Hipposideros larvatus, (Horsfield), 1823
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0179555 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F3F77F-FF86-FF9A-FDB4-D0BDBB62F9D7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Tatiana (2020-11-06 15:23:09, last updated 2020-11-06 16:10:10) |
|
scientific name |
Hipposideros larvatus |
| status |
|
Hipposideros larvatus [Horsfield, 1823]
Rhinolophus larvatus Horsfield, 1823: 6 ; Java, INDONESIA (Collector unknown; Type unknown) [ 102].
Hipposideros larvatus [ 8].
Common English name: Intermediate Roundleaf Bat
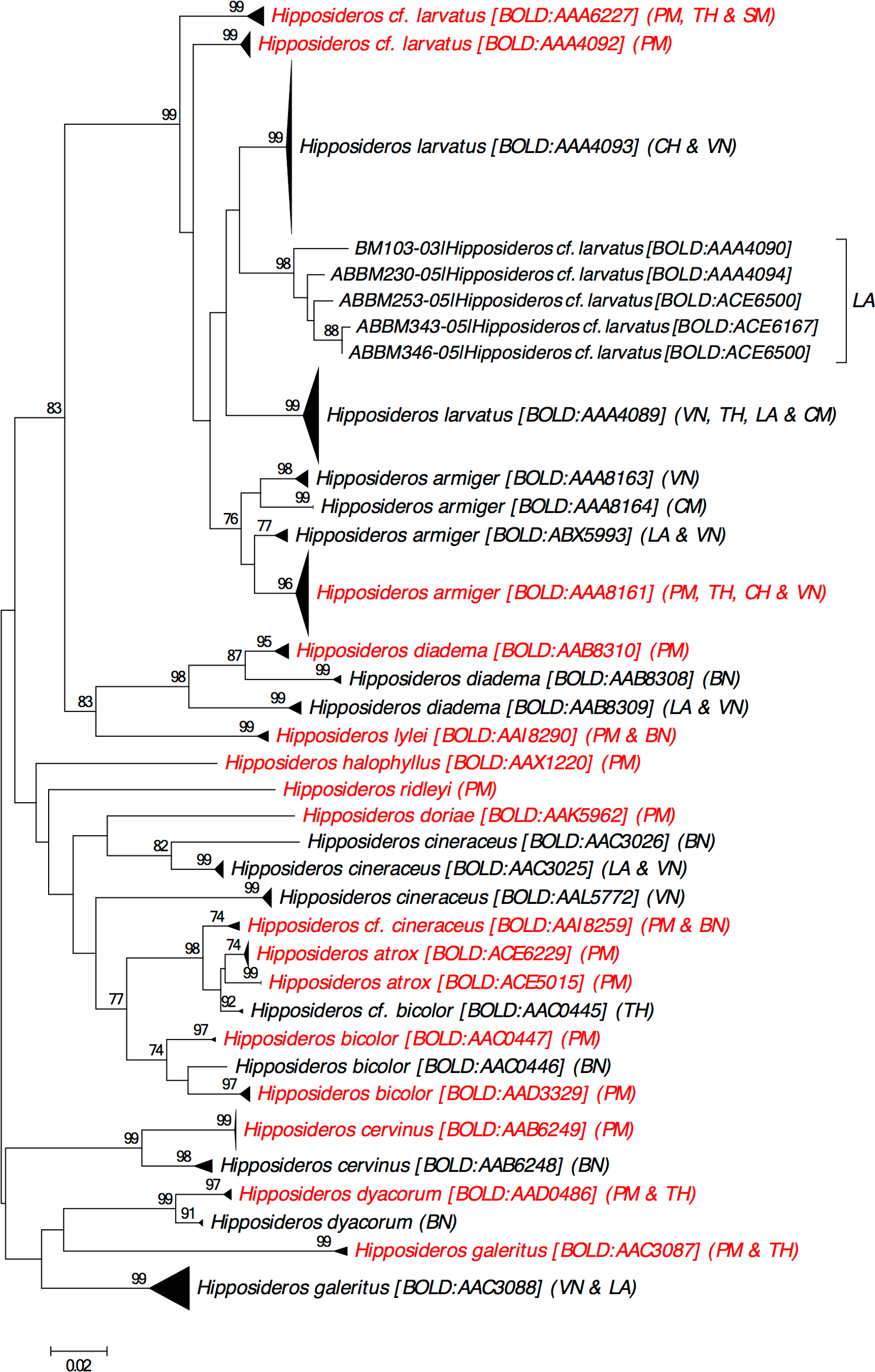
Barcode Index Number: BOLD: AAA 4092 (11 DNA barcodes from Peninsular Malaysia) and BOLD: AAA 6227 (1 DNA barcode from Peninsular Malaysia; Fig 4 View Fig 4 )
Remarks: Thabah et al. [ 18] reported that specimens of H. larvatus sensu lato from the Indo-Malayan region ( India, Myanmar, Malaysia, China) have variable echolocation frequencies (~82 kHz to ~100 kHz) and those from Peninsular Malaysia emitted the highest frequency (100–102 kHz). They also reported size variation with female specimens from Peninsular Malaysia having the lightest body mass and shortest forearm. DNA barcodes recorded as H. larvatus formed five clusters, consistent with geograpahical origin of the sequences (see Fig 5 View Fig 5 in [ 18]). The variations in echolocation, morphology and mtDNA suggest that H. larvatus is a speciescomplex [ 18, 32, 125].
DNA barcodes on BOLD recoded as H. larvatus are associated with eleven BINs. DNA barcodes from Peninsular Malaysia fell into two BINs ( Fig 4 View Fig 4 ; see Fig 5 View Fig 5 in [ 18]). One BIN comprises DNA barcodes from Perlis, northern Peninsular Malaysia, and Thailand, while the other contains barcodes from across Peninsular Malaysia. Lim et al. [ 134] identified the specimens on an island in Peninsular Malaysia (Pulau Tioman) as H. l. barbensis (type locality: Sainte Barbe Island = Pulau Penjantan), however, Thabah et al. [ 18] stated that H. larvatus in Malaysia represents H. larvatus sensu stricto on the basis of their shorter forearms and type locality. Our NJ analysis suggested at least two distinct forms of H. larvatus are occurring in Peninsular Malaysia ( Fig 4 View Fig 4 ) and clustered DNA barcodes of BIN, BOLD:AAA4092 with ABBSI021-04 which shares the same locality with specimens examined by Thabah et al. [ 18]. We tentatively retained a single name, H. larvatus for this species complex in this checklist pending further research.
IUCN status: Least Concern
Recorded at: Pahang: Krau Wildlife Reserve [ 11, 42], Pulau Tioman [ 23, 79], Kuala Atok, National Park [ 44], Fraser Gill Forest Reserve [ 56], Kemasul, Klau Besar, Kenong and Gunung Aais [ 100]; Terengganu: Pasir Raja, Dunggun [ 15], Tasik Kenyir [ 69], Bukit Dendong [ 97], Gunung Tebu Forest Reserve [ 101]; Kedah: Pulau Langkawi [ 23], Ulu Muda Forest Reserve [ 57], Bukit Hijau [ 100], Gunung Angsi Forest Reserve [ 100, 101]; Johor: Pulau Aur [ 23], Endau-Kota Tinggi Forest Reserve [ 56], Gunung Panti and Labis Forest Reserve [ 100]; Perak: Bukit Jerneh Cave and Tumang Lembing Cave [ 30], Temenggor Lake [ 69], Kledang Saiong Forest Reserve [ 100]; Negeri Sembilan: Pasoh Forest Reserve [ 45]; Perlis: Wang Kelian State Park [ 50]; Selangor: Bukit Kutu Wildlife Reserve [ 51], Ulu Gombak [ 52], Semangkok Forest Reserve,[ 101]; Kelantan: Air Panas-Gua Musang [ 61], Gunung Reng and Gua Musang [ 62], Gunung Stong State Park [ 100]; Melaka: Unspecified [ 68]; Pulau Pinang: Bukit Panchor [ 100].
H. larvatus has been reported roosting in limestone caves, buildings, old mines rock and crevices in primary and secondary forests [ 11, 14].
42. Anan S, Rashdi AM, Abdul J, Lim BL. A survey of small mammals at Sungai Chenderoh, Perlok, Krau Wildlife Reserve, Pahang. Journal of Wildlife and Parks. 1998; 16: 104 - 109.
8. Chasen FN. A handlist of Malaysian mammals (A systematic list of the mammals of the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo and Java, including the adjacent small islands). Bulletin of the Raffles Museum; 1940.
79. Csorba G, Fuisz T, Kelen B. New birds and bats from Pulau Tioman, Malaysia. Mal Nat J. 1997; 50: 197 - 200.
30. Douangboubpha B, Bumrungsri S, Soisook P, Murray SW, Puechmaille SJ, Satasook C, et al. A taxonomic review of Hipposideros halophyllus, with additional information on H. ater and H. cineraceus (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) from Thailand and Myanmar. Acta Chiropt. 2010; 12 (1): 29 - 50.
45. Francis CM. Trophic structure of bat communities in the understorey of lowland dipterocarp rain forest in Malaysia. J Trop Ecol. 1990; 6: 421 - 431.
14. Francis CM. A field guide to the mammals of South-East Asia. New Holland Publishers; 2008.
61. Hasan NH, Khan K, Senawi J, Ketol B, Sait I, Abdullah MT. A report on bats survey at Air Panas-Gua Musang, Kelantan, Malaysia. J Trop Biol Conserv. 2012; 9 (2): 156 - 162.
102. Horsfield, T. Zoological researches in Java. Kingbury, Parbury and Allen, London; 1823 - 1824.
50. Jayaraj VK, Daud SH, Azhar MI, Sah SA, Mokhtar SI, Abdullah MT. Diversity and conservation status of mammals in Wang Kelian State Park, Perlis, Malaysia. Check List. 2013; 9 (6): 1439 - 48.
62. Jayaraj VK, Khan FA, Azhar I, WeeChen E, Ali MR, Ahmad A, et al. Diversity and conservation status of small mammals in Kelantan, Malaysia. Warasan Songkhla Nakharin. 2016; 38 (2): 213 - 20.
101. Joann CL, Fletcher C, Rahman KA. Spatial effects of virgin jungle reserves (VJR) on the community of insectivorous bats in Peninsular Malaysia. J Trop For Sci. 2013; 25 (1): 118 - 130.
32. Khan FAA, Vicki J, Solari S, Peter A, Ketol B, Marni W, et al. Using genetics and morphology to examine species diversity of Old World bats: report of a recent collection from Malaysia. Occas Pap Tex Tech Univ Mus. 2008; Number 281.
11. Kingston T, Lim BL, Akbar Z. Bats of Krau wildlife reserve. Penerbit Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia; 2006.
134. Lim BL, Lim KP, Yong HS. The terrestrial mammals of Pulau Tioman, Peninsular Malaysia, with a catalogue of specimens at the Raffles Museum, National University of Singapore. Raffles Bull Zool. 1999; 6: 101 - 123.
51. Lim BL, Majid RA, Norsham Y. Studies on the mammal fauna of Bukit Kutu Wildlife reserve, Hulu Selangor. Journal of Wildlife and Parks. 1999; 17: 1 - 6.
100. Lim LS, Mohd-Adnan A, Zubaid A, Struebig MJ, Rossiter SJ. Diversity of Malaysian insectivorous bat assemblages revisited. J Trop Ecol. 2014; 30 (02): 111 - 121.
52. Medway L. The Ulu Gombak Field Studies Centre. Malayan Scientist. 1966; 2: 1 - 6.
23. Medway L. The wild mammals of Malaya. London: Oxford University Press. 1969.
56. Mohd-Hanif RM, Nur-Aida MT, Zahirunisa AR, Mohd-Ridwan AR, Abdullah MT. Contribution of regenerated forest in conservation of bats in Peninsular Malaysia. J Trop For Sci. 2015; 27 (4): 506 - 16.
125. Murray SW, Campbell P, Kingston T, Zubaid A, Francis CM, Kunz TH. Molecular phylogeny of hipposiderid bats from Southeast Asia and evidence of cryptic diversity. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2012; 62 (2): 597 - 611. https: // doi. org / 10.1016 / j. ympev. 2011.10.021 PMID: 22079552
57. Norsham Y, Shariff F, Norhayati A, Nordin M, Lim BL. Pre-logging survey of mammal fauna at Sungai Weng sub-catchment, Ulu Muda Forest Reserve Forest Reserve, Kedah. Journal of Wildlife and Parks. 1999; 17: 28 - 43.
68. Shahfiz MA, Shahrul-Anuar MA, Nor-Zalipah M, Kaviarasu M, Pan KA, Yusof MO, et al. Surveys of bats at selected sites in Melaka Forest Reserves, Peninsular Malaysia. In: Rahman A, Koh HL, Muhamad A, Yusof WKW, Latiff A, editors. Proceedings for Forestry Department of Peninsular Malaysia, 1 - 2 April 2009 2008. Department of Wildlife and National Parks, Malaysia; 2009. pp. 265 - 270.
69. Syaripuddin K, Kumar A, Sing KW, Halim MR, Nursyereen MN, Wilson JJ. Mercury accumulation in bats near hydroelectric reservoirs in Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicology. 2014; 23 (7): 1164 - 1171. https: // doi. org / 10.1007 / s 10646 - 014 - 1258 - y PMID: 24840106
18. Thabah A, Rossiter SJ, Kingston T, Zhang S, Parsons S, Mya KM, Akbar Z, Jones G. Genetic divergence and echolocation call frequency in cryptic species of Hipposideros larvatus sl (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) from the Indo-Malayan region. Biol J Linn Soc Lond. 2006; 88 (1): 119 - 130.
44. Tingga RCT, Khan FA, Ridwan AM, Senawi J, Abdullah MT. Small Mammals from Kuala Atok, Taman Negara Pahang, Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2012; 41 (6): 659 - 669.
15. Wilson JJ, Sing KW, Halim MR, Ramli R, Hashim R, Sofian-Azirun M. Utility of DNA barcoding for rapid and accurate assessment of bat diversity in Malaysia in the absence of formally described species. Genet Mol Res 2014; 13 (1): 920 - 5. https: // doi. org / 10.4238 / 2014. February. 19.2 PMID: 24634112
97. Yeap CA. A brief survey of Microchiropterans at Bukit Dendong and Bukit Keluang, Tembila, Terengganu Darul Iman. Mal Nat J. 2003; 56 (4): 397 - 401.
Fig 4. Neighbour-joining tree showing all available DNA barcodes for species in family Hipposideridae reported from Peninsular Malaysia. The percentage of pseudoreplicate trees (±70%) in which the DNA barcodes clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 pseudoreplicates) are shown above the branches. Abbreviation as follows: PM = Peninsular Malaysia,VN = Vietnam, BN = Borneo (including Sabah & Sarawak of East Malaysia, Brunei and Kalimantan Indonesia), TH = Thailand, LA = Laos, SM = Sumatera Indonesia, CH = China, CM = Cambodia. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179555.g004
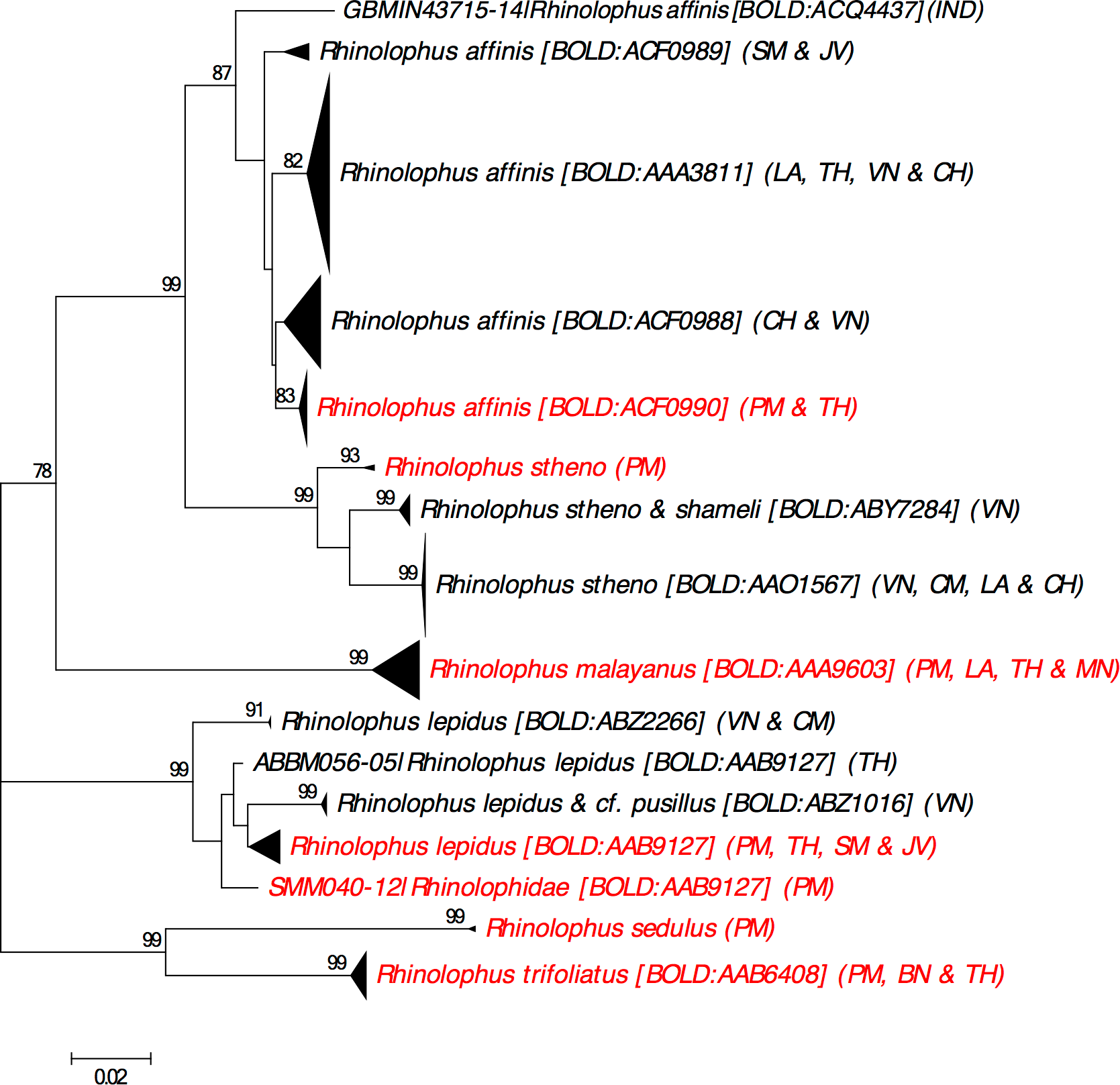
Fig 5. Neighbour-joining tree showing all available DNA barcodes for species in family Rhinolophidae reported from Peninsular Malaysia. The percentage of pseudoreplicate trees (±70%) in which the DNA barcodes clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 pseudoreplicates) are shown above the branches. Abbreviation as follows: PM = Peninsular Malaysia,VN = Vietnam, BN = Borneo (including Sabah & Sarawak of East Malaysia, Brunei and Kalimantan Indonesia), TH = Thailand, LA = Laos, SM = Sumatera Indonesia, JV = Java Indonesia, IND = India, CH = China, CM = Cambodia,MN = Myanmar. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179555.g005
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hipposideros larvatus
| Voon-Ching Lim, Rosli Ramli, Subha Bhassu & John-James Wilson 2017 |
Rhinolophus larvatus
| Horsfield 1823: 6 |
1 (by tatiana, 2020-11-06 15:23:09)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2020-11-06 15:29:08)
3 (by ExternalLinkService, 2020-11-06 15:42:12)
4 (by tatiana, 2020-11-06 16:10:10)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2020-12-17 22:57:40)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-01-29 17:49:13)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-11-11 05:07:18)
8 (by plazi, 2023-10-31 23:00:56)