Camptocercus vietnamensis D. N. Than, 1980
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.205932 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6191224 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A687F8-FFAC-FF8A-FF6C-FB2CFCD5FD33 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Camptocercus vietnamensis D. N. Than, 1980 |
| status |
|
Camptocercus vietnamensis D. N. Than, 1980 View in CoL .
Than et al., 1980: 233–234, fig 144 (Figs. 1,2)
Type locality. Given as “Hanoi region”.
Type material. Holotype: a parthenogenetic female in the Zoological museum of Hanoi University.
Studied material: 16 parthenogenetic females from stream in Cat Tien National Park, Dong Nai Province, Vietnam, 0 5.05.2009, N 11° 27.274‘, E 107° 25.172’, coll. Sinev A.Y.; 6 parthenogenetic females and 1 ephippium from the same location, 13.12.2009, coll. A.B. Vasilieva; numerous parthenogenetic females from three streams in Cat Tien National Park, Dong Nai Province, Vietnam, 01– 10.10.2010, (N 11° 27.274, E 107° 25.172; N 11° 26.364’, E 107° 25.551’; and N 11° 26.250’, E 107°25.621’), coll. Sinev A.Y.
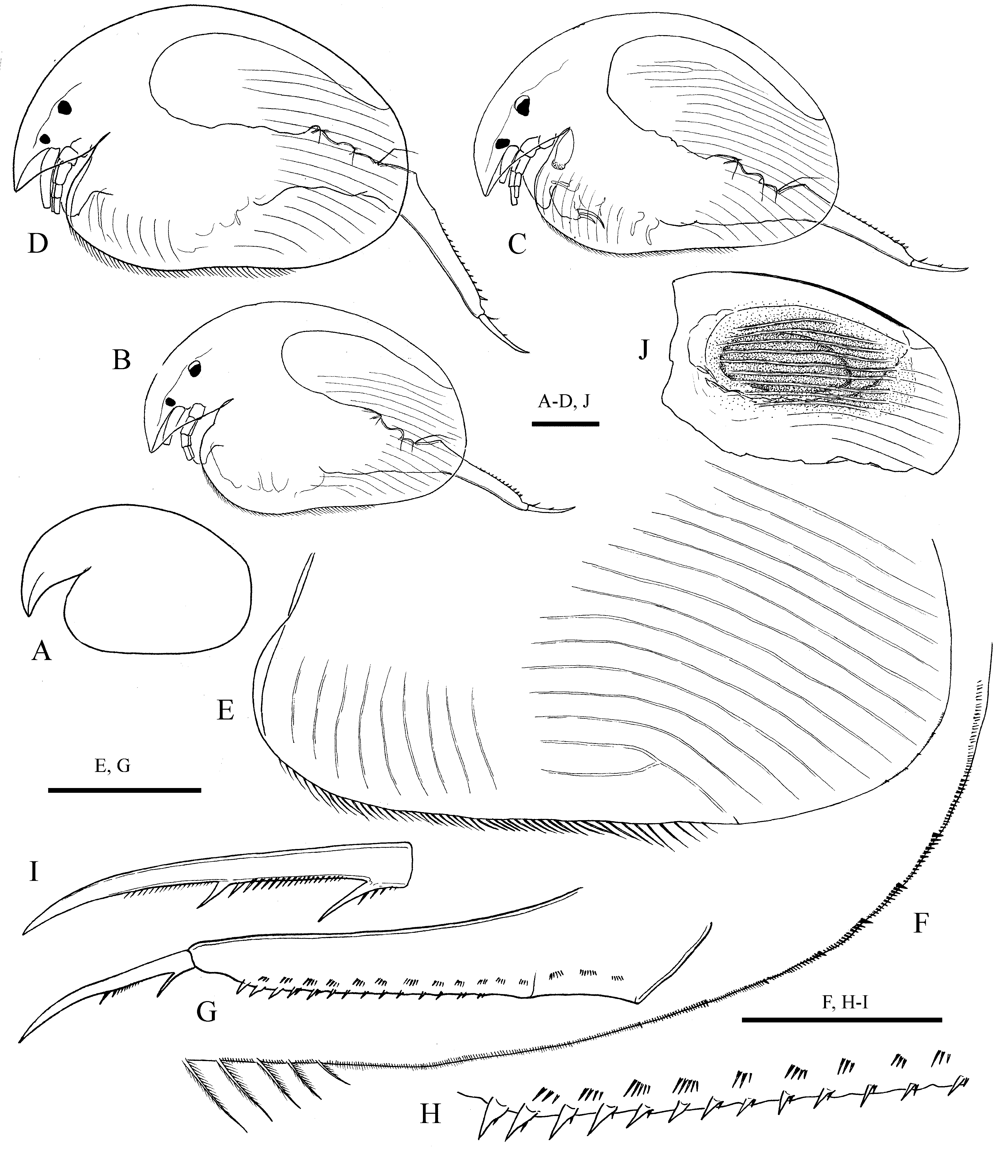
Description. Parthenogenetic female: Body ( Fig.1 View FIGURE 1 A–D) with well-expressed dorsal keel, moderately high, egg-shaped in lateral view (height/length ratio from 0.66 to 0.72 in adult), with maximum height in the second quarter of body, strongly compressed laterally. Dorsal margin highly arched, without depression between valves and head shield. Posterodorsal angle broadly rounded, posterior margin convex. Posteroventral angles broadly rounded. Ventral margin from almost straight to irregularly convex, with about 45–50 short ventral setae ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E). Row of ventral setae ends at about 2/3 length of ventral margin, followed by the groups of numerous, very short setules, increasing in size posteriorly ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 F). In groups on posteroventral angle, last setules being largest, denticle-like. Anteroventral angle rounded. Valves with prominent sculpture in shape of diagonal, almost never anostomosing lines, in anteroroventral portion of valves curved upward, anterodorsal part of valves oblique in some specimens.
Head with well-developed keel; distance between eye and margin of keel varies about 1–1.5 eye diameters. In lateral view, rostrum acute, pointed downward. Eye 1.5–2 times larger than ocellus Three connected main head pores located on a widened area of head shield keel. Lateral pores minute.
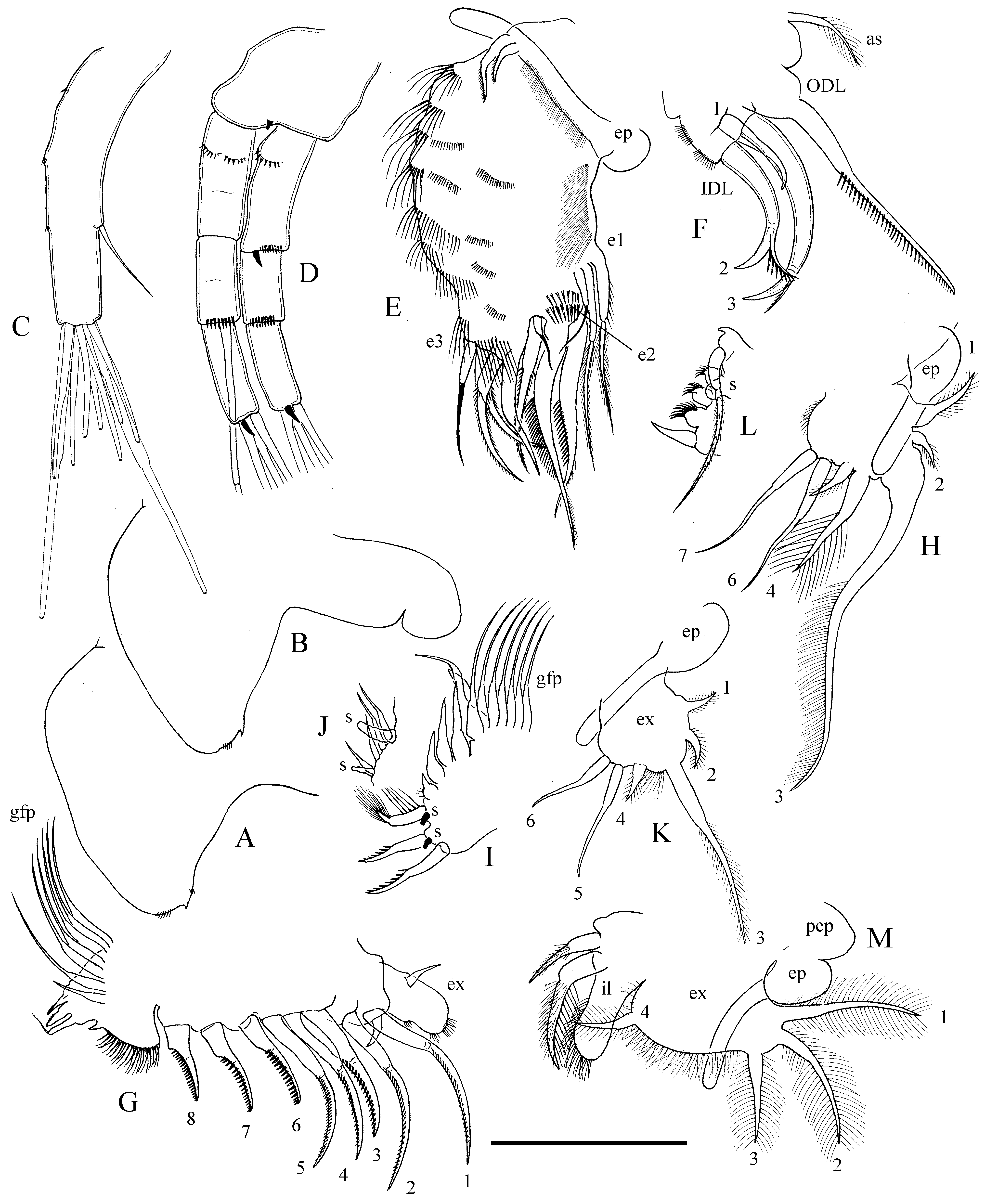
Antennule ( Fig.2 View FIGURE 2 C) long and narrow; length about 4.5 width. Three groups of very short setules at anterior face. Two long and seven short terminal aesthetascs, longer aesthetascs almost as long as antennule itself, short ones about 1/3 of antennule length. Antennular seta thin, about 1/4 length of antennule, arising at 2/3 distance from the base.
Antenna ( Fig.2 View FIGURE 2 D) less than 1/5 of body length. Antennal formula, setae 0-0-3/0-1-3, spines 1-0-1/0-0-1. Branches long and slender, of equal length. Basal segments about 1.5 times longer than others. All apical setae of same thickness and similar length, about two times longer than branches itself. All spines very short, about 1/5 length of apical segment.
Labrum ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A,B) with subtriangular keel; height about 1.5 width. Apex of keel rounded. Dorsal margin with denticle and 1–2 groups of very short setules.
Thoracic limbs: five pairs. Limb I ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E, F) large in comparison with limbs III–V. Epipodite rounded, with finger-like projection four times longer that epipodite itself. Accessory seta short. ODL with one long seta, armed with large setules in distal part. IDL with three setae and two clusters of setules. IDL seta 1 large, well developed, about 1/3 length of ODL seta. Setae 2 and 3 thick, curved, hook-like with thin, setulated distal portion; seta 3 slightly shorter than ODL seta; seta 2 about 2/3 length of seta 3. Endite 3 with four setae subequal in length. Endite 2 with two long distally setulated setae, both of them shorter than ODL seta, a shorter seta near their base, and a naked seta on anterior face of limb. Endite 1 with two 2-segmented setae and a long naked seta on anterior face of limb 1.5 times longer than naked seta of endite 2. Seven-eight rows of setules on ventral face of limb. Two ejector hooks, one two times smaller than other.
Limb II subtriangular ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 G). Exopodite narrow, elongated, with short seta. Inner portion of limb (“endopodite”) with eight scraping spines; scrapers 1–5 long, scrapers 6–8 much shorter, armed with more robust setules. Scraper 3 only a little thicker and shorter that neighbors, There is a soft seta near the base of scraper 1. Distal armature of gnathobase with four elements. Filter plate of seven setae, the posteriormost one considerably shorter than others.
Limb III ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 H–J). Epipodite oval, with finger-like projection 1.5 times longer than epipodite itself. Exopodite ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 H) of irregular shape, with seven setae; seta 3 being longest, seta 6–7 about half-length of seta 3, seta 4 of about 1/3 length of seta 3, other setae short. Seta 3 unilaterally armed with long thin setules, seta 4 bilaterally armed with long thick setules, setae 6–7 naked, other setae armed with short setules. Distal endite ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 I) with three setae decreasing in length basally, two sensilla located between their bases. Two distalmost setae slender, sharp, with short denticles in distal part; basalmost setae flattened, setulated. Basal endite with 4 stiff setae with wide bases, increasing in length basally. Gnathobase not clearly separated from basal endite. Four soft setae ( Fig.2 View FIGURE 2 J) increasing in size basally; a sensillum near the base of distalmost seta. Distal armature of gnathobase with three elements; the first one an elongated, cylindrical sensillum, the second a geniculated seta, the third a short spine. Filter plate of seven setae.
Limb IV ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 K–L). Epipodite oval, with finger-like projection two times longer that epipodite itself. Exopodite ( Fig.2 View FIGURE 2 K) small, quadrangular, with six setae. Seta 3 being longest, setae 5–6 about 2/3 length of seta 3, other setae very short. Setae 1–4 bearing short setules, setae 5–6 naked. Inner portion of limb IV ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 L) with four setae and large round sensillum arising from the side of lobe. Scraping seta short, with wide base and small denticles in distal part. Flaming-torch setae short and broad, decreasing in size basally. Three soft setae increasing in size basally. Gnathobase with a very long two-segmented seta and a small hillock distally. Filter plate of five setae.
Limb V ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 M). Epipodite suboval, with finger-like projection two times longer that epipodite itself. Exopodite oval, with four plumose setae, their length gradually decreasing from seta 1 to seta 4. Inner limb portion as elongated, very narrow lobe, with short setules on the inner margin. At inner face, two setae setulated in distal part, the distal one 1.5 times longer and thicker than proximal. Filter plate absent.
Postabdomen ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 G) very long and narrow, narrowing distally, length about 4.5–5 height. Ventral margin concave in basal half, straight in distal half. Distal margin and distal angle not developed, dorsal margin evenly comes to the base of claws. Dorsal margin straight in postanal portion and weakly concave in anal one; distal part about four times longer than preanal one; postanal portion 2.5 times longer than anal one. Preanal angle well defined; postanal angle not defined. Postanal margin of postabdomen provided with 13–15 small triangular denticles ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 H), some with small spinules on posterior side or near their base. About 15 lateral fascicles of very short setules, distalmost fascicles consisting of 3–5 setules only.
Postabdominal claw ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 I) long, straight, with slightly curved tip. Basal spine short, straight and thin, about 0.15 length of claw itself. Spine at the end of pecten well-developed, thick, exceeding width of claw there.
Ephippial female unknown. Ephippium ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 J) yellow-brown, with well-developed egg locule covered by thick longitudinal lines.
Male unknown.
Size. In the studied population, instar I juvenile females length 0.35–0.37 mm, height 0.23–0.24 mm; instar II, length 0.45–0.49 mm, height 0.30– 0 32 mm; adult female, length 0.52–0.60 mm, height 0.37–0.40 mm. According to Than et al. (1980), maximum length of specimens in North Vietnam populations is 0.65 mm.
Differential diagnosis: Camptocercus vietnamensi s clearly differs from most species of the genus by morphology of IDL, with setae 2 and 3 of similar morphology, thick, curved, hook-like with thin, setulated distal portion; this feature is shared with C. uncinatus . From the latter species, C. vietnamensis differs in smaller size, more high, egg-shaped body, triangular denticles of postabdomen, and labrum with denticle on posterior margin.
Ecology. According to Than et al. (1980), C. vietnamensis inhabits only streams and rivers, in both mountainous regions and plains of North Vietnam. Present data confirms the reophilic nature of the species. During April– May 2009 (beginning of wet season) small number of specimens was found within the single small forest stream among dead leaves, together with Guernella raphaelis and Kurzia longirostris . During September–October 2010 C. vietnamensis was abundant in several small and moderately-sized forest streams, among submerged vegetation and dead leaves, together with Nicsmirnovius eximius, Pleuroxus sp. and Kurzia longispina . Despite intensive sampling efforts (over forty water bodies were studied), the species was never found in any lentic water bodies, as well as within the large river Dong Nai and streams and channels within the agricultural area.
Distribution. So far known from North and South Vietnam.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.