Peromyscus madrensis, Merriam, 1898
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6707142 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6726356 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F06D13-FFC1-2008-08B0-11400063F50F |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Peromyscus madrensis |
| status |
|
287. View Plate 18: Cricetidae
Tres Marias Deermouse
Peromyscus madrensis View in CoL
French: Péromyscus des Marias / German: Tres-Marias-Hirschmaus / Spanish: Raton ciervo de Tres Marias
Other common names: Tres Marias Island Mouse
Taxonomy. Peromyscus madrensis Merriam, 1898 View in CoL , Maria Madre Island, Tres Marias Islands, Nayarit, Mexico.
Peromyscus madrensis is in the boyliu species group. It was originally described as a distinct species and then considered a subspecies of P. boylii . Chromosomal and DNA sequences data support treatment as a species. Monotypic.
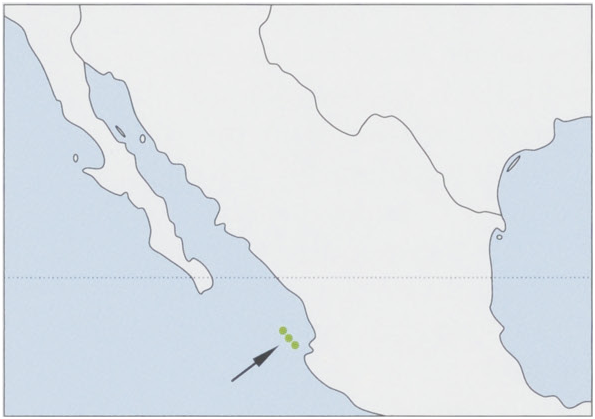
Distribution. Tres Marias Is (Maria Madre, Maria Cleofas, and San Juanito), off the coast of Nayarit, Mexico. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 104-120 mm, tail 99-130 mm, ear 17-20 mm, hindfoot 23-28 mm. No specific data are available for body weight. The Tres Marias Deermouse is medium-sized, with light tan to ocher dorsum and indistinct darker band posteriorly. Venter is white, with salmon spot in pectoral region. Feet are white. Tail is as long as head-body length and indistinctly bicolored (darker above and lighter below), except distal one-third is entirely dark. It is morphologically similar to other species in the boylii species group, and genetic data are often required for accurate identification.
Habitat. Tropical deciduous forests, thorn forests, and xeric scrublands from sea level to elevations of ¢.600 m. The Tres Marias Deermouse lives in hollows offallen logs, tree roots, and rocks and can found along streams with rocky substrates.
Food and Feeding. The Tres Marias Deermouse probably eats seeds, plant materials, and insects.
Breeding. Juvenile, scrotal, pregnant, and lactating Tres Marias Deermice have been captured in March.
Activity patterns. The Tres Marias Deermouse is presumably nocturnal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Endangered on The IUCN Red List. No individuals have been seen recently on Maria Magdalena Island, so it may have disappeared there.
Bibliography. Alvarez-Castaneda & Méndez (2005), Carleton (1977), Carleton et al. (1982), Merriam (1898), Osgood (1909), Tiemann-Boege et al. (2000), Wilson (1991, 2014).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Myomorpha |
|
SuperFamily |
Muroidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Peromyscus madrensis
| Don E. Wilson, Russell A. Mittermeier & Thomas E. Lacher, Jr 2017 |
Peromyscus madrensis
| Merriam 1898 |