Rheomys thomasi, Dickey, 1928
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6707142 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6726754 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F06D13-FF2F-20E6-0DA1-12FF0980F3D0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Rheomys thomasi |
| status |
|
350. View Plate 19: Cricetidae
Thomas's Water Mouse
French: Ichthyomys de Thomas / German: Thomas-\ Wassermaus / Spanish: Ratén de agua de Thomas
Other common names: Thomas’ Ichthyomyine
Taxonomy. Rheomys thomasi Dickey, 1928 View in CoL , Cerro Cacahuatique (= Cacaguatique), 3500 ft (= 1067 m), Finca San Felipe, San Miguel, El Salvador.
Subspecies chiapensis considered synonymous with stirtoni . Two subspecies recognized.
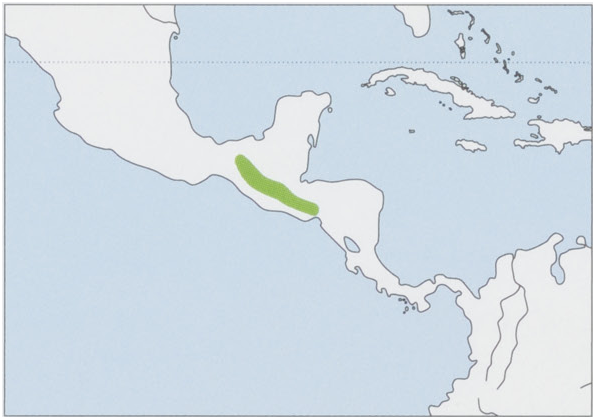
Subspecies and Distribution.
R.t.thomasiDickey,1928—EElSalvador.
R. t. stirtoni Dickey, 1928 — highlands of SW Mexico, Guatemala, and W El Salvador; it may occur in Honduras. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 102-136 mm, tail 109-140 mm, ear 8-12 mm, hindfoot 30-35 mm. No specific data are available for body weight. Thomas’s Water Mouse is reportedly similar to the Mexican Water Mouse ( R. mexicanus ) but smaller. Dorsum is dark brown; venter is grayish; and tail is bicolored, dark above and paler below. Thomas’s Water Mouse differs from Goldman’s Water Mouse ( R. raptor ) by having longer and broader hindfeet;tail that averages longer than head—body length (less in Goldman’s Water Mouse); thicker, more coarsely grizzled dorsal pelage; and venter more abundantly washed with silver-tipped hair.
Habitat. Along streams in most forest types, including second growth.
Food and Feeding. Thomas’s Water Mice eat insects (terrestrial and aquatic larvae), snails, crabs, birds, salamanders, mammals, and parts of catfish.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. Thomas’s Water Mouse is semi-aquatic.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Near Threatened on The IUCN Red List. Thomas’s Water Mouse probably occurs in not much more than 20,000 km? and extent and quality of its habitat are declining.
Bibliography. Ceballos (2014d), Dickey (1928b), Hooper (1947), Reid, Vazquez, Emmons & Cuarén (2008), Stirton (1944), Voss (1988).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.