Alexandromys limnophilus (Büchner, 1889)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6707142 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6706985 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F06D13-FF9A-2052-0848-13E60B0AFC36 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Alexandromys limnophilus |
| status |
|
120. View On
Lacustrine Vole
Alexandromys limnophilus View in CoL
French: Campagnol lacustre / German: Seewiihlmaus / Spanish: Topillo lacustre
Taxonomy. Microtus limnophilus Buchner, 1889 View in CoL , Syrtyn, Qaidam, Qinghai, China.
In the past, A. limnophilus was considered subspecies of A. oeconomus or separate species closely related to A. oeconomus and placed in subgenus Pallasiinus . Recent genetic and morphometric studies demonstrated phylogenetic and taxonomic position of limnophilus in subgenus Alexandromys , but allocation into species group remains ambiguous. Nominate subspecies limnophilus is morphologically close to A. mongolicus , but subspecies malygini is similar to maximowiczii species group, although it genetically clusters to fortis species group. Significant morphological and chromosomal differences between subspecies limnophilus and malygini probably indicate that they are separate species. Some authors distinguished two separate subspecies of limnophilus in China ( limnophilus and flaviventris), but recent studies demonstrated absence of real differences between them. Two subspecies recognized.
Subspecies and Distribution.
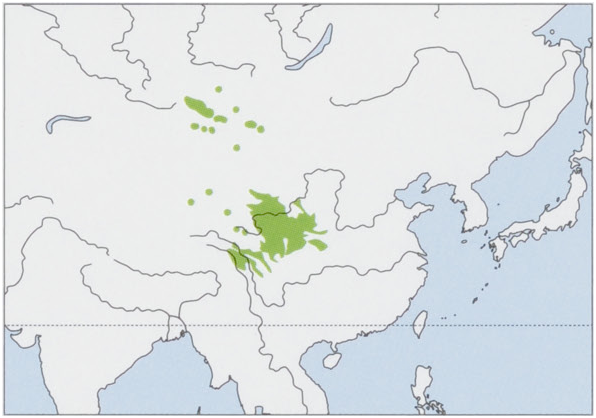
A. l. malygini Courant et al., 1999 — W Mongolia. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 88-120 mm, tail 29-49 mm, ear 9-16 mm, hindfoot 14-21 mm; weight 35-54 g. Fur color of head and upperparts of the Lacustrine Vole varies from light yellowish pale buff to reddish brown, underparts vary from whitish with yellowish pale tinge to pale yellowish brown, and tail is distinctly bicolored. Sole of foot hasfive plantar pads. Chromosomal complementis 2n = 38 and FN = 58 for the nominate limnophilus and 2n = 38 and FN = 60 for malygini.
Habitat. Desert, semi-desert, mountain steppe, and mountain forest zones. In desert and semi-desert zones, the Lacustrine Vole occupies wet meadows and salt marshes along lakeshores and around springs. In mountains, it is found in wet meadows with shrubs along riverbanks and lakeshores, on dry grasslands, and in scrublands and shrublands.
Food and Feeding. In summer, the Lacustrine Vole eats green plant parts. In mountain grasslands of Qinghai,it prefers Elymus nutans (Poaceae) .
Breeding. Breeding of wild Lacustrine Voles was recorded in April-October. Litters have 4-8 young. Juveniles reach sexual maturity at 70 days of age. Individuals born in spring normally start breeding in the year of birth.
Activity patterns. No information.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. During reproduction season, mean home range is 3385 m? for males and 958 m” for females; at the end of reproduction, home ranges expand to 1600 m? for females but shrink to 1077 m® for males. During reproduction, home ranges of females are isolated or marginally overlap, but home ranges of males widely overlap with those of females and other males. Size of home ranges significantly decreases with increases in density. Level of aggression among males is high at low densities but significantly decreases as densities increases. Acoustic communication is expressed with quiet (only in females) and sharp squeals and songs (males at contacts with females).
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List (as Microtus limnophilus ).
Bibliography. Allen (1940), Bannikov (1954), Bannikova et al. (2010), Bian Jianghui et al. (2015), Courant et al. (1999), Giraudoux et al. (1998), Lissovsky & Obolenskaya (2011), Nie Haiyan & Liu Jike (2005), Rutovskaya (2015), Sun Ruyong et al. (1982), Zhang Yongzu et al. (1997).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Alexandromys limnophilus
| Don E. Wilson, Russell A. Mittermeier & Thomas E. Lacher, Jr 2017 |
Microtus limnophilus
| Buchner 1889 |