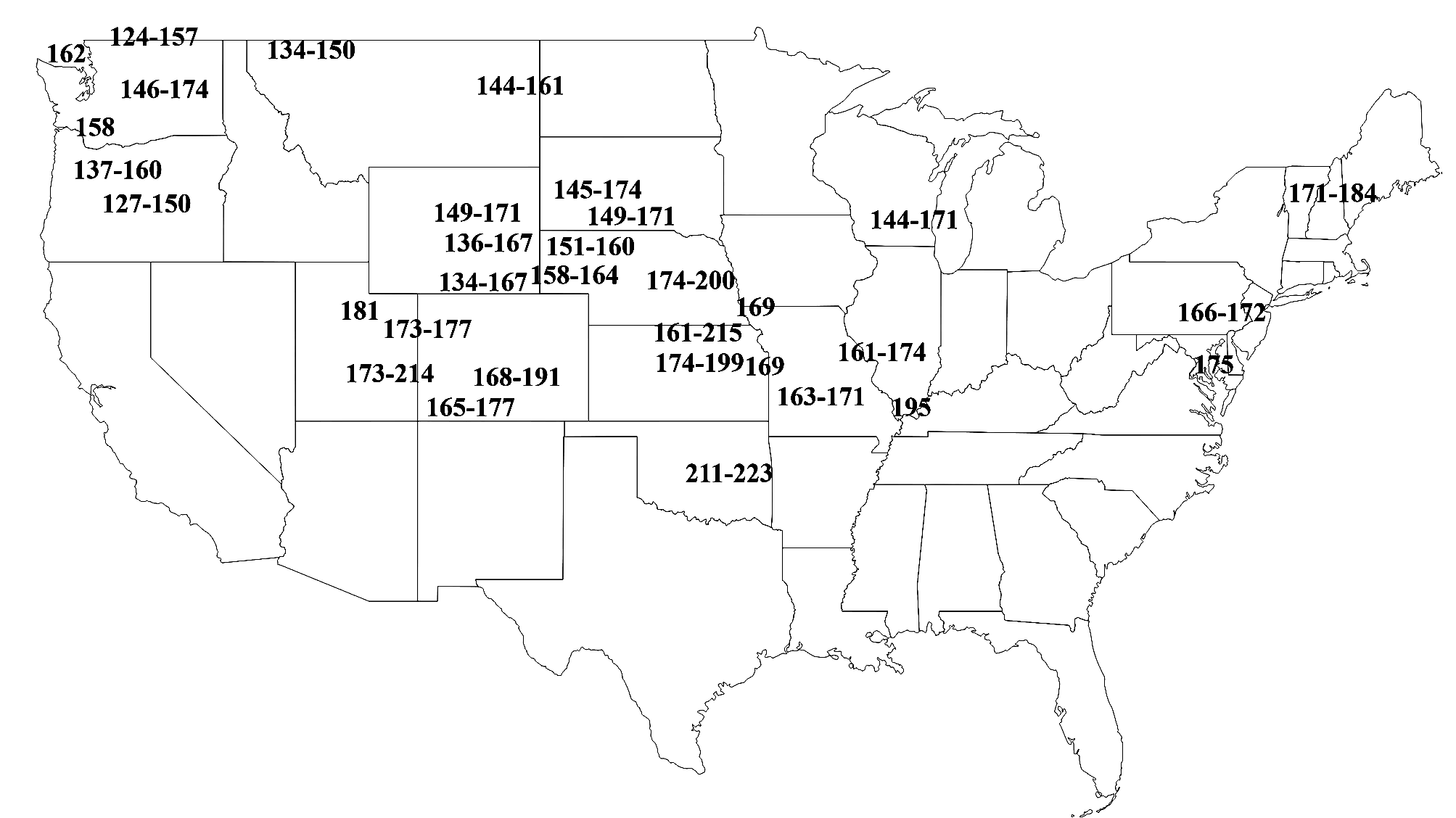
Variation. Body length: Northern specimens ( Michigan) considerably smaller than those from Kansas ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 ). Hind wing length: Rare adults of both sexes with long hind wings, including two of five females from Lincoln, NB (S02-52). Number of file teeth (see Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 ): Range from 124–223 with more northern and smaller males having shorter files and fewer total teeth. Teeth/mm also higher where tooth number highest in Nebraska, Colorado, Kansas, Missouri, and Oklahoma. In 13 males from Salina , Kansas (S02-49), teeth ranged from 161–215, or a 54-tooth range. This parameter usually varies by <30 teeth over an entire species’ range (Weissman, unpublished). Ovipositor length: Range from 10.43 to 22.29 mm (Lincoln, Nebraska, S02-52) with larger females having longer ovipositors (for example, Fig. 35 View FIGURE 35 , S02-49). Pulse rate: Varies from 10.4–25.0, with males with higher number of teeth having lower pulse rates (see Fig. 52 View FIGURE in Hybrid Zones, p. 68).
Specimens examined. CANADA. Alberta: Drumheller Municipal Airport , 2470’, 15-viii-2005 , 51° 29.028’ -112° 43.235’ (S05-73). Horseshoe Canyon 14km W Drumheller, 15-viii-2005 , 51° 25.128’ -112° 52 (S05-72). British Columbia: 3 m N Osoyoos, Haynes Ecological Reserve , 1200’, 26-viii-2000 (S00-27) . Vancouver , 15- viii-1983 (S83-125) S. Tanaka ; 22-ix-2000 (S00-54) . Vancouver Island, near Butterfly Zoo in Saanich , 16-ix-2007 (S07-90) . USA. Colorado: Garfield Co., Rifle, 5140’, 15-viii-2009 (S09-109) . Mesa Co., Fruita, 4420”, 16-viii- 2009 (S09-114) . Illinois: Madison Co., 10-viii-2002 (S02-60) . Kansas: Cloud Co., Concordia, 1100’, 7-viii-2002 (S02-50) . Saline Co., Salina, 1100 ’, 7-viii-2002 (S02-49) . Maryland: Prince George Co., College Park, 500’ 30-v- 2004 (adult molt 6-viii-2004) S04-35. Missouri: Cape Girardeau Co., Millersville, 9-viii-2002 (S02-58) . Jackson Co., Kansas City, 8-viii-2002 (S02-54) . St. Louis Co., St. Louis , 10-viii-2002 (S02-61) . Montana: Richland Co., Sidney , 1840’, 31-vii-1997 (adults and late instars) (S97-95) . Hwy 23 5 m SE Sidney , 1920’, 31-vii-1997 (adults and late instars) (S97-94) . Nebraska: Dawes Co., Hwy 385 ~ 4 m S Hwy 20. 3680’ 13-ix-1999 (S99-143) . 3 m W and 13 m S Chadron near Coffee Grinder Butte , 3680’, 28-vii-1997 (S97-84) . 4 m W and 4 m S Chadron , 3100”, 28-vii-1997 (S97-83). Fillmore Co., Geneva, 1420”, 7-viii-2002 (S02-51) . Lancaster Co., Lincoln, 940” 7-viii-2002 (S02-52) . Scotts Bluff Co., Scottsbluff, 3960’, 13-ix-1999 (S99-144) . Sioux Co., Agate Beds National Monument, 4500’, 13-ix-1999 (S99-141) . New Jersey: Morris Co., Pequannock, 13-ix-1987 (S87-100) . Oklahoma: Oklahoma Co., Oklahoma City, 1000’, 6-viii-2002 (S02-48) . Oregon: Benton Co., Corvallis, 15-viii-1983 (S83-122) , S. Tanaka. Lane Co., Eugene , 14-x-2006 (S06-128) . Pennsylvania: Chester Co., New London, 406’, August, 2011, 39.767099° -75.897706° (S11-107), D.H. Funk . South Dakota: Jackson Co., Badlands National Park , 2200-2400’, 30-vii-1997 (S97-90) . Kadoka , 2200’ 30-vii-1997 (S97-87) . Texas: Lubbock Co., Lubbock, 18-ix-2013 (S13-80) . Utah: Uintah Co., Jensen, 4740’, 10-ix-1999 (S99-127) . Naples , 5200’, 10-ix-1999 (S99-126) . Wayne Co., Hanksville, 4500’, 1-viii-1992 (S92-109) ; 11-ix-1998 (S98-88) ; 9-ix-1999 (S99-119); 12-ix-2004 (S04-128). Vermont: Addison Co., Middlebury, 6-x-2006 (S06-117) ; 5-x-2008 (S08-74) . Washington: Mason Co., Shelton, 16-viii-1983 (S83-123) S. Tanaka. Skamania Co., Mt St Helens , 3800’, 16-ix-2015 , 46° 15’ 59” -122° 04’ 50”, pit fall trap, D.C. Lightfoot. Whatcom Co., Birch Bay State Park , 5’, 17-viii-2004 , 48.54407° -122.45758° (S04-91). West Virginia: Mercer Co., Camp Creek State Park , 2025’, 19-vii-2011 (adult molt 9-ix-2011) , 37.504477° -81.134305° (S11-108), D.H. Funk. Wyoming: Platte Co., Guernsey, 4300’, 12-ix-1999 (S99-138) . Road 270 3.9 m N Hwy 26, 4300’, 28- vii-1997 (mid-instars) (S97-82) ; 12-ix-1999 (S99-139).
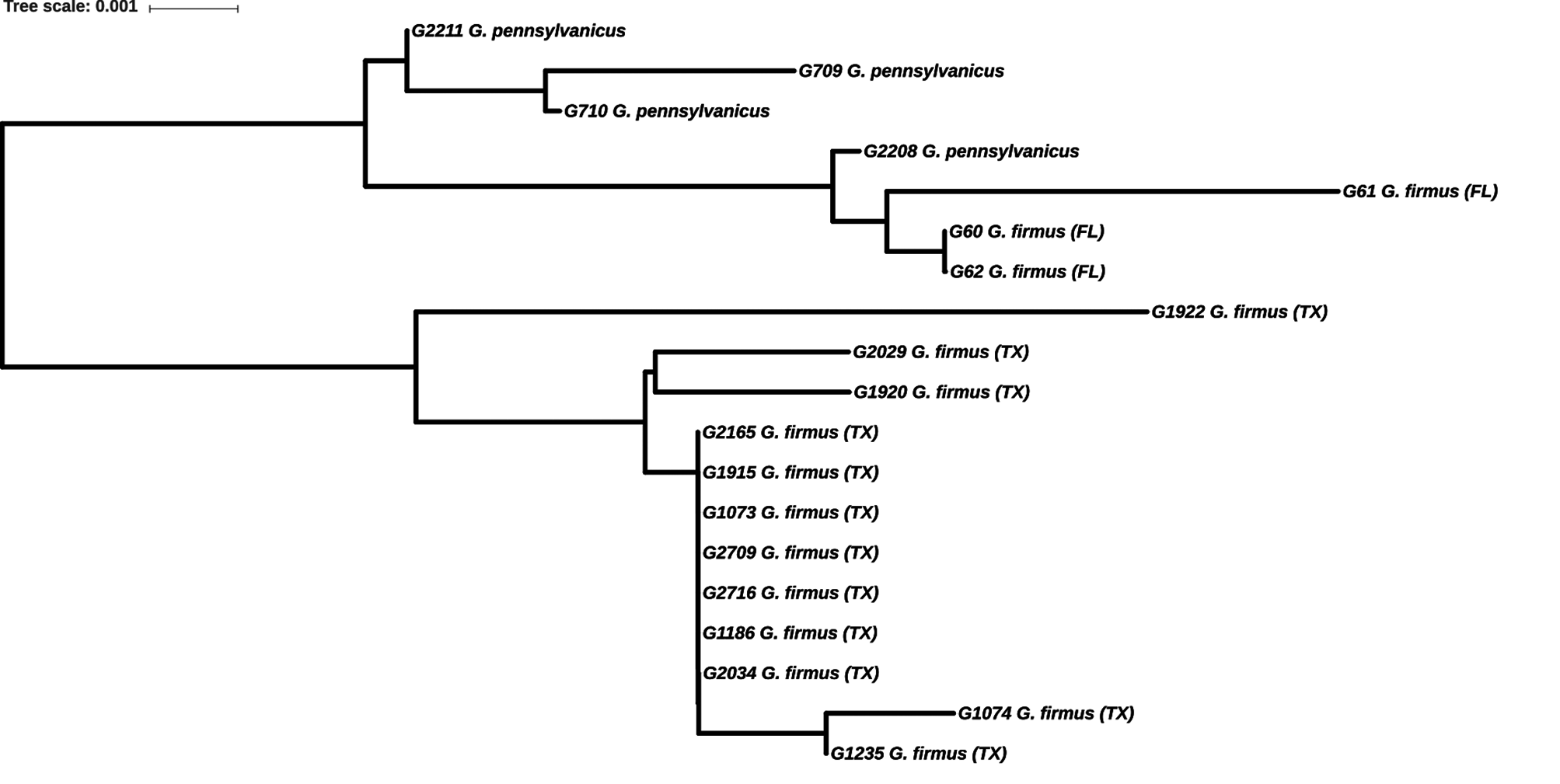
DNA. Multilocus G710 Middlebury, Vermont (S08-74); G368 Hanksville, Utah (S04-128); and G2708 Lubbock, Texas (S13-80) map (Gray et al. 2019) closest to Florida G62 Gainesville (S03-85), and Texas G1915 Bastrop State Park (S10-67); G1917 Schulenburg (S10-65); G1920 Brackettville (S10-63); G2029 Sea Rim State Park (S11- 29); and G2715 Matagorda Island (S13-59) G. firmus .
Discussion. We initially considered western US G. pennsylvanicus to be several species given the range of file tooth counts and the geographic isolation of some populations. Because further collecting has not made the situation any clearer, combined with the multilocus DNA tree indicating close relatedness between these populations, we treat them as one species, although we believe further investigation is indicated.
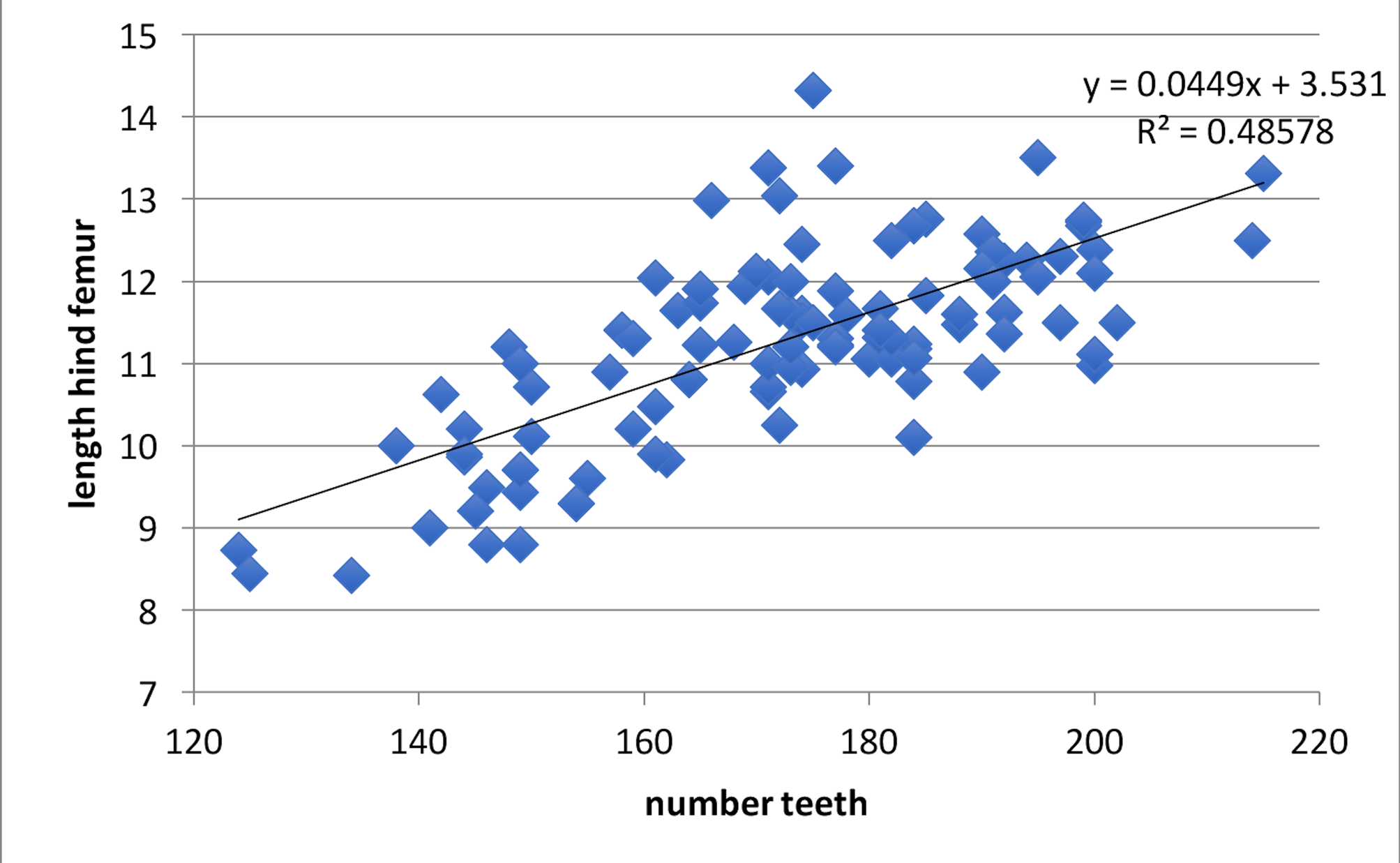
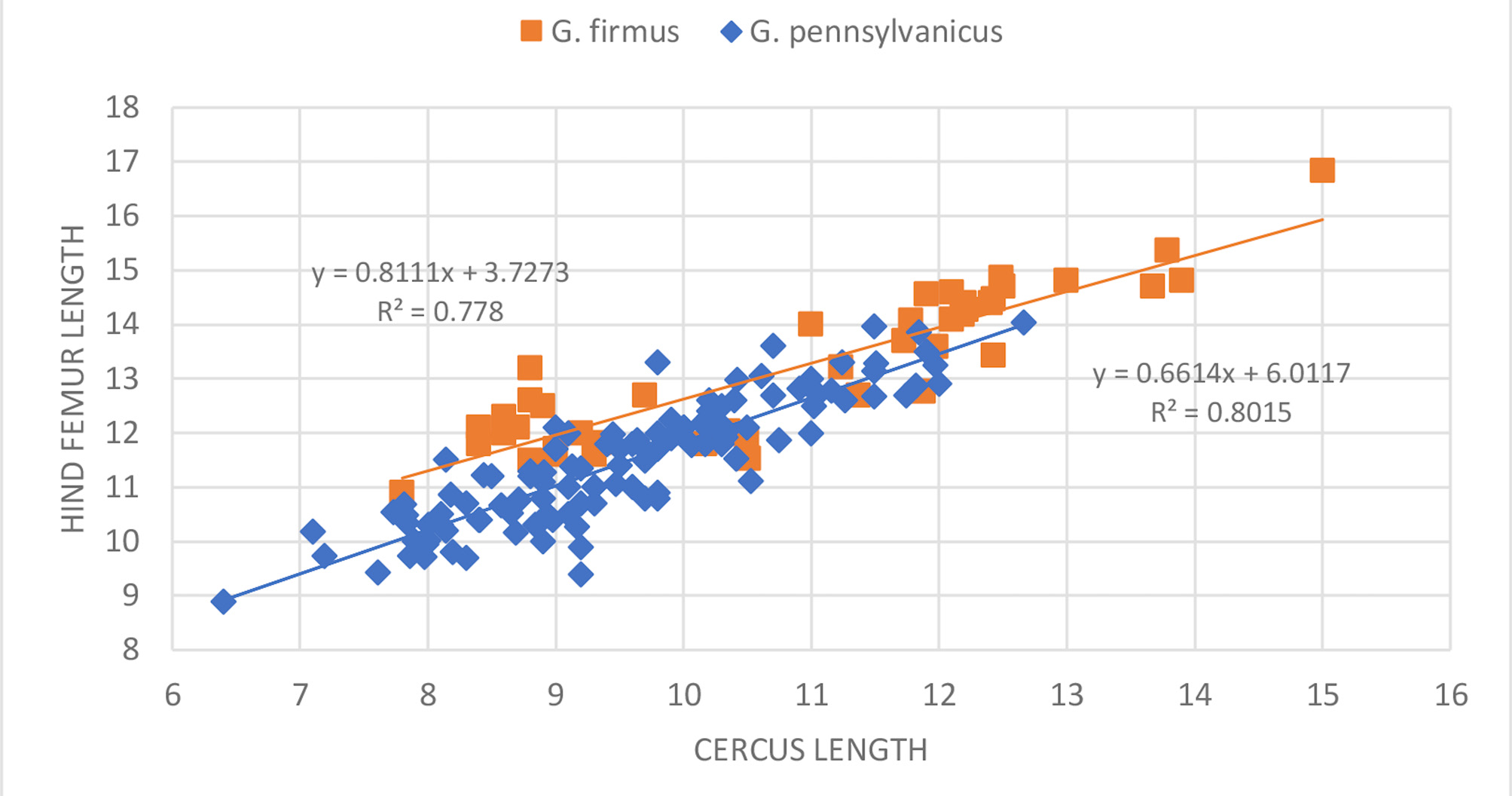
Only G. veletis has a more widespread US distribution than G. pennsylvanicus . It thus seems prudent to compare the two taxa over their ranges since both may represent groups composed of several sister species. Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 suggests a clear north to south cline in increasing tooth count in files of G. pennsylvanicus . Northern males from Vancouver may have as few as 124 teeth while a male in Oklahoma had 223 teeth, a difference of 99 teeth. Regressing number teeth vs. hind femur length ( Fig. 36 View FIGURE 36 ) (the latter a good measurement of overall body size—see p. 17) we demonstrate that this cline in number of teeth is weakly related to body size (R 2 =0.486). In contrast, while males of G. veletis similarly double in size over their north to south distribution, number of teeth only increase from 116 to 175 (a difference of 59) in going south ( Fig. 141 View FIGURE 141 , p. 140 View FIGURE 140 ).
Where G. pennsylvanicus is sympatric and synchronic with G. veletis , as at Kadoka, South Dakota (S97-87); Jensen, Utah (S99-127); Concordia, Kansas (S02-50); Kansas City, Missouri (S02-54); and Geneva (S02-51) and Lincoln, Nebraska (S02-52), then ovipositor length in G. veletis considerably shorter than G. pennsylvanicus ( Fig. 37 View FIGURE 37 ).
As an example, the two collected female G. pennsylvanicus from Kadoka, SD (S97-87), both had ovipositors of 17.6 mm and hind femurs of 11.0 and 11.2 mm. A single female G. veletis , from the same locality, had an ovipositor of 11.7 mm and a hind femur of 10.6 mm. Both species sang from deep grass where individuals were difficult to collect. When synchronic and at the same temperature, field differences in PR between the two taxa are also easily appreciated as pulses in G. pennsylvanicus , at 20–25°C, are countable (as also seen in G. longicercus and G. firmus ) especially when males have more than 170 file teeth. Pulses in G. veletis are not countable by ear at 20–25°C and the chirp rate is noticeably faster. For instance, we could hear a PR difference in Lincoln, Nebraska (S02-52) when a G. veletis male, with 148 teeth, was singing at 5 AM adjacent to a G. pennsylvanicus male with 169 teeth. We wonder if these two species, in such areas of synchronicity, may display character displacement in pulse rate as evidenced by some of the highest numbers of file teeth seen in any G. pennsylvanicus males? In other words, having more teeth in the file could result in a slower pulse rate since more teeth are being struck. We suspect that synchronicity between these two taxa is also more common than we document (also see Alexander & Meral 1967) because most of our field collecting was done in early summer since that is when most other Gryllus species are adult.
G. pennsylvanicus has been used for studies on pest potential ( Carmona et al. 1999), calling and courtship ( Zuk 1987, Harrison et al. 2013) and behavior ( French & Cade 1987, 1989), as well as an extensive study of Hybrid Zones done in the R. Harrison lab—see discussion starting on p. 61.
Mermithids ( Poinar & Weissman 2004) present in one male from Sidney, MT (S97-95).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Gryllinae |
|
Genus |