Epomophorus grandis (Sanborn, 1950)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6448815 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6448969 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AD87FA-FFEE-F600-8CB6-3515FA57F817 |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Epomophorus grandis |
| status |
|
70. View Plate 4: Pteropodidae
Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Bat
Epomophorus grandis View in CoL
French: Epomophore de Sanborn / German: Sanborn-Epaulettenflughund / Spanish: Epomdforo de Sanborn
Taxonomy. Micropteropus grandis Sanborn, 1950 ,
Dundo, LLunda, Angola.
Epomophorus grandis is the only member of the grandis species group. W. Bergmans in 1988 transferred it from Mucropteropus to Epomophorus . It is known from only three adults and one young. Monotypic.
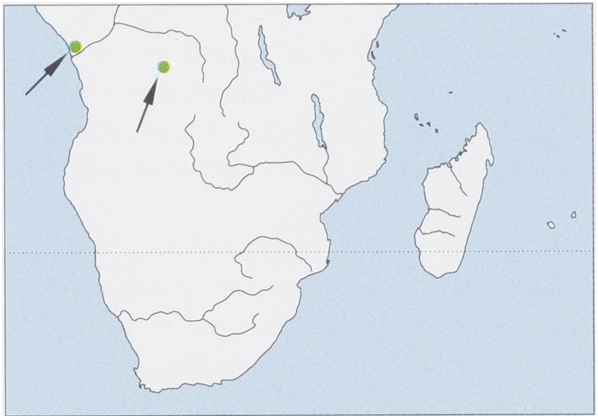
Distribution. Only known from type locality in NE Angola and Pointe Noire on the coast of the Republic of Congo. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 99 mm (single male), tail 4 mm (single male) and 8 mm (single female), ear 17-18 mm (males) and 16 mm (single female), hindfoot 18 mm (males) and 19- 6 mm (single female), forearm 62-63 mm (males) and 66 mm (single female). Head is pale brown, and muzzle is rather long but short and broad for the genus. Eyes are large; ears are relatively short, slightly pointed, and naked, with brown pigmentation and anterior and posterior light ear patches. Adult males have white epaulettes. Dorsum is pale reddish brown; hairs are unicolored to slightly dark brown at bases; and pelage is dense. Venter is very light brown to whitish brown, pelage is sparser than on dorsum, and throat is nearly naked. Wings have claw on second digits, and membranes are light brown and attach to second toes. Rostrum is relatively short and broad, zygomatic width is relatively large, and post-dental palate is weakly concave. There are six palatal ridges, first is large hastate and fifth is thick; only last ridge is post-dental;fifth is level with posterior molars; and ridges 2-6 are divided by medial gap (2-4 not divided in juveniles).
Habitat. Southern Rainforest-Savanna Mosaic, just south of Rainforest biotic zone. Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Bat might be a woodland species and also found in woodland savanna habitats. Holotype was collected in an area with Borassus (Arecaceae) palms and lower shrubs behind a beach at sea level.
Food and Feeding. Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Batis frugivorous and nectarivorous.
Breeding. Holotype of Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Bat was captured in September and was carrying a young, suggesting that births take place just before start of wet seasons.
Activity patterns. Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Bat is nocturnal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Data Deficient on The IUCN Red List. There is an absence of recent information on Sanborn’s Epauletted Fruit Bat. Deforestation in parts ofits distribution might pose a threat, but it is unknown how it adapts to habitat change. It is not known to occur in any protected area.
Bibliography. Bergmans (1988), Fahr & Mildenstein (2016), Happold, M. (2013d), Monadjem, Taylor et al. (2010).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Epomophorus grandis
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Micropteropus grandis
| Sanborn 1950 |