Cephalophus hooki, St. Leger, 1934
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6512484 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6773233 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F50713-99EA-FF51-03D8-FDC2F899FA8A |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Cephalophus hooki |
| status |
|
268. View On
Mount Kenya Duiker
French: Céphalophe de Hook / German: Kenia-Schwarzstirnducker / Spanish: Duiker del Monte Kenia
Taxonomy. Cephalophus hook: St. Leger, 1934 ,
Southwest face of Mt Kenya, 8500 10,000 ft.
Formerly considered to be a subspecies of C. nigrifrons . Monotypic.
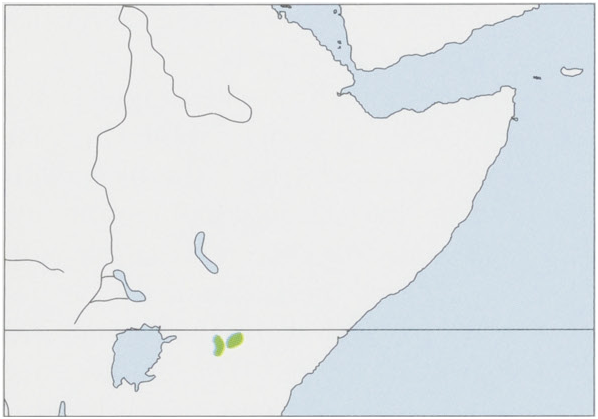
Distribution. Mountains of C Kenya. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body ¢.85-95 cm, tail c.11-15 cm; weight c.13-16 kg. No specific measurements of the Mount Kenya Duiker have been reported; those given above are for the former C. nigrifrons cluster in East Africa. This is a small duiker; skull measurements are only slightly larger than for the Mount Elgon Duiker (C. foster). Overall coloration is dull chestnut or reddish-gray; individual hairs are banded, with pinkish-gray bases and dark brown subterminal bands. The Mount Kenya Duikeris duller in color than the Black-fronted Duiker ( C. nigrifrons ) and has longer, softer, and thicker pelage. The tail has a very large terminal tuft. The hooves are long (front hooves are 2:8—-4-4 cm in length), resembling those of the Mount Elgon Duiker and the Black-fronted Duiker. The face and sides of the neck of the Mount Kenya Duiker are grayer than the body. A dark blaze from muzzle to forehead is bordered by red stripes. The chin (and often the underside of the jaw) is reddish-white. The coronal tuft is short and completely black. Dental formulais10/3,C0/1,P 3/3, M 3/3 (x2) = 32.
Habitat. High-elevation bamboo forests and moorlands; highest elevation recorded is around 3500 m. The Mount Kenya Duikeris rarely found below 2600-3000 m. Dense thickets, riverside forests, and marshy terrain are used as refugia.
Food and Feeding. There is no specific information available for this species, but presumably frugivorous/folivorous like similar species.
Breeding. There is no information available for this species.
Activity patterns. There is no specific information available for this species, but presumably diurnal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. There is very little specific information available for this species. Field observations indicate that the Mount Kenya Duiker produces a loud thumping noise when fleeing, as does the Black-fronted Duiker. It is not known whether these noises are vocalizations or from the large inguinal glands.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List (under C. nigrifrons ). The Mount Kenya Duiker is rare due to its highly restricted range, but it can be locally common. It is protected within Mount Kenya National Park. It is known to have inhabited the Aberdare Mountains, but there are very few recent records from this locale and the species may now be locally extinct.
Bibliography. East (1999), Grubb & Groves (2001), Hillman et al. (1988), IUCN/SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2008h), Kingdon (1982), Wilson (2001).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Cephalophus hooki
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2011 |
Cephalophus hook:
| St. Leger 1934 |