Caligus lini, Ho, Ju-Shey & Cheng, Yu-Rong, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4079.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:38F69743-EA63-4F24-B897-F495C745AD69 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6075377 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AD7518-8407-3F6B-DED3-E48E5C3DFD6D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Caligus lini |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Caligus lini n. sp.
( Figs 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Type material. Four adult ♀♀ obtained from gill rakers (1 individual) and caudal fin (3 individuals) of 42 brilliant pomfret, Eumegistus illustris Jordan & Jordan 1922, landed at Cheng-Gong Fishing Port in Tai-Dong County between September 2014 and August 2015. Holotype ♀ (ASIZCR000329) deposited in the Biodiversity Research Museum, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan, and 3 ♀♀ paratypes ( NTUIO –COPEPOD s002) deposited in the Institute of Oceanography, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
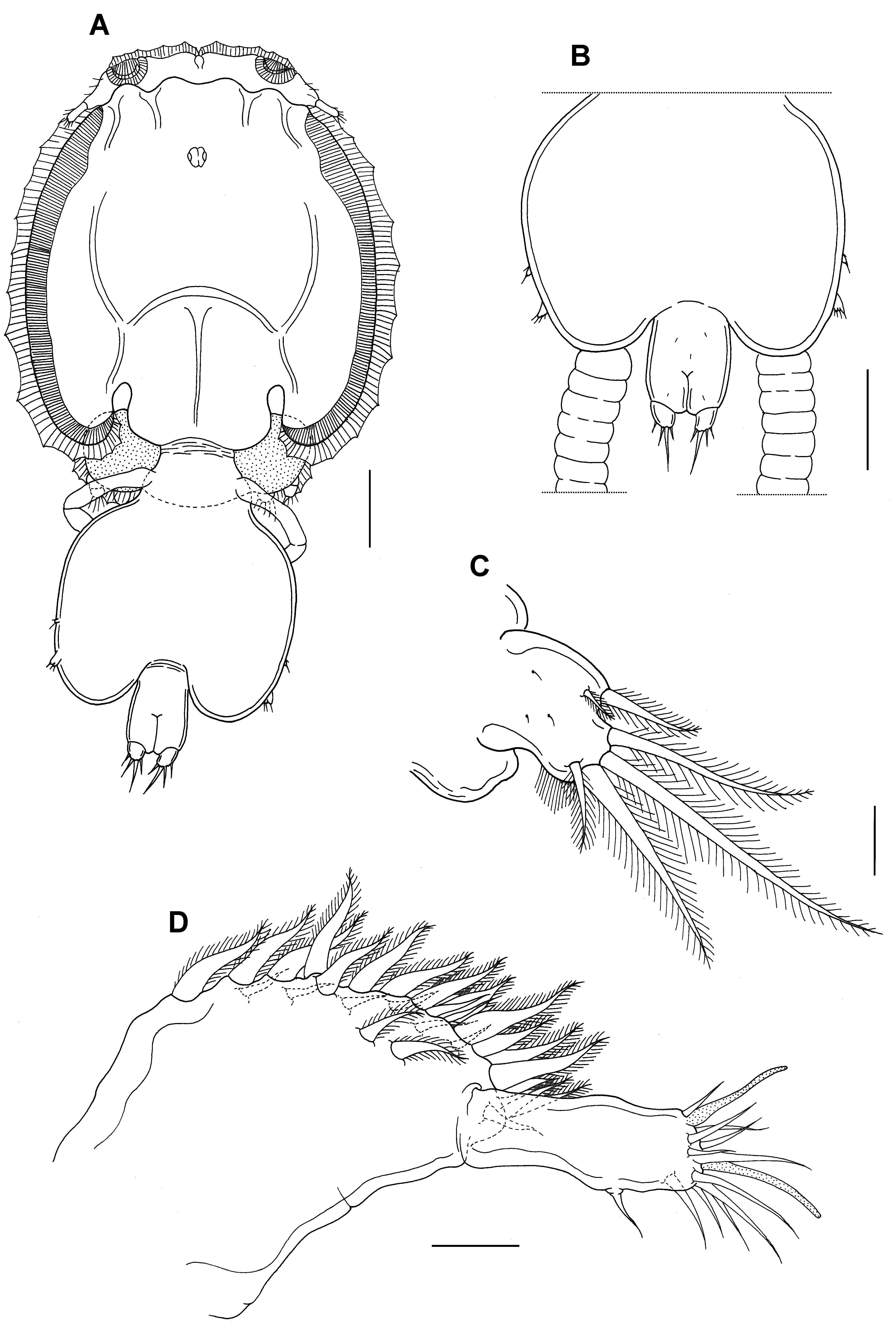
Description. Body ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) 4.78 (4.70–4.82) mm long, excluding setae on caudal ramus. Cephalothoracic shield subcircular, 3.67 mm long and 2.28 mm wide, excluding lateral, hyaline membrane. Fourth pediger distinctly wider than long, 0.79 (0.77–0.81) × 0.38 (0.37–0.40) mm. Genital complex ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) subquadrate, 1.50 (1.46–1.52) × 1.67 (1.65–1.69) mm, with posterolateral protrusions. Abdomen ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) 1-segmented and longer than wide, 0.59 (0.58–0.60) × 0.40 (0.39–0.41) mm. Caudal ramus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C) slightly longer than wide, 110 (108– 111) × 99 (97–100) µm, armed with usual 3 short and 3 long plumose setae, dorsal surface bearing 3 sensilla and posteromedial margin ornamented with a row of setules. Egg sac 7.62 (7.40–7.84) mm long.
Antennule ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D) 2-segmented. Proximal segment strong, carrying 25 setose and 2 naked (on dorsal side) setae on anterodistal surface; distal segment short, cylindrical, about 2.25 times as long as wide, with 1 subterminal seta on posterior margin and 11 setae plus 2 aesthetascs on distal margin.
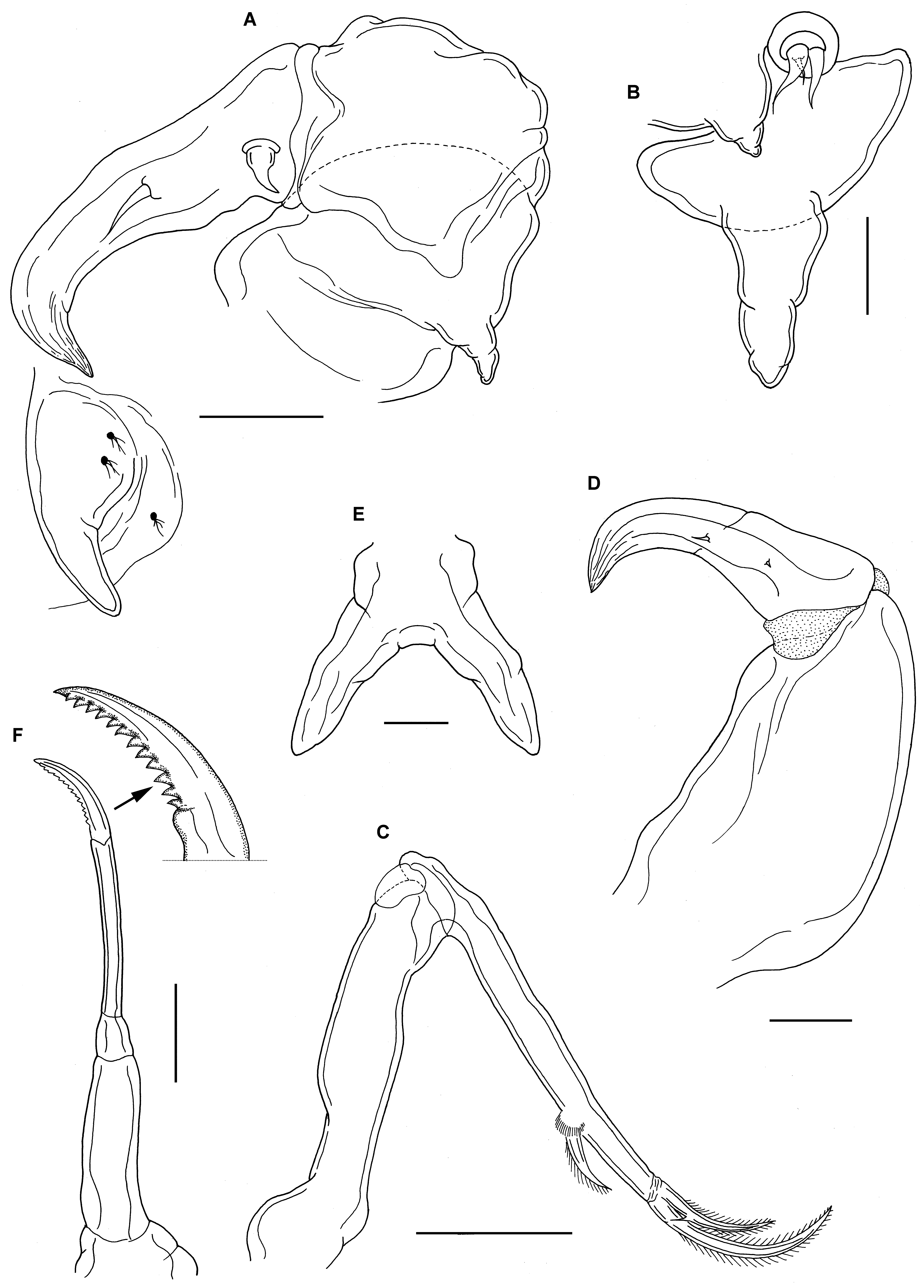
Antenna ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A) 3-segmented; proximal segment with blunt process on posteromedial corner, second segment squarely and unarmed, distal segment represented by long, curved claw bearing 2 setae, one proximal and other one close to medial region. Postantennal process ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A) represented by bluntly tipped spine with two papillae on basal region bearing 3 setules, another similar setule-bearing papilla close to cephalon.
Mandible ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 F) with 4 sections; proximal 3 sections unarmed, distal section forming slender blade bearing 12 teeth along medial margin (arrowed in Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 F). Maxillule ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B) comprising large stout dentiform process and proximal basal papilla armed with 3 unequal setae; another small process situated by basal papilla. Maxilla ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C) 2-segmented; proximal segment (lacertus) unarmed; slender distal segment (brachium) with subterminal outer short spiniform element ornamented only on outer edge; terminal calamus longer than subterminal canna, both elements pinnate along medial and outer margins. Maxilliped ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D) 3-segmented, with distal 2 segments almost completely fused to form subchela; proximal segment (corpus) unarmed; middle (shaft) and distal (claw) segments each carrying minute seta; claw strongly bent at tip. Box of sternal furca ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E) indistinct; tines blunt, widely divergent.
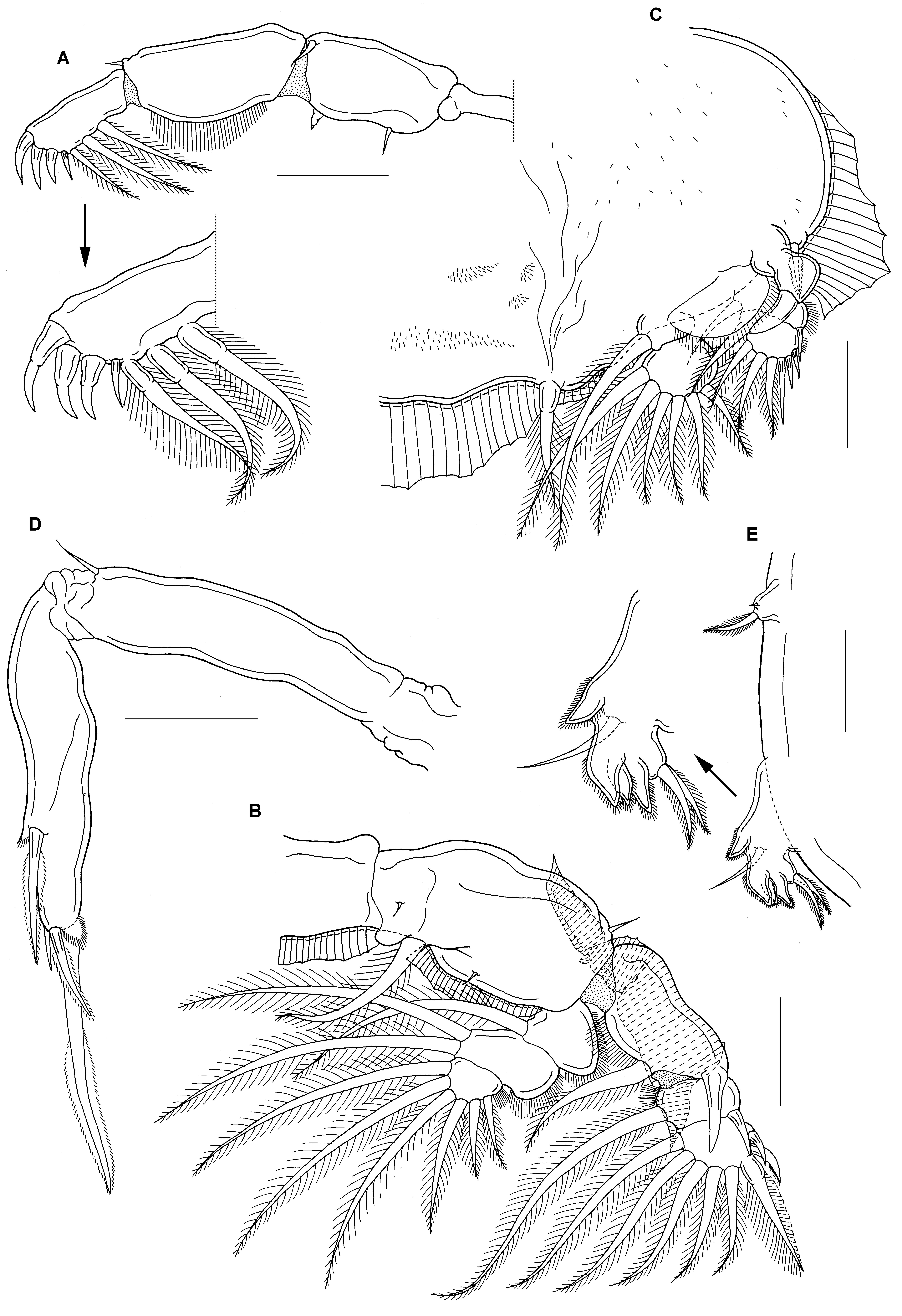
Armature on rami of legs 1–4 as follows (Roman numerals indicating spines and Arabic numerals, setae): Leg 1 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A) protopod carrying simple outer seta and another similar inner seta in addition to a vestigial endopod; first segment of exopod with row of setules along posterior margin plus small, spiniform outer seta; middle 2 of 4 terminal spines on last exopodal segment simple (without accessary process) (arrow in Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A); fourth terminal element smallest and shortest.
Leg 2 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B) protopod carrying large plumose inner seta on posteromedial edge, setule-bearing papillae on ventral surface, and small, simple, outer seta; posterior edge of protopod fringed with marginal membrane and outer edge of endopodal segments together with medial edge of proximal two exopodal segments fringed with row of setules.
Leg 3 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C) protopod (apron) with short outer and long inner setae; wide marginal membrane on outer edge and another marginal membrane on posterior edge of basis inner to velum; ventral surface of protopod with patches of spinules as shown in Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C.
Leg 4 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 D) protopod with small, simple outer seta; exopod 2-segmented; proximal segment of exopod with single, moderately long spine; tip of exopod with 2 short outer and 1 long, inner elements (outermost element a simple seta; inner 2 elements spiniform); pecten on exopodal segments at insertion of proximal outer and distal innermost spines.
Leg 5 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 E) comprising 2 processes with simple anterior process tipped with 1 plumose seta and quadripartite posterior process carrying 3 (1 simple and 2 plumose) setae. Leg 6 absent.
Male. Unknown.
Etymology. The new species is named after the late Professor Ching-Long Lin (Department of Aquatic Biosciences, National Chiayi University) who made great contributions to our knowledge on the parasitic copepod fauna of Taiwan.
Type locality. Off Tai-Dong County, Taiwan.
Type host. Eumegistus illustris Jordan & Jordan 1922
Infection site and intensity. One individual and three individuals of copepods appear on the gill rakers and caudal fin, respectively. Prevalence: 0–18.2%; mean intensity: 1.0–1.5 parasites per fish specimen (Table. 1).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.