Manota
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.207480 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6189534 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FE87F8-D643-FFD7-FF4C-FA1FFA0AF877 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Manota |
| status |
|
Key to the Oriental and Palaearctic species of Manota View in CoL View at ENA
Some species are keyed out at several places due to variation in the characters used, in some cases also due to a suspicion that variation may occur or because the used characters are not known with certainty. Couplet 60 is reached in two ways for the case the characters in couplet 56 are misinterpreted.
1. Anepisternum nonsetose................................................................................ 2
- Anepisternum setose.................................................................................. 10
2. Preepisternum 2 (katepisternum) setose; anterior margin of sternite 9 straight; the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa with a fringe of long setae ( Hippa 2008: fig. 11 B)......................... M. fimbriata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- Preepisternum 2 (katepisternum) nonsetose; anterior margin of sternite 9 medially incised; the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa without a fringe of long setae....................................................................... 3
3. R joining C well on the basal half of the costal margin of wing (similar to Hippa & Ševčík 2010: fig. 1 A), gonostylus divided into two subequal lateral and mesial lobes ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: figs. 10 B, C)..................................................................................................... M. radula Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Brunei]
- R joining C at the middle of the costal margin of wing (e.g. Hippa & Ševčík 2010: 1 B, C), gonostylus one-lobed or with a small lobe at the mesial margin ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 B, C) or with a curved finger-like lobe basolaterally ( Hippa 2009: figs. 2 B, D).....4
4. Laterotergite nonsetose................................................................................. 5
- Laterotergite setose.................................................................................... 8
5. Middle and hind femur yellow, parastylar lobe shorter than broad, nonsetose.. M. unifurcata Lundström View in CoL [Palaearctic: Europe]
- Middle and hind femur dark brown/black, parastylar lobe several times longer than broad, apically setose.............. 6
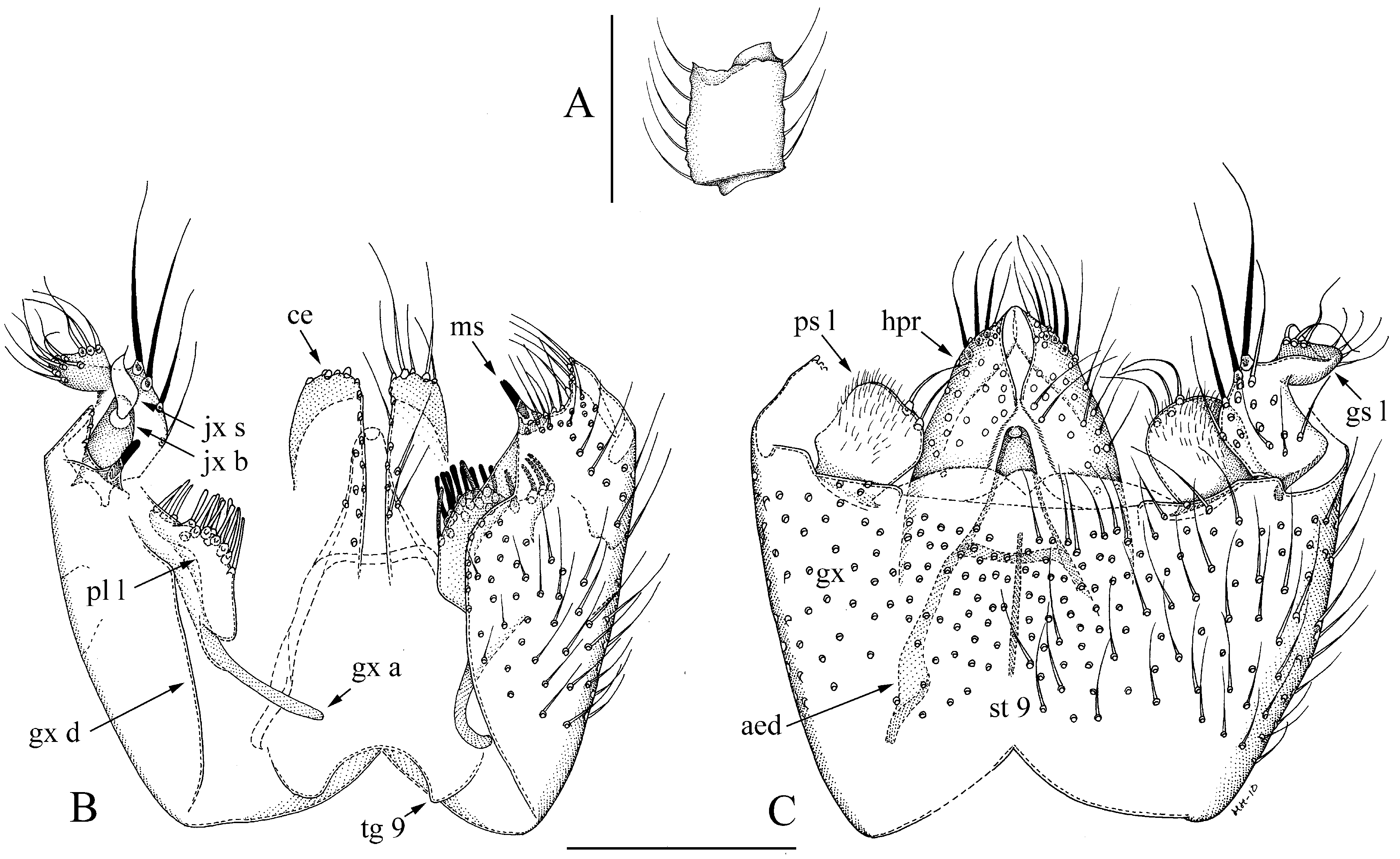
6. Sternite 9 posteromedially deeply cleft, gonostylus with a narrow lobe mesially on its basal half ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, B)..................................................................................... M. aquila View in CoL sp. n. [Oriental: Thailand]
- Sternite 9 posteromedially only slightly notched, gonostylus without a lobe mesially on its basal half................... 7
7. Parastylar lobe narrowing from base to apex, apically with a narrow sickle-shaped appendix beyond the setae; gonostylus broadest at its basal third ( Hippa & Papp 2007: figs. 6 A, B)................ M. forceps Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe evenly broad, without an appendix beyond the setae, gonostylus broadest near its middle ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: fig. 13 A, B)............................................ M. subforceps Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Sumatra]
8. Middle and hind femur dark brown/black; sternite 9 posteromedially deeply cleft, gonostylus with a narrow lobe subbasally at the mesial margin ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, B)............................................. M. aquila View in CoL sp. n. [Oriental: Thailand]
- Middle and hind femur yellow, sternite 9 posteromedially entire, with a small posteromedial knob, gonostylus without a lobe at the mesial margin..................................................................................... 9
9. Gonostylus with a basolateral finger-like lobe curving mesiad over the dorsal side ( Hippa 2009: figs. 2 B, D)..................................................................................... M. avita Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Gonostylus simple ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: figs. 11 B, C).............. M. sinepollex Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Sumatra)]
10. Preepisternum 2 (katepisternum) nonsetose or with at most 3 setae............................................. 11
- Preepisternum 2 (katepisternum) setose, with at least 10 setae................................................ 24
11. Laterotergite nonsetose, sternite 9 laterally separated from gonocoxa, with a distinct lateral margin ( Papp 2004: figs.. 21, 23).................................................................................................... 12
- Laterotergite setose, sternite 9 laterally fused with gonocoxae................................................. 13
12. Gonostylus broadening towards the apex, with 4 megasetae at the apical part of the mesial margin ( Papp 2004: figs. 23, 24, 25)...................................................................... M. meilingae Papp View in CoL (Oriental: Taiwan)
- Gonostylus tapering towards the apex, without megasetae in any position ( Papp 2004: figs. 20, 21)........................................................................................... M. delyorum Papp View in CoL [Palaearctic: Korea]
13. Sternite 9 laterally separated from gonocoxa by a distinct long margin anteriorly extending to the base of gonocoxa, the hypopygium giving a ventrally open impression ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 7 B)................................................................................................... M. inusitata Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand)]
- Sternite 9 laterally fused with gonocoxa, without a lateral margin, the hypopygium giving a ventrally closed impression (e.g. Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C)............................................................................................ 14
14. Gonostylus deeply V-shaped two-lobed, the lobe at dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa with 3+1 long megasetae ( Hippa 2006: figs. 6 B, C).................................................... M. biloba Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- Gonostylus one-lobed or with a lobe-like appendix apically (e.g. Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 B, C)................................... 15
15. Gonocoxa posterolaterally with unusually long setae, the longest ones of which being almost as long as gonocoxa ( Hippa 2006: fig. 7 E)..................................... M. ulu Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Penisular Malaysia, Sumatra, Thailand]
- Gonocoxa posteriorly with normal setae, the longest ones being at most one third of the length of gonocoxa............ 16
16. Dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa subapically with one to three megasetae or setae deviating from the other marginal setosity (not to be mixed with the juxtagonostylar setae or setae on a separate lobe ventrally from the dorsal mesial margin) (e.g. Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A, Hippa 2006: figs. 7 B, C)........................................................................... 17
- Dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa subapically without megasetae or strong setae deviating from the other marginal setosity.................................................................................................... 19
17. The dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa subapically with one to three slender megasetae which are apically attenuated, often appearing flame-shaped ( Hippa 2006: figs. 7 B, C).... M. simplex Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
- The dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa subapically with one stout apically rounded megaseta........................ 18
18. The juxtagonostylar seta megaseta-like, flat and flame-shaped, its basal body longer than the megaseta; parastylar lobe with 2– 3 setae ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 B, C)................................................... M. flammula View in CoL sp. n. [Oriental: Thailand]
- The juxtagonostylar seta seta-like, not flattened, its basal body shorter than the seta; parastylar lobe with ca. 8 setae ( Hippa 2009: figs. 7 B, C)....................................................... M. obtecta Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
19. The setae/megasetae on the lobe at the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa in a single straight longitudinal marginal row.. 20
- The setae/megasetae on the lobe at the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa in a curved transverse partly double row or in an unarranged group..................................................................................... 22
20. The number of megasetae ca. 7 ( Hippa 2006: fig. 6 F).... M. heptacantha Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand)]
- The number of megasetae ca. 10......................................................................... 21
21. The megasetae stout, blunt; length of gonostylus ca. 2.5 times the length of gonocoxa ( Hippa & Papp 2007: figs. 5 A, B).................................................................... M. dentata Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- The megasetae slender, sharp; length of gonostylus ca. 4 times the length of gonocoxa ( Hippa 2008: figs. 20 B, C)................................................................... M. subdentata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
22. The narrow apical part of aedeagus shorter than the broad basal part; the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa subapically with a hyalinous finger-like lobe ( Hippa 2008: figs. 8 B, C).............................. M. confixa Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo]
- The narrow apical part of aedeagus longer than the broad basal part; the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa without subapical finger-like lobe...................................................................................... 23
23. The megasetae on the lobe at the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa evenly broad, apically abruptly cut; parastylar lobe with two setae ( Hippa 2008: figs. 14 B, C)................................ M. juncta Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- The megasetae on the lobe at the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa narrowing from base to sharp apex; parastylar lobe with 4 or more setae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 8 B, C)....................... M. clausa Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia]
24. Laterotergite setose................................................................................... 25
- Laterotergite nonsetose................................................................................ 36
25. Aedeagus apically with long lateral lobes making ca. one third of the total length of aedeagus ( Hippa & Papp 2007: figs. 4 A, B)....................................................... M. bifida Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo, Thailand]
- Aedeagus apically simple.............................................................................. 26
26. Aedeagus with a short broad basal part and a long rod-like median part which posteriorly is expanded into a broader apical part ( Hippa 2006: fig. 3 B)........................................... M. spadix Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- Aedeagus subtriangular in shape......................................................................... 27
27. Cerci medially separate, each cercus with a long mesial margin................................................ 27
- Cerci medially fused, posteriorly separated by a notch which is narrower than the width of the free apical part of each cercus................................................................................................... 31
28. Gonostylus apically with megasetae ( Hippa & Papp 2007: figs. 7 A, B)..... M. inusitata Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand)]
- Gonostylus without megasetae in any position............................................................. 29
29. Gonostylus elongate oval, ca. 2.5 longer than broad, simple, with a fringe of ca. 15 long setae along the ventral mesial margin ( Hippa 2006: fig. 5 B).................................... M. ovata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
- Gonostylus nearly parallel-sided, at least 3 times longer than broad, with a narrow setose apicomesial lobe ( Hippa 2006: fig. 5 E) or with a subapical mesiodorsal crest bearing a row of setae, the mesial margin with only a few long setae ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 1 A, B).................................................................................... 30
30. Gonostylus with a narrow setose apicomesial lobe, without a mesiodorsal subapical crest bearing a row of setae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 5 E).................................................... M. angustata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia)]
- Gonostylus with a subapical mesiodorsal oblique crest bearing a row of setae, without a subapical setose lobe ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 1 A, B).......................... M. biunculata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental/Australasian: Papua New Guinea, Thailand]
31. Gonostylus deeply bilobed, each lobe with two megasetae, parastylar lobe large, extending far mesiad from the ventral mesial margin of gonocoxa ( Hippa 2008: figs. 12 B, C)....................... M. index Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- Gonostylus unilobed or with a lobe-like appendix apically, without megasetae in any position, parastylar lobe small, partly concealed under the ventral mesial part of gonocoxa, often difficult to distinguish as a separate sclerite............... 32
32. The small rounded lobe on the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa with a long thick seta which conspicuously deviates from the other dorsal setosity of gonocoxa ( Hippa 2006: figs. 4 B, D).................................................. 33
- The small rounded lobe on the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa without a long thick seta which conspicuously deviates from the other dorsal setosity of gonocoxa.................................................................... 34
33. Number of juxtagonostylar setae 1: a flat Y-shaped megaseta............. M. pollex Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- Number of juxtagonostylar setae 2: a flat apparently branched megaseta the detailed character of which is unknown and a rather normal seta placed on its anterior side ( Hippa 2006: fig. 4 B)......... M. yongi Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
34. The setae on the parastylar lobe very thick, much thicker than the adjacent setae on the ventral side of gonocoxa ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 2)....................................... M. roslii Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
- The setae on the parastylar lobe thin, similar to the adjacent setae on the gonocoxa ( Hippa & Papp 2007: figs. 9 A, B, 10 B, C)................................................................................................... 35
35. Gonostylus twice longer than broad, apically attenuated and slightly bilobed ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 9 A, B)............................................................................ M. occulta Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Gonostylus ca. 2.5 times longer than broad, the apical half evenly broad with no indication of being bilobed ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 10 A, B)................................................ M. secreta Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
36. Anterior basalare setose, with at least 2 setae.............................................................. 37
- Anterior basalare nonsetose........................................................................... 55
37. Gonostylus geniculate, the apical mesiad bent part bilobate ( Hippa 2008: figs. 18 B, C)............................................................................................. M. perlobata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Burma, Thailand]
- Gonostylus straight, unilobate........................................................................... 38
38. Parastylar lobe lacking; cerci medially fused, posteromedially separated by a low notch the depth of which is less than the width of the free apical part of cercus ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: figs. 15 A, B).... M. pappi Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo, Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe present; cerci separate, with a long free mesial margin each...................................... 39
39. Gonostylus with blunt-ended megasetae on apical half....................................................... 40
- Gonostylus without blunt-ended megasetae on apical half, if there are strong setae deviating from the other setosity they are attenuating to a long fine apex.......................................................................... 42
40. Gonostylus broadening from base to apex, the apical width ca. twice the subbasal width ( Papp 2004: figs. 23, 24, 25)............................................................................. M. meilingae Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Taiwan]
- Gonostylus apically as broad as or narrower than subbasally.................................................. 41
41. The number of gonostylar megaseta ca. 4, placed as a claw-like group at the apex of gonostylus ( Hippa 2009: figs. 3 B, C)..................................................................... M. chaelapex Hippa [Oriental: Thailand)]
- The number of gonostylar megasetae ca. 30, placed in ventral, lateral and dorsal longitudinal rows ( Hippa & Kjaerandsen 2010: figs. 8, 9)................................................... M. tunoae Hippa & Kjaerandsen View in CoL [Palaearctic: Japan]
42. Gonostylus with a longitudinal comb-like row of 5 closely placed strong setae subbasally at its ventral mesial margin ( Hippa 2008: Fig. 10 c, Hippa & Kjaerandsen 2010: figs. 2, 3)...................................................... 43
- Gonostylus without a comb-like row of setae ventrally on its basal part......................................... 44
43. Hypoproct (sternite 10) with two very long setae anteromesially on each side, these setae several times longer than the other ventral setae ( Hippa 2008: Fig. 10 C)....................................... M. cristata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Hyporoct (sternite 10) anteromesially with all the ventral setae short and similar ( Hippa & Kjaerandsen 2010: figs. 2, 3)........................................................... M. satoyamanis Hippa & Kjaerandsen View in CoL [Palaearctic: Japan]
44. Aedeagus apically nearly as broad as basally, subquadrangular, with prominent rounded ear-like apicolateral lobes ( Hippa 2008: figs. 5 B, C)..................................................... M. auriculata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Aedeagus apically much narrower than basally, subtriangular, without ear-like apicolateral lobes..................... 45
45. Parastylar lobe in anterior-posterior direction long, at least 3 times longer than broad, with at most ca. 6 setae on the mesial margin............................................................................................ 46
- Parastylar lobe in anterior-posterior direction short, at most twice longer than broad, in the cases the length is nearly twice the width the number of setae is ca. 15 and they are widely distributed on the mesial part of the lobe..................... 48
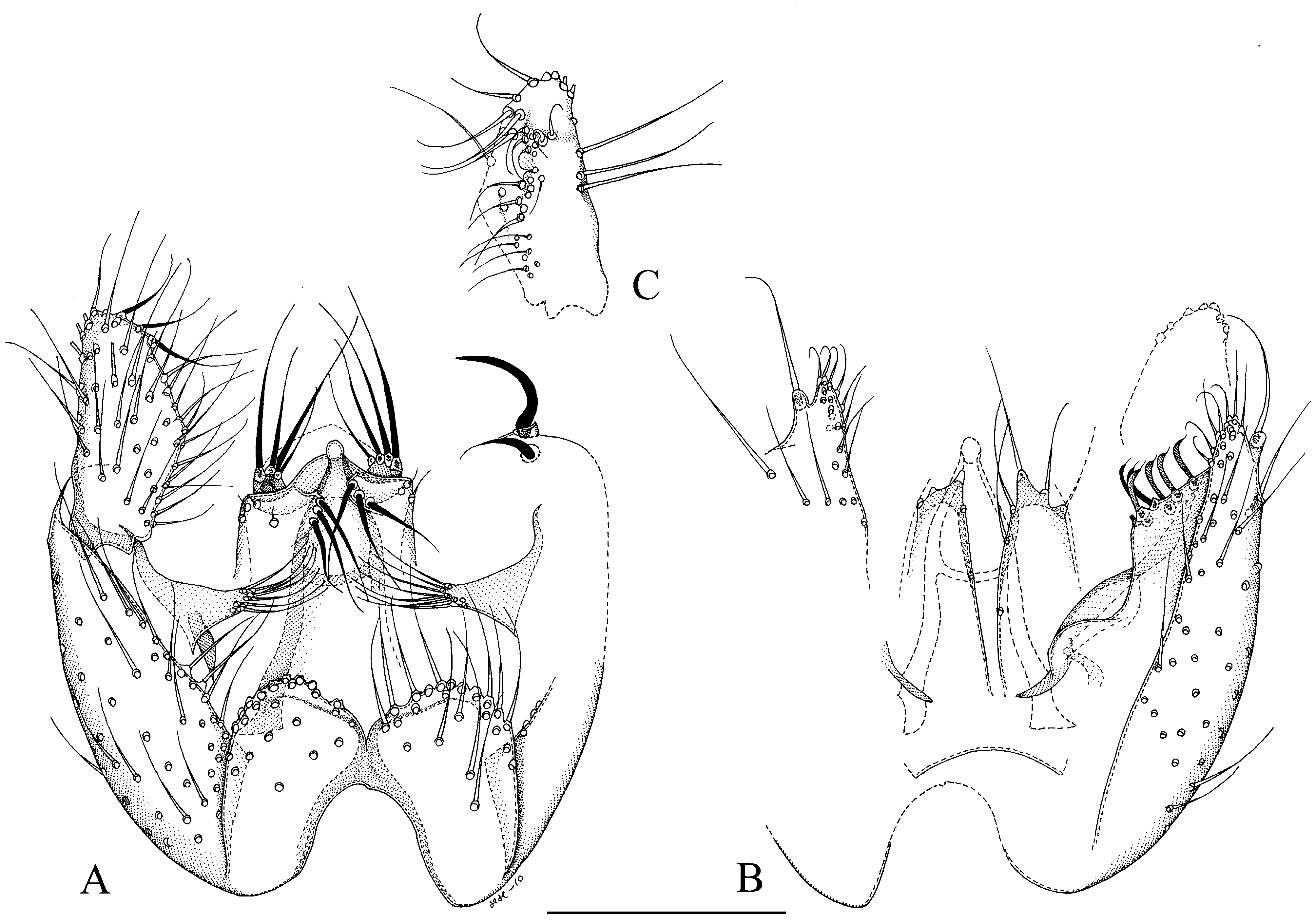
46. Parastylar lobe anteriorly curved mesiad, its setae on that curved part ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C)....... M. falcata View in CoL sp. n. [Oriental: Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe without anterior curvature mesiad, its setae along the mesial margin............................... 47
47. Parastylar lobe a narrow stripe, ca. 10 times longer than broad; apical part of aedeagus directed posteriad; gonostylus without needle-like pale setae dorsally ( Hippa & Papp 2007: fig. 8 B).............. M. mirifica Hippa & Papp View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe broader, ca. 3 times longer than broad; apical part of aedeagus curved ventrad, gonostylus with needle-like pale setae dorsally ( Hippa 2008: fig. 21 C).................................... M. submirifica Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
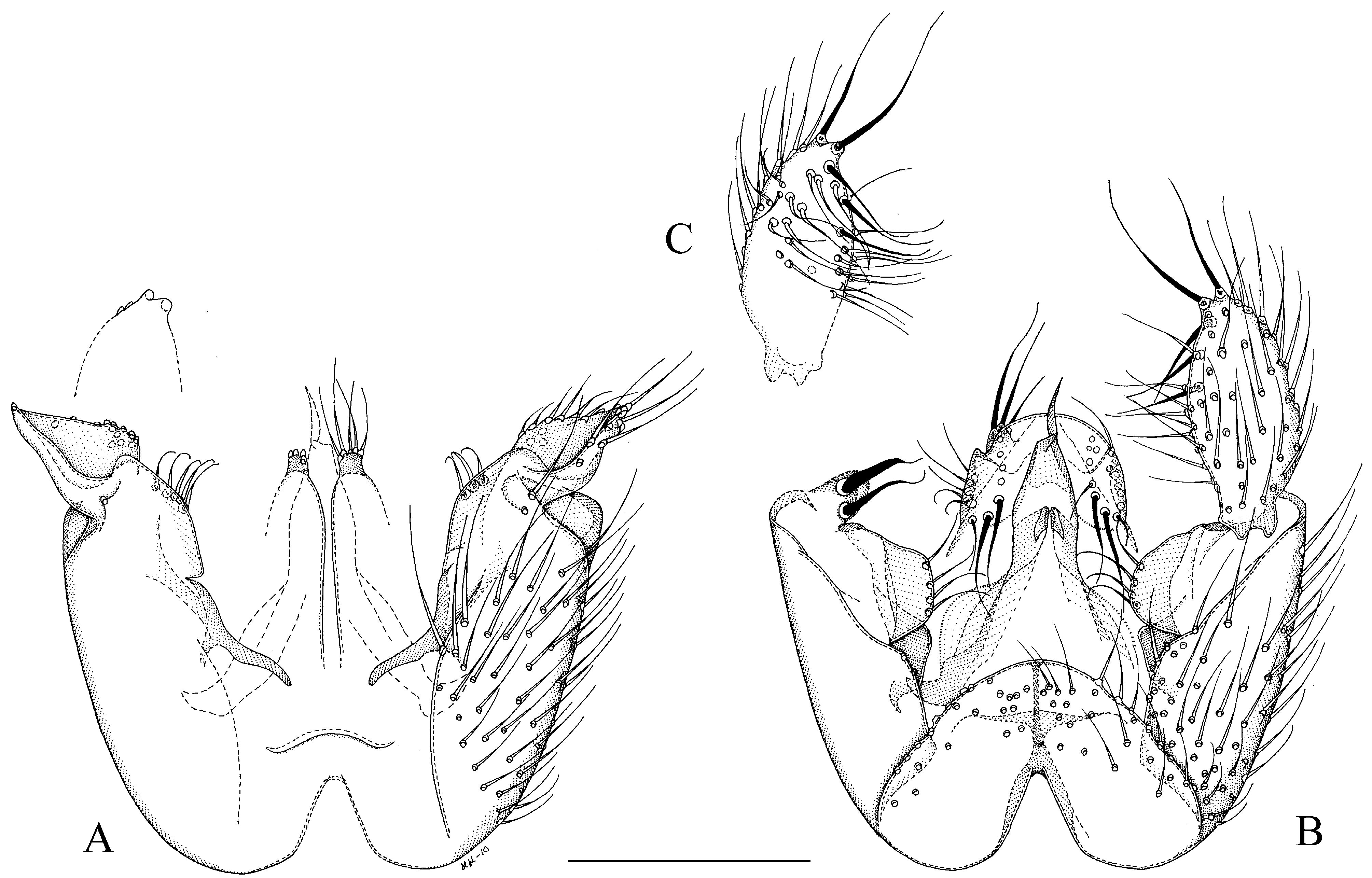
48. Aedeagus apically asymmetrical, with the left side longer than the right side, the left side appearing as a knife-like appendix ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 B)............................................................ M. aconcinna Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Aedeagus apically symmetrical, simple.................................................................. 49
49 The setae mesiodorsally on gonostylus fine, not deviating from the other gonostylar setosity......................... 50
- Some, usually 3–6, of the mesiodorsal setae on the apical half of gonostylus strong, often elongate flame-shaped, sharply deviating from the other gonostylar setosity................................................................... 52
50. The dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa without an apical lobe ( Hippa & Kjaerandsen 2010: fig. 5); wing unicolorous yellowish; wing length 2.0 mm.......................................... M. indahae Hippa & Kjaerandsen View in CoL [Palaearctic: Japan]
- The dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa apically with a thumb-like lobe ( Hippa 2008: fig. 7 B); wing bicolorous, the basal part yellowish, the apical part darker greyish or brownish ( Hippa 2009: fig. 1 E)...................................... 51
51. Parastylar lobe semicircular ( Hippa 2008: fig. 7 C).............................. M. collina Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe subtriangular ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A)..................................... M. subcollina View in CoL sp. n [Oriental: Thailand]
52. Aedeagus apically tri-lobed, appearing as three parallel lamellae, ventral side of aedeagus subapically with a pair of posteriorly directed lamellae crossing in the middle line ( Hippa 2008: Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 b, c)................. M. chi Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Aedeagus apically one-lobed, at most with a small apicolateral tooth, without ventral subapical lamellae............... 53
53 The outline of gonostylus elongate subquadrangular, with three strong setae at apicomesial margin, two at the apex and one at the apical third ( Hippa 2008: figs. 19 B, C)................................ M. planilobata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- The outline of gonostylus elongate oval, with 4 or 5 strong setae at the apicomesial margin.......................... 54
54. The strong setae at the apicomesial margin of gonostylus equal in length, hypoproct posterodorsally with a transverse comblike row of 4 strong setae on each side, the setae medioventrally on hypoproct (sternite 10) fine, similar to other ventral setae of hypoproct ( Hippa 2009: figs. 9 B, C)....................................... M. seducta Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- The strong setae at the apicomesial margin of gonostylus diminishing in length towards the apex of gonostylus, hypoproct posterodorsally with one stronger seta only, the setae medioventrally on hypoproct (sternite 10) strong, claw-like, conspicuously deviating from the other ventral setae of hypoproct ( Hippa 2008: figs. 6 B, C)..... M. clavulosa Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand)]
55. One of the two juxtagonostylar setae greatly expanded, flattened, complicated in structure; sternite 9 very broad, ca. three fourths of the width of hypopygium, with ca. 100 setae; gonocoxa apicodorsally with a posteriod directed long narrow hyalinous nonsetose lobe ( Hippa 2009: figs. 8 B, C, D).............................. M. prisca Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- The juxtagonostylar setae simple, if flattened, then elongate parallel-sided in shape ( Hippa 2006: fig. 13 B, Hippa 2008: fig. 16 B); sternite 9 ca. half the width of hypopygium or narrower, with at most ca. 50 setae; gonocoxa apicodorsally without a long hyalinous nonsetose lobe............................................................................. 56
56. The dorsal apical margin of gonocoxa simple, without any kind of setose or nonsetose lobe (the basal body of juxtagonostylar setae/megasetae, which often in mounts is near the gonocoxal margin, should not be mixed with the lobe in question; the number of the juxtagonostylar setae is two, at least one being a megaseta, and they arise from a smaller or large lobe-like basal body which is free from the dorsal gonocoxal margin in a more ventral level), the placement of the lobe varies between apicolateral and apicomesial............................................................................... 57
- The dorsal apical margin of gonocoxa with a posteriod or obliquely posteromesiad directed lobe bearing from one to numerous setae, in some cases the lobe may be rather inconspicuous and partly concealed under the more mesial part of the apical margin (e.g. Hippa 2006: figs. 16 D, E, 17 C, D)................................................................. 61
57. Hypoproct ventrally, on each side, without an isolated row or double row of setae flanking the apex of aedeagus, either the whole ventral side of hypopygium is widely setose or the setosity is restricted to the posterior part.................... 58
- Hypoproct (sternite 10) ventrally, on each side, with an isolated row or double row of setae, flanking the apex of aedeagus...................................................................................................... 61
58. Gonostylus with a large striated plate-like lobe on the mesial side, the lobe being as broad as the rest of the gonostylus; the juxtagonostylar setae equally sized megasetae; aedeagus not constricted at base ( Ševčík 2002: figs. 1, 2, 3)...................................................................................... M. chinensis Ševčík View in CoL [Palaearctic: China]
- Gonostylus without a large striated mesial lobe; juxtagonostylar setae unequal in size, one a shorter simple seta, the other a longer slightly flattened megaseta; aedeagus constricted near the base........................................... 59
59. Parastylar lobe distinct, directed posteromesiad, with ca. 4 apical setae; the lobe on the mesial side of the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa with blunt megasetae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 13 B).... M. globigera Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
- Parastylar lobe not distinct from the ventral mesial margin of gonocoxa; the lobe on the mesial side of the dorsal mesial margin of gonocoxa with long acute setae....................................................................... 60
60. The setae at the posteroventral and posterolateral margin of gonocoxa numerous and long, the longest ones ca. three fourths of the length of gonocoxa ( Hippa 2008: fig. 16 C).................... M. parvistylata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- The setae at the posteroventral and posterolateral margin of gonocoxa few and short, the longest ones less than half of the length of gonocoxa ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: fig. 5 C).................... M. capillata Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Sumatra]
61. The apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa inconspicuous, partly covered by more mesial parts of the apical margin............. 62
- The apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa conspicuous, fully exposed or only the basalmost part covered by the gonocoxal margin 64
62. Gonostylus apically with a row of long flat megasetae/setae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 15 B).............................................................................. M. horrida Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand)]
- Gonostylus without flat megasetae apically................................................................ 63
63. The ventral mesial margin of gonostylus on its basal half with a fringe of ca 10 long setae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 17 B).......................................................... M. plusiochaeta Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
- The ventral mesial margin of gonostylus on its basal half with a fringe of ca. 5 long setae Hippa 2006: fig. 16 D)............................................................ M oligochaeta Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand]
64. The apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa cylindrical or elongate conical, not flattened, and resembling the basal body of the juxtagonostylar setae, in M. anceps the lobe is two-branched, composed of a longer and a shorter conical part and their common base is broad and can be regarded as flat, even in this case the lobe gives an impression of the juxtagonostylar setae ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: fig. 3 B)................................................................................ 65
- The apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa flattened, dissimilar to the basal body of the juxtagonostylar setae.................. 70
65. The apicodorsal gonocoxal lobe divided into a shorter and a longer branch, each with a strong apical seta ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: fig. 3 B).................................................. M. anceps Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Sumatra]
- The apicodorsal gonocoxal lobe simple, with 1–4 apical setae................................................ 66
66. The apicodorsal gonocoxal lobe slightly constricted in the middle, with 3–4 setae at the apex; gonostylus curved, very long, ca 4 times longer than broad ( Hippa 2006: fig. 15 E)...................... M. duplex Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia]
- The apicodorsal gonocoxal lobe evenly broad or elongate conical, with 1 seta at apex; gonostylus straight, at most ca. twice longer than broad.................................................................................... 67
67. Gonostylus with a very long flattened seta at its basomesial angle, greatly deviating from other gonostylar setae ( Hippa 2006: fig. 16 A; Hippa 2009: figs. 13 C, D)............. M. perpusilla Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra, Thailand]
- Gonostylus basomesially without setae deviating from other gonostylar setosity.................................. 68
68. Gonostylus with a comb-like row of very long setae subapically at the mesial margin, the setae nearly as long as the length of gonostylus, at these setae on the dorsal side of gonostylus a patch of tightly placed setae; paraapodemal lobe inflated; hypoproct without a row of setae flanking the apical part of aedeagus ( Hippa 2009: figs. 12 B, C).............................................................................................. M. vesicaria Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Gonostylus without a comb-like row of very long setae subapically at the mesial margin, all the apical setae shorter than half the length of gonostylus, the dorsal side of gonostylus without a patch of tightly placed setae; paraapodemal lobe flat; hypoproct on each side with a row of setae flanking the apical part of aedeagus........................................ 69
69. Gonostylus oval, at apical margin with ca. 10 black curved setae deviating from the other setosity ( Hippa 2008: figs. 17 A, B)........................................................................ M. pellii Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- Gonostylus attenuating on apical third, at apicomesial margin with one pale stout seta deviating from the other setosity ( Hippa & Ševčík 2010: figs. 7 B, C)..................................... M. hexacantha Hippa & Ševčík [Oriental: Borneo]
70. Gonostylus long and narrow, over 4 times longer than broad at the middle; part of the setae at the mesial margin of the apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa flat, blade-like ( Hippa 2006: figs. 13 D, E)................................................................................................. M. curvata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra]
- Gonostylus at most 3 times longer than broad; all the setae on the apicodorsal lobe of gonocoxa normal, not flattened..... 71
71. The basomesial angle of gonostylus with two conspicuous very long curved setae which are thicker than the other ventral gonostylar setae and ca. twice longer than the width of gonostylus............................................. 72
- The basomesial part of gonostylus without conspicuous setae deviating from the general setosity, the length of the basomesial gonostylar setae at most equal with the width of gonostylus................................................... 73
72. The basomesial angle of gonostylus rounded; gonostylus with short curved black setae apicodorsally ( Hippa 2006: fig. 12 D)....................................................... M. ferrata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo]
- The basomesial angle of gonostylus lobe-like produced; gonostylus without black curved setae apicodorsally ( Hippa 2009: figs. 10 B, C)........................................................ M. subferrata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
73. The setae on the ventral part of hypoproct widely distributed, not concentrated on a single straight mesial row.......... 74
- The setae on the ventral part of hypoproct concentrated on a single straight mesial row on each half, the two rows in normal position flanking the apical part of the aedeagus, in mounts often moved posteriod................................ 80
74. Gonostylus divided into a broad basal half and a narrow apical half, the former double as broad as the latter; paraapodemal lobe very large, inflated ( Hippa 2008: figs. 13 B, C)......................................................... 75
- Gonostylus not divided into a broad basal and a narrow apical part; paraapodemal lobe small, flat.................... 76
75. The narrow apical part of gonostylus as long as the broad basal part ( Hippa 2008: figs. 13 B, C)............................................................................................... M. inflata Hippa View in CoL [Oriental: Thailand]
- The narrow apical part of gonostylus shorter than the broad basal part ( Papp 2004: figs. 15, 16)........................
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |