Xenasmatella roseobubalina Z.B. Liu & Yuan Yuan, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.556.2.8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6974989 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CAFF2D-0557-FF96-EBB3-F96FB13FFE49 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Xenasmatella roseobubalina Z.B. Liu & Yuan Yuan |
| status |
sp. nov. |
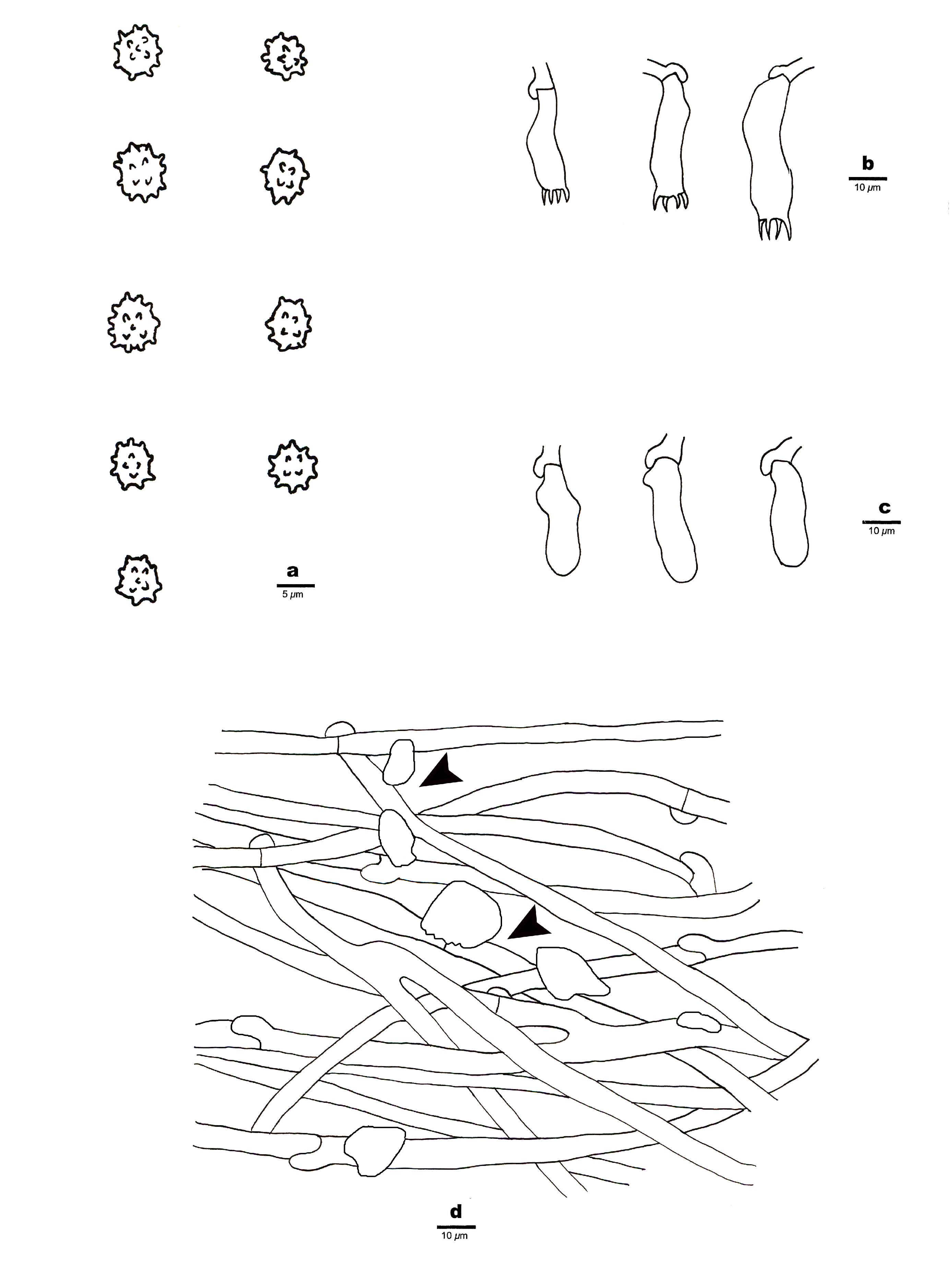
Xenasmatella roseobubalina Z.B. Liu & Yuan Yuan , sp. nov. ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
MycoBank no.—MB 843185
Etymology:—‘ roseobubalina ’ (Lat.): refers to the species having a pinkish buff hymenophore.
Type:— CHINA. Yunnan Province, Mengla County, Yulingu , on rotten bamboo, 18 August 2019, Y.C. Dai, Dai 20506 (Holotype, BJFC 032174 View Materials , isotype in SWFC) .
Description:—Basidiomata annual, resupinate, adnate, detachable, membranaceous, without odor or taste when fresh, brittle when dry, up to 6.5 cm long, 2.5 cm wide and less than 0.1 mm thick. Hymenial surface smooth, pinkish buff (5A3), uncracked when fresh and dry, and with some scattered crevices upon drying. Sterile margin distinct, fimbriate and white; subiculum not found.
Hyphal structure:—Hyphal system monomitic; clamped, hyaline, thin-walled generative hyphae in subhymenium, frequently branched, 2–8 µm in diameter, IKI–, CB–. Abundant crystalline matter present among hyphae. Tissues unchanged in KOH.
Hymenium:—Cystidia and cystidioles absent; basidia pleural or clavate, with 4 sterigmata and a basal clamp connection, 20–26 × 5–8 µm; basidioles in shape similar to basidia, but shorter than basidia.
Basidiospores:—Broadly ellipsoid to subglobose, hyaline, thin-walled, warted, IKI–, CB–, (3.5–)3.8–5(–6) × 3.3–4(–5) µm, L = 4.43 µm, W = 3.9 µm, Q = 1.14 (n = 60/1).
| SWFC |
Southwest Forestry College |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.