Aethalops alecto, Thomas, 1923
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6448815 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6448865 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AD87FA-FFD4-F63A-89B0-3DE4F75CFA66 |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Aethalops alecto |
| status |
|
22. View Plate 2: Pteropodidae
Common Pygmy Fruit Bat
French: Cynoptére pygmée / German: Gewohnlicher Zwergflughund / Spanish: Aethalops pigmeo
Other common names: Pygmy Fruit Bat
Taxonomy. Aethalodes alecto Thomas, 1923 View in CoL ,
“Indrapura Peak, Sumatra [ Indonesia]. Alt. 7300" [= 2225 m].”
Three subspecies are recognized.
Subspecies and Distribution.
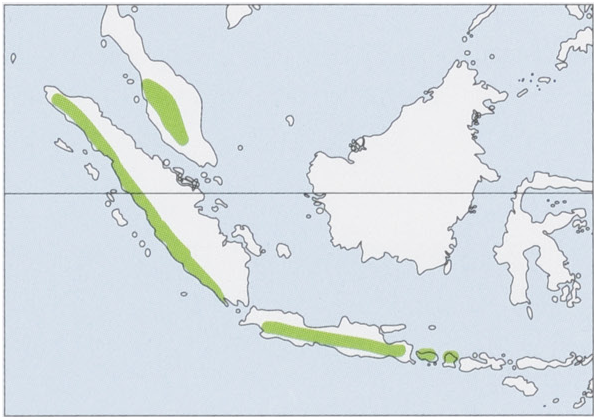
A.a.alectoThomas,1923—WPeninsularMalaysiaandWSumatra.
A.a.boeadntKitcheneretal,1993—BaliandLombokIs.
A. a. ocypete Boeadi & Hill, 1986 — Java. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 63-75 mm (tailless), ear 9-15 mm, hindfoot 9-14 mm, forearm 43-48 mm; weight 17-22- 5 g. Head of the Common Pygmy Fruit Bat has moderately elongated muzzle and is naked with blackish skin; nostrils are shortly tubular and divergent; philtrum is divided into two parallel grooves; and lower lip pads are triangular. Eyes are moderately large; iris is blackish brown. Ears are short, rounded, and black, and medial rim is slightly paler than pinna. Head pelage is short, soft, and dark grayish brown; nape and dorsum are densely haired, dark grayish brown, and woolly. Reduced uropatagium and tibia are thickly furred, and calcar is minute. Throat is thinly haired;sides of neck are glandular and inconspicuously yellowish brown; and chest and belly are mouse-gray. Wing membranes are black from sides of body and attach between first and second toes. Skull lacks basicranial deflection; rostrum is pointed, sloping to forehead; orbit is large; zygomatic root is only slightly above alveolar line; zygoma is very thin and arched posteriorly; and braincase is globose. Dorsally, rostrum is tapering; paranasal recesses are inflated; postorbital process is blunt; no postorbital foramina, almost no postorbital constriction; skull is rounded; and temporal lines and nuchal crest are inconspicuous. Ventrally, palate is flat and rather narrow; post-dental palate is long; palatine spine is inconspicuous and joined to sphenoidal crest; and ectotympanic is small and wide anteriorly, edged internally by ribbon-like entotympanic. Mandible is thin and straight; coronoid is long, low, and sloping; condyle is level with lower alveolar line; and angle is salient ventrally and slightly pointed posteriorly. I*is long and bent medially; I' is conspicuously shorter, thinner, and straight; C' is small, weak, and slightly decurved; P' is minute; next premolar (P?) is large and laterally triangular; and last cheekteeth decrease in height and have rectangular outlines. I, is very small and bifid with inner side longer; 1, is absent; C,is very small and low; P| is conspicuously pointed; next premolar (P,) is very large, triangular, and as high as C; and posterior cheekteeth are low and small.
Habitat. Generally montane rainforests but also Lesser Sundas deciduous forests (Lombok Island) at elevations of 1000-2700 m.
Food and Feeding. The Common Pygmy Fruit Bat is primarily frugivorous, but morphology (e.g. relatively long snout and small canines) suggests some use of flower products.
Breeding. Pregnant Common Pygmy Fruit Bats were recorded in February—June in Peninsular Malaysia.
Activity patterns. No information.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. The Common Pygmy Fruit Bat roosts alone or in small groups of 2-3 individuals, and it appears to move solitarily.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red Lust.
Bibliography. Boeadi & Hill (1986), Giannini & Simmons (2007a), Kitchener, Hisheh et al. (1993), Kumaran, Tingga & Struebig (2016), Medway (1978), Olson et al. (2001), Thomas (1923).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Aethalops alecto
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Aethalodes alecto
| Thomas 1923 |