Capsaloides hoffmannae LamotheArgumedo, 1996
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.172308 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C21EA9A2-6A92-452C-849D-DC11B657E4C4 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC8787-E16D-FFC3-FED3-FB689EB1FBB9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Capsaloides hoffmannae LamotheArgumedo, 1996 |
| status |
|
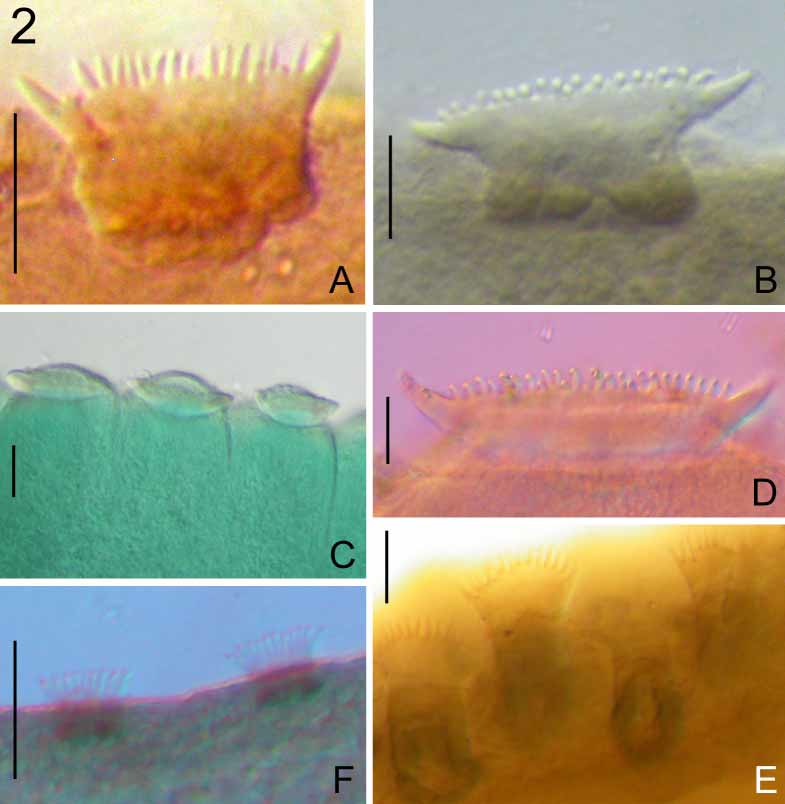
Capsaloides hoffmannae LamotheArgumedo, 1996 ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 2 C)
Typehost: Tetrapterus audax (Philippi, 1887) ( Istiophoridae ).
Typelocality: Mazatlan, Sinaloa, Mexico [Pacific Ocean].
Site: Gills.
Specimens examined: One paratype ( CNHE 002718).
Remarks
The key of LamotheArgumedo ( 1996) distinguishes C. hoffmannae from most other members of Capsaloides by the ratio of the haptor diameter to total body length between 1.2 to 1.3. He states that the haptor diameter/total body length ratio is similar for C. magnaspinosus . Based on this finding LamotheArgumedo ( 1996) subsequently goes on to distinguish between these 2 species to the exclusion of the other species in Capsaloides . Using ratios of soft body measurements to distinguish between species is fraught with problems since they depend of the method of fixation and subsequent preparation (i.e. flattened versus unflattened). LamotheArgumedo ( 1996) does not state how the specimens of C. hoffmannae were prepared but the paratype is not strongly flattened and as such, the sinuations are close together making the surface appear annulated ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). We also do not know if the haptoral diameter/total body length ratio given by Lamothe Argumedo ( 1996) for C. magnaspinosus was from typematerial or from the drawing of Price ( 1939).
Capsaloides hoffmannae was described from the same host species as C. sinuatus and C. hoffmannae is very similar to C. cristatus and C. sinuatus ; these latter 2 species, as we discussed above, may be synonymous. Comparison of the morphology of the haptoral accessory sclerites of C. hoffmannae to those of other species is difficult because they are not completely flattened in a dorsoventral plane. The haptoral accessory sclerites of C. hoffmannae ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C) are considerably shorter than those of C. cristatus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) and C. sinuatus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 G). However, length of the haptoral accessory sclerites may increase as the parasite grows like other capsalids (e.g. Kearn 1990). The dorsomarginal body sclerites ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) have 15–20 cusps. The left isolated anterior group of dorsomarginal body sclerites could not be seen in the paratype but the illustration of LamotheArgumedo ( 1996) depicts 5 sclerites. The presence of a right anterior group of dorsomarginal body sclerites was not noted by LamotheArgumedo ( 1996) and could not be seen in the paratype examined by us. The annulated body margin of C. hoffmannae closely resembles that of the unflattened voucher specimen of C. cristatus adding further support to our view that C. hoffmannae may be an invalid taxon and together with C. cristatus , may be synonymous with C. sinuatus . However, we refrain from making this decision until more material is available.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |