Thomsonia Signoret, 1879
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4679.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CAFEA77F-1A4B-49D0-91DB-E55BE443B28C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3797779 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CC87C7-0576-4863-418D-FE89FDC81AFD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thomsonia Signoret |
| status |
|
Genus Thomsonia Signoret View in CoL
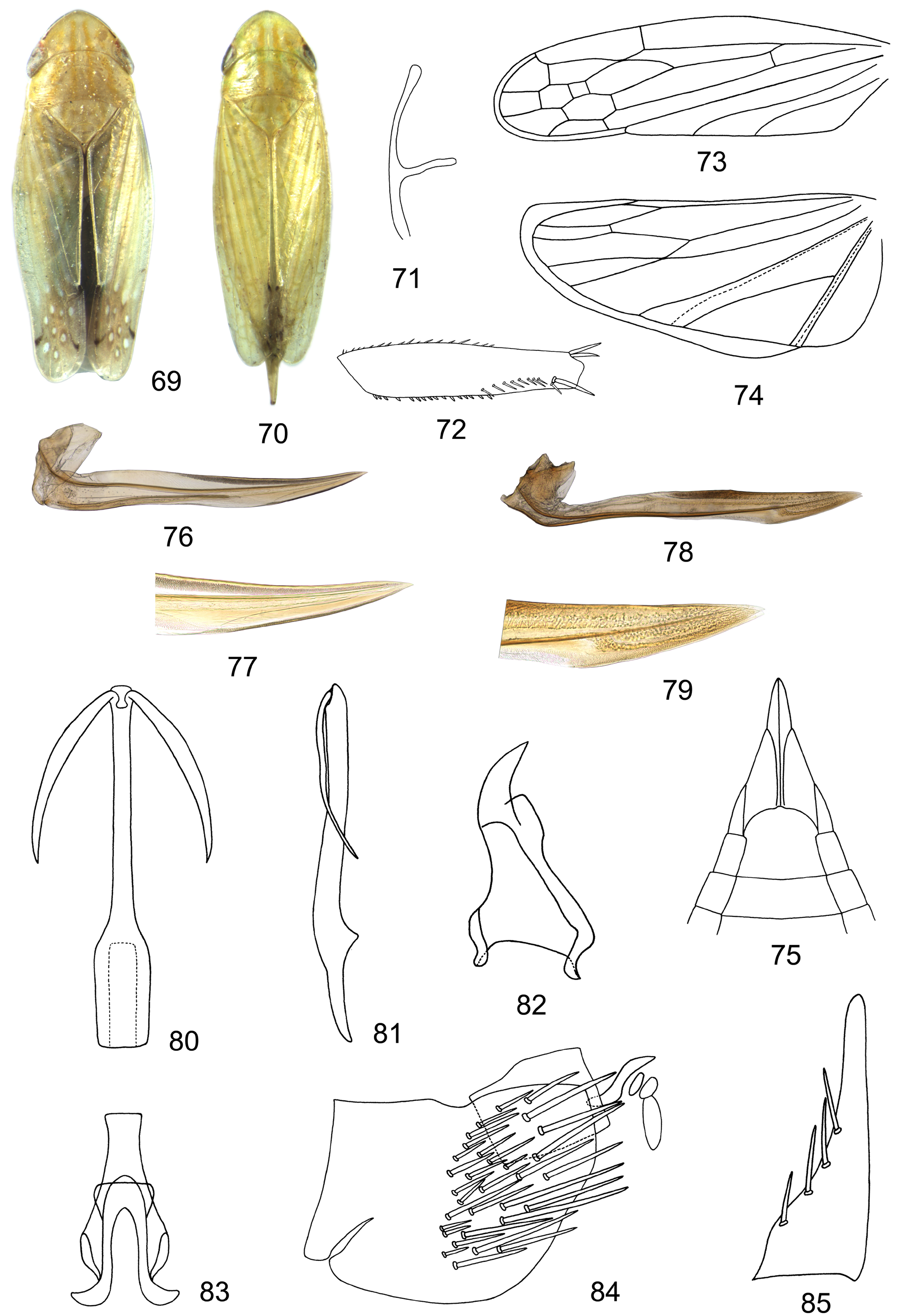
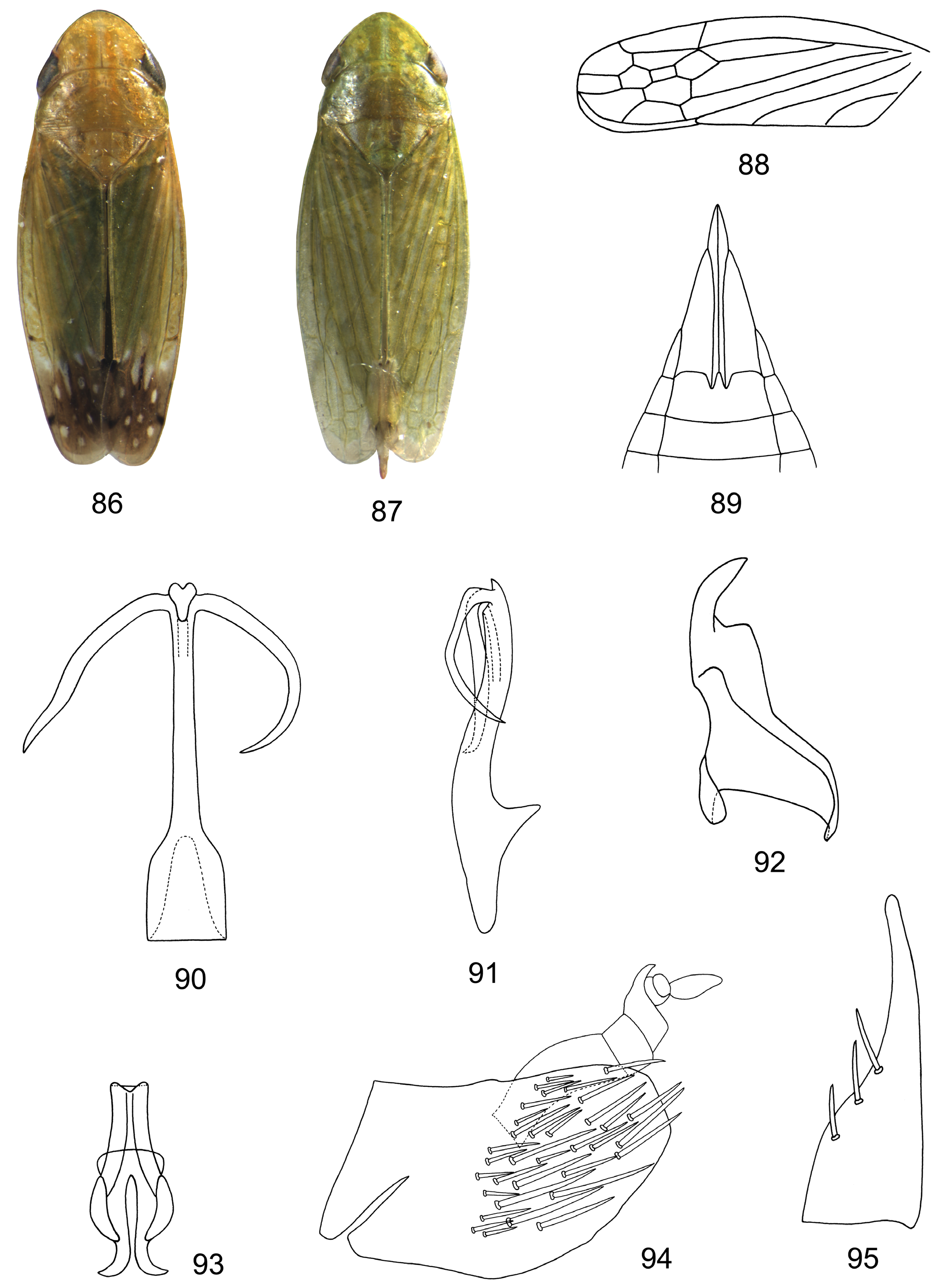
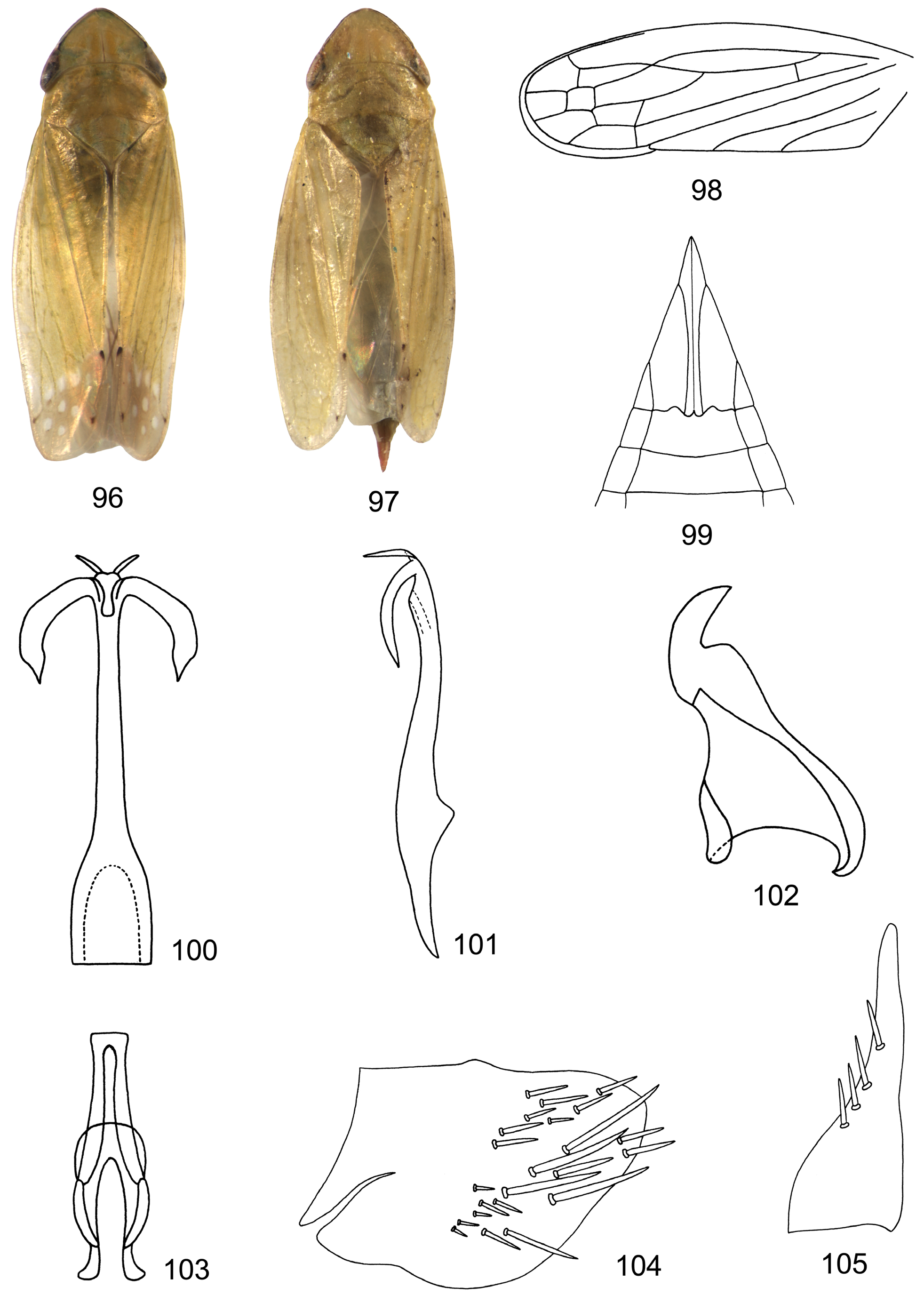
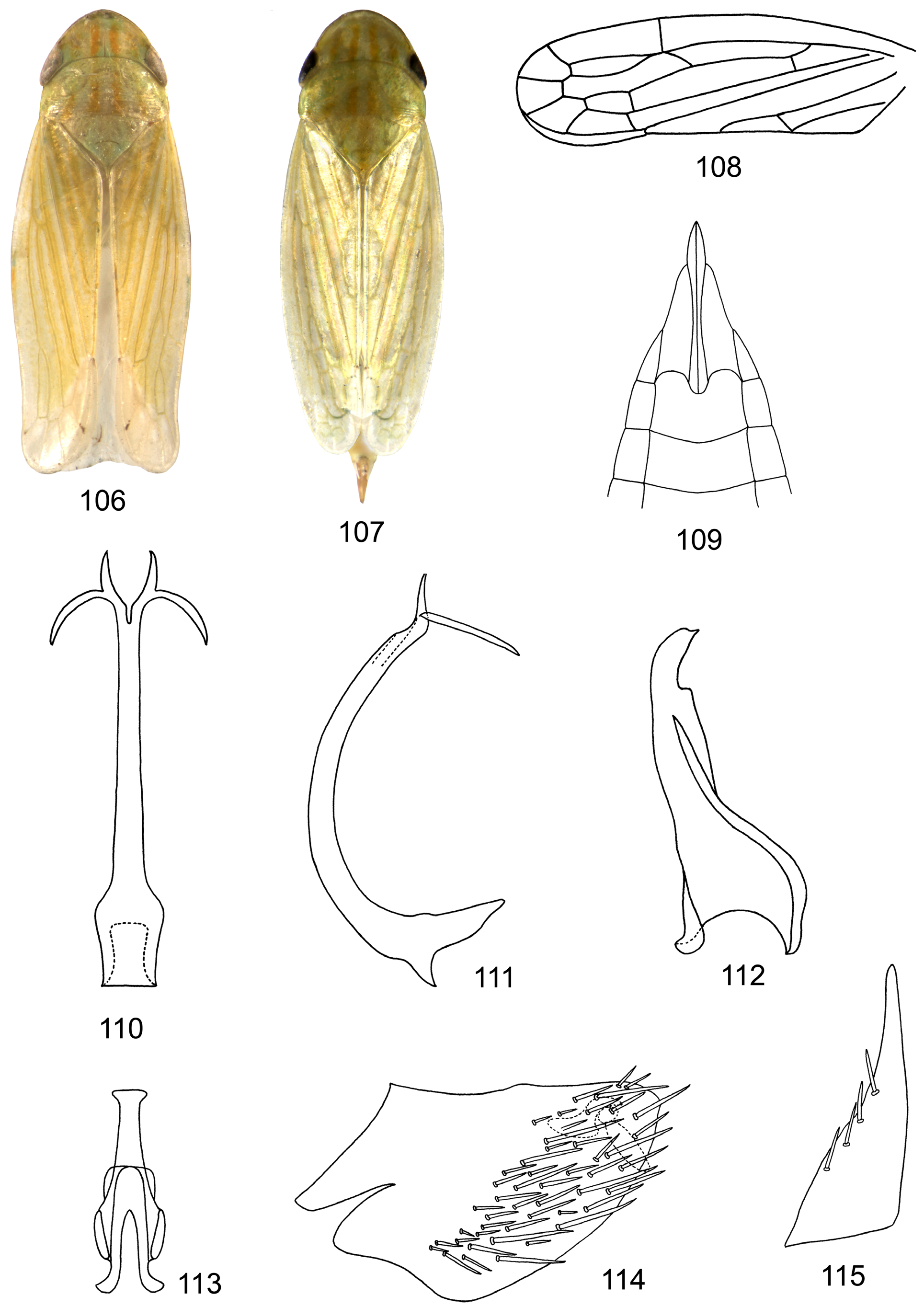
( Figs 69–115 View FIGURES 69–85 View FIGURES 86–95 View FIGURES 96–105 View FIGURES 106–115 )
Type species: Hecalus kirschbaumii Stal 1870 c: 737 View in CoL
Description. Colour. Green or yellow-green, vertex margin anteriorly with transverse submarginal dorsal and ventral fuscous lines respectively. Body with orange or yellow 4, 6 and 3 longitudinal lines on vertex, pronotum and scutellum respectively. Forewing with apical 1/3 light brown, with faint white spots in apical and anteapical cell in male, somewhat faint; 3 tiny dark spots at tip of clavus, M3+4, and R 2+3, usually faint or absent in female.
Body. 5.0– 7.5 mm in length. Stout. Vertex upturned anteriorly. Anterior tentorium ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 69–85 ) slender, furcate. Ocelli close to corresponding eyes. Pronotum as wide as or slightly wider than head. Profemur ( Fig. 72 View FIGURES 69–85 ) with 22 AV (anteroventral) setae and two apical dorsal setae; intercalary row with 9 setae; AM1 setae (anteromedian) present. Hind tibia compressed; first tarsomere with 6 teeth in two rows on plantar surface, 4 platellae and 2 terminal lateral spines at apex; second tarsomere with 4 teeth, 2 platellae and 2 terminal lateral spines; hind femoral setal formula 2-2-1. Forewing without reflexed vein from outer margin of outer anteapical cell in costal area; m-cu 2 present; claval vein A1 complete and separate from claval suture, A2 complete; appendix narrow and long, extending to or beyond end of M 1+2.
Male genitalia: Valve visible, broadly triangular, laterally articulated with pygofer. Subgenital plate subtriangular, usually with 4–6 setae laterally, tapering apically. Pygofer side usually without obvious ventral lobe and rounded or truncated posteriorly, heavily setose in posterior half. Style subtriangular, dorsoventrally flattened. Connective Y-shaped. Aedeagus with one or 2 pairs of terminal processes; aedeagal shaft rounded, smooth, S-shaped, without ridge or cleft; gonopore subapical in groove; dorsal apodeme usually reduced.
Female genitalia: Ovipositor extending beyond pygofer, first valvulae ( Fig. 76 View FIGURES 69–85 ) sword-shaped, tapering apically; sculpturing pattern on first valvula granulose, submarginal; first valvula with distinctly delimited ventroapical sculptured area; second valvulae ( Fig. 78 View FIGURES 69–85 ) slender, expanded ventrally at 1/3 apically, dorsally fused from base to apical 1/3; second valvulae ( Figs 77, 79 View FIGURES 69–85 ) without dorsal teeth. Seventh sternum with or without medial projection and notch.
Distribution. Afrotropical, Australian, Oceanian, and Oriental regions.
Remarks. This genus is similar to Hecalus in adult size, but can be easily distinguished from the latter by the unique dorsal colour pattern, distinctive anteriorly upturned vertex, m-cu 2 present, and smoothly rounded aedeagal shaft.
There are five species in China.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Deltocephalinae |
|
Tribe |
Hecalini |
|
SubTribe |
Hecalina |