Neacomys, Thomas, 1900
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4876.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:190EC586-E14B-4AEF-A5EF-3DA401656159 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4566570 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A587ED-321B-FFF1-83E9-FA312FCAF85C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Neacomys |
| status |
|
Neacomys sp. 2
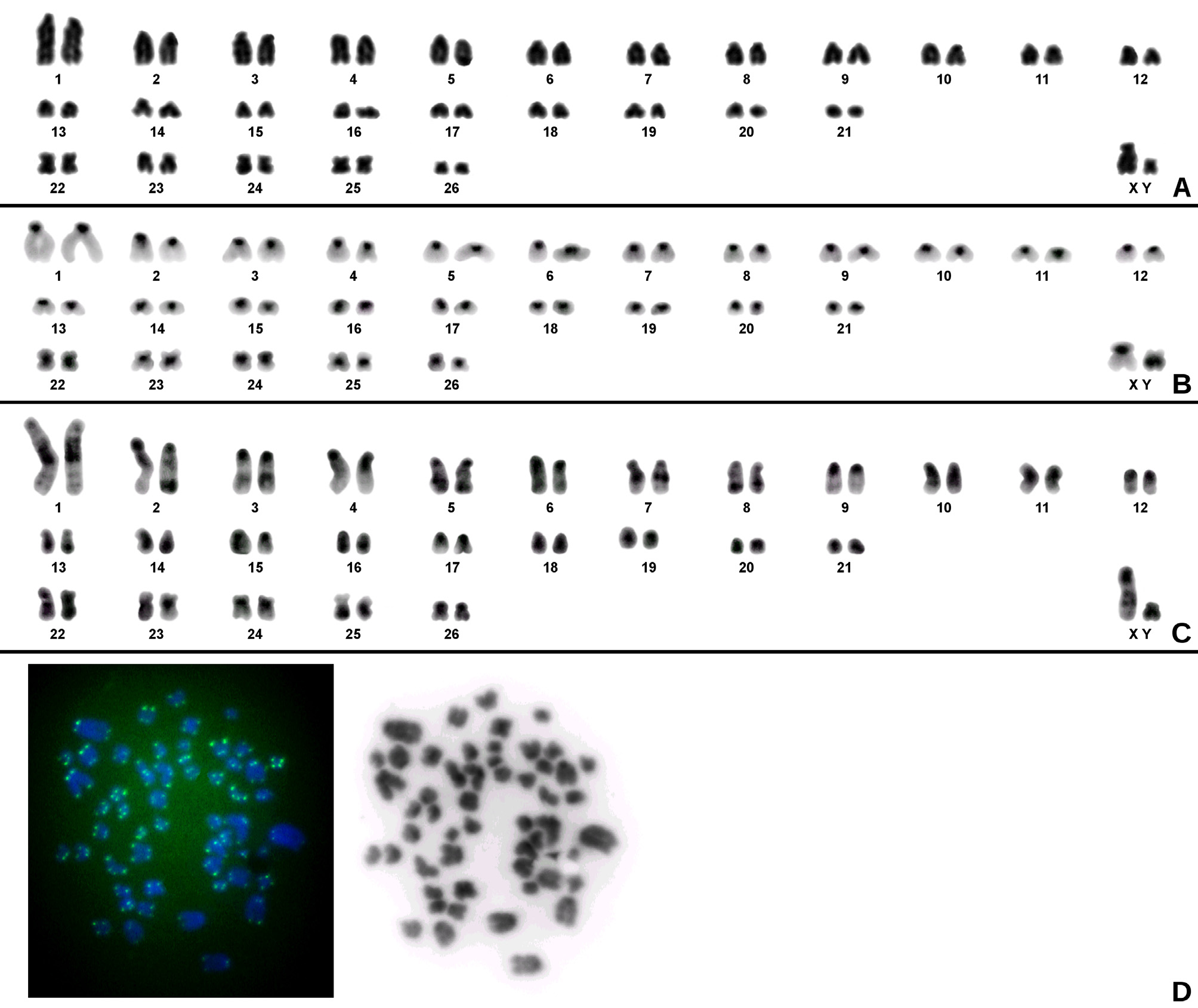
Karyotype: 2n = 54 and FN = 62. Autosomal complement: five medium to small metacentric and submetacentric pairs, and 21 acrocentric pairs (one large and the remaining medium to small decreasing in size). Sex chromosomes: X, a medium subtelocentric; Y, a small submetacentric ( Fig. 10A View FIGURE 10 ). C-banding metaphases exhibited blocks of constitutive heterochromatin on the pericentromeric region of all autosomes. The X chromosome presented the short arm entirely heterochromatic. The Y chromosome presented the long arm entirely heterochromatic ( Fig. 10B View FIGURE 10 ). G-banding was performed to allow the correct identification of all homologous pairs ( Fig. 10C View FIGURE 10 ). FISH with telomeric sequences revealed signals exclusively at the ends of all chromosome arms and no interstitial signals were observed ( Fig. 10D View FIGURE 10 ). The same diploid number (2n=54) and a similar fundamental number (FN=66) was reported by Silva et al. (2017) for Neacomys sp. B. However, the former karyotype presented five large and two small biarmed pairs, different from the karyotype presented by us that comprises five medium to small biarmed pairs. The sex chromosomes morphology was also distinctly between the two karyotypes.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.