Imperata cylindrica var. major, (Nees) C. E. Hubb. (Nees) C. E. Hubb.
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.113076 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8257115 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B287E8-FF9D-FFA3-FFEA-FAA4FBEBF9C0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Imperata cylindrica var. major |
| status |
|
2.2. Anti-inflammatory activity screening and structure-activity relationships analysis of compounds from I. cylindrica var. major View in CoL
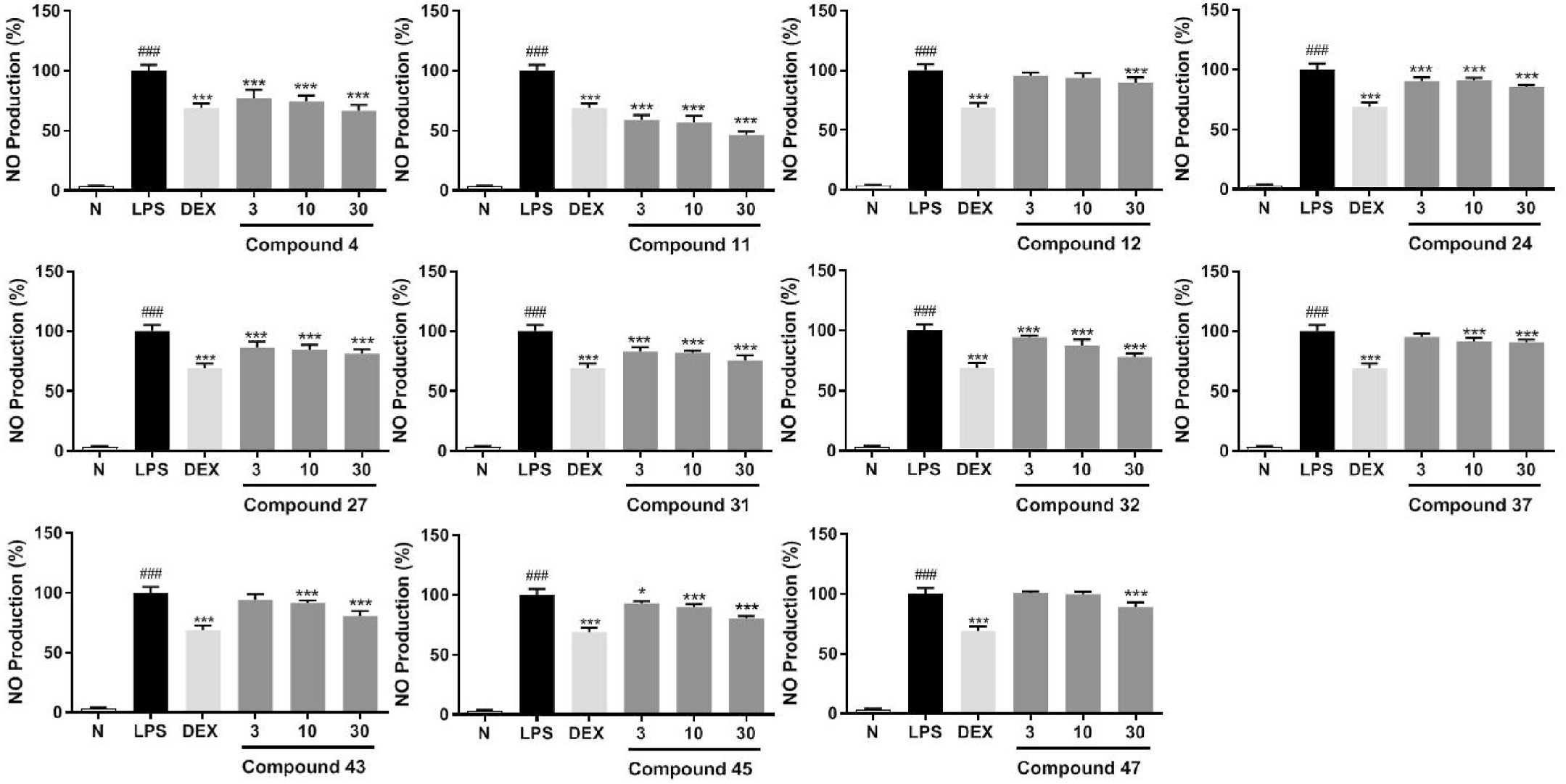
The effects of compounds 1–47 on lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated nitric oxide (NO) release in RAW264.7 cells were measured through the Griess reaction at the concentration without significant cytotoxicity (Fig. S70) to clarify their potentical anti-inflammatory effects ( Chen et al., 2020). As results, 4, 11, 12, 24, 27, 31, 32, 37, 43, 45, 47 exhibited significant inhibitory effects on the releasement of NO at 30 μ M ( Table 5 View Table 5 ).
Furthermore, we summarized the structure-activity relationship of the isolated compounds. The result showed that the increase of phenolic hydroxyl groups in phenylpropanoids might strength the NO release inhibitory activity (relative NO content: 31, 32 < 30). In addition, the similar NO inhibitory activities of 31 and 33 indicated that the carboxyl group in the caffeic acid structure was not an important factor in their NO inhibitory activity. On the other hand, when the phenolic hydroxyl in phenolic glycosides was replaced by methoxy, the activity would decrease (relative content of NO: 12 < 15; 24 < 25), while the activity would be increased by m -dimethoxy substitution (relative content of NO: 27 < 25).
Further study showed that compounds 4, 11, 12, 24, 27, 31, 32, 37, 43, 45, as well as 47 inhibited NO release from RAW 264.7 in a concentration dependent manner at 3, 10, and 30 μ M ( Fig. 8 View Fig ).
2.3. Compounds from I. cylindrica var. major View in CoL exerted anti-inflammatory effects through NF-κB signaling pathway
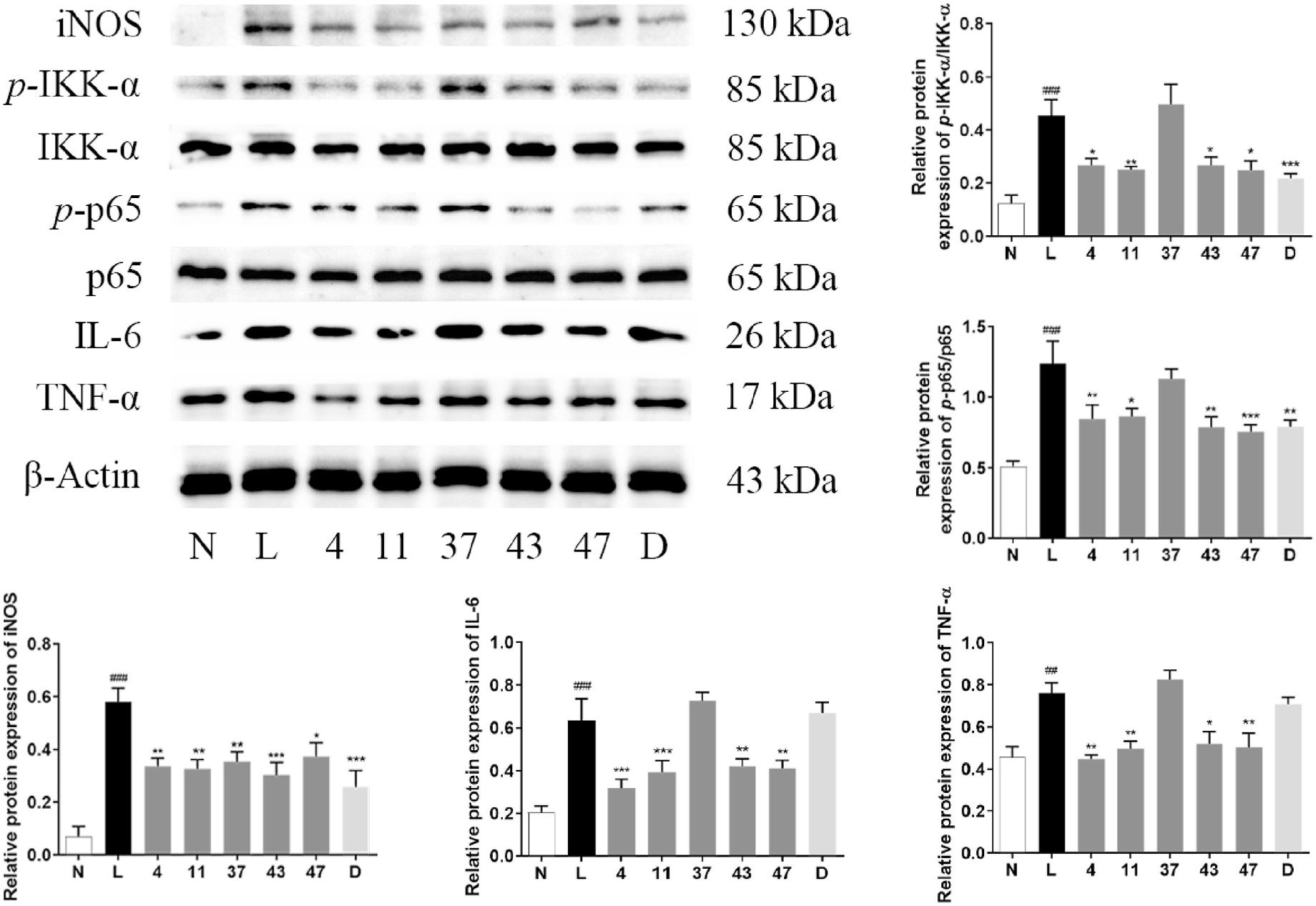
Nuclear factor kappa-B (NF- κ B) pathway plays an important role on inflammation. In general, the activity of NF- κ B was inhibited by inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B (I κ B) α, β or ε ( Law et al., 2010). The inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase (IKK) complex may trigger the phosphorylation of I κ B α, then the NF- κ B dimer are liberated, which may lead NF- κ B translocating to the nucleus. Then, cytokines or mediators, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor- α (TNF- α) associated with inflammation will be released ( Hoffmann et al., 2006; Ruan et al., 2021).
In order to clarify the in vitro anti-inflammatory mechanism of the bioactive compounds obtained from I. cylindrica var. major , western blot assays towards phenylpropanoids 4 and 37, phenol 11, flavone 43 and flavonoid-phenylpropane dimer 47 were conducted according to the method reported previously ( Ruan et al., 2021). As results, the inflammatory cytokines, iNOS, IL-6 and TNF- α were decreased in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells by the treatment of 4, 11, 43, and 47, and the concentrations of p -NF- κ B/p65, as well as p -IKK were down-regulated. The results indicated that 4, 11, 43, and 47 exhibit anti-inflammatory activities, at least in part, by suppressing the expression of inflammatory factors through NF- κ B signaling pathway. While compound 37 only possessed moderate down-regulatory effects on iNOS, and didn’ t show obviously inhibitory activities on the protein expression of IL-6, TNF- α, p -NF- κ B/p65 and p -IKK, which might be closely related to its poor NO inhibitory activity ( Fig. 9 View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |