Axonchium neoeletum Rahman, Jairajpuri & Ahmad, 1985
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.215075 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6169973 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03994F22-FFC2-E64F-21C1-DC5FFE27FE27 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Axonchium neoeletum Rahman, Jairajpuri & Ahmad, 1985 |
| status |
|
Axonchium neoeletum Rahman, Jairajpuri & Ahmad, 1985
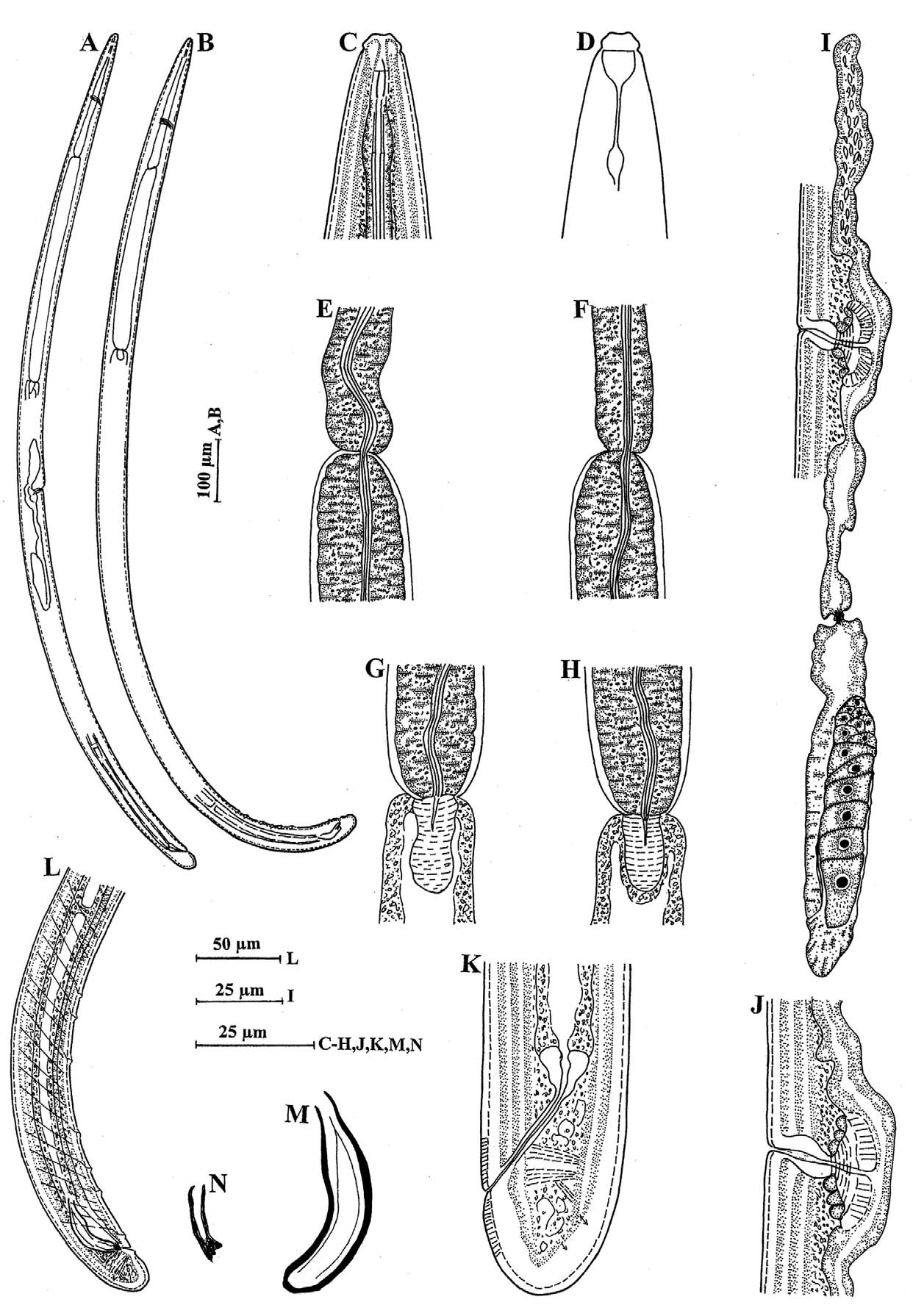
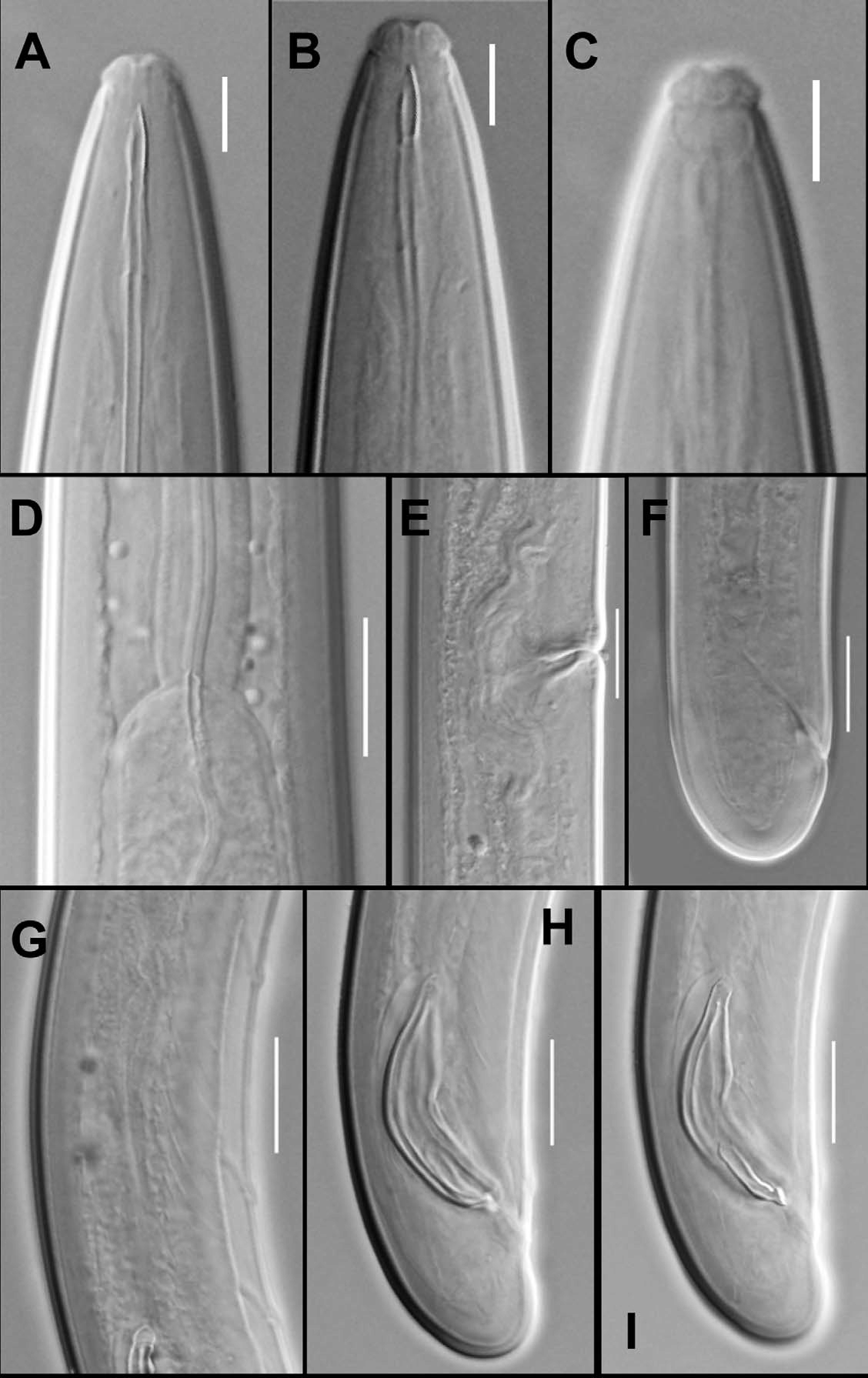
( Fig. 5–6 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 )
Measurements. Table 3 View TABLE 3 .
Characters Female Males Paratype female Paratype male Description. Female: Cuticle 2 µm thick at mid body and 6 µm thick on tail. Lateral chords about one-fourth of body width at mid body.
Lip region offset by constriction, about one-fifth as wide as body width at neck base; lips separate. Amphids cup-shaped, their aperture slightly less than one lip region width. Odontostyle about one lip region width long. Odontophore 1.5 times the odontostyle length. Anterior part of pharynx muscular, separated from the posterior expanded part by a deep constriction or abutting it, the latter occupying 64% of total neck length. Cardia conoid, about one-half of the corresponding body width long.
Anterior genital branch represented by uterine sac, measuring 87 µm long and filled with sperms. Posterior branch well developed; ovary reflexed, not reaching the oviduct-uterus junction, measuring 80 µm; oviduct measuring 90 µm, consisting of a long slender part with prismatic cells and a slightly wider pars dilatata with wide lumen; well developed sphincter present at oviduct-uterus junction. Uterus measuring 80 µm, tripartite, having distal and proximal dilated parts with wide lumen and an intermediate narrower tube-like part with narrow lumen. Vagina slightly bent posteriad extending inwards slightly more than half of the corresponding body width; pars distalis vaginae well developed, about as long as pars proximalis vaginae; pars refringens vaginae absent. Prerectum about seven times anal body width long. Rectum about one anal body width long. Tail broadly rounded, 0.8 times anal body width long. Caudal pores two on each side.
Male: Spicules dorylaimoid, ventrally curved with blunt distal end, 1.7–1.8 times the cloacal body width in length. Lateral guiding pieces sclerotized, slightly curved with bifurcated distal ends, about one-third of the spicule length. Supplements an adcloacal pair and six to seven irregularly spaced ventromedians, starting within the range of spicules. Prerectum about 6–7 times and rectum 1.1–1.2 times cloacal body width in length, respectively. Tail broadly rounded, 0.7–0.9 times cloacal body width long. Two caudal pores on each side.
Habitat and locality. Soil around the roots of forest trees (unidentified) from Lathan, district Lohit, Arunachal Pradesh, India. GPS coordinate 27.90645/96.17432; latitude 27o54’E, longitude 96o10’ N.
Remarks. Rahman et al. (1985) described this species from Meghalaya, India. The present population conforms well to the type population except for having a slightly shorter anterior uterine sac (G1=6.1% vs 7–9%). A paratype female and a male of this species available in the collection of the Department of Zoology, Aligarh Muslim University were also examined and were found to fit well with the present population except for having slightly more posterior vulval position (V = 52.8 vs 49.9) and slightly shorter anterior uterine branch (G1= 6.1% vs 7.7%). This species closely resembles A. elegans Jairajpuri, 1964 and A. eletum Dhanachand & Jairajpuri, 1981 . From A. elegans , it differs in the size and shape of spicules ( vs spicules 1.5 times cloacal body width long with unusually wide distal end), and in the shape of the lateral guiding pieces and greater number of ventromedian supplements ( vs lateral guiding pieces rod-like with bifid distal ends and four ventromedian supplements). From A. eletum , this species differs in the shape of vagina and in having a proximal constriction in the anterior uterine sac; in the shape of lateral guiding pieces ( vs lateral guiding pieces almost straight without sclerotization); irregularly arranged and fewer ventromedians ( vs nine ventromedians in two groups of three and six). This is the first report of this species after its original description.
TABLE 3. Morphometrics of Axonchium neoeletum Rahman, Jairajpuri and Ahmad, 1985 (All measurements in µm (except L) and in the form: mean ± standard deviation (range).
| n: 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L (mm) 1.4 | 1.5±0.11 (1.4–1.6) | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| a 36.0 | 37.2±3.8 (33.7–41.2) | 34.3 | 43.5 |
| b 2.4 | 2.9±0.28 (2.5–3.1) | 2.9 | 3.1 |
| c 62.7 | 67±6.6 (59.4–74.2) | 70 | 63 |
| c`0.8 | 0.85±0.12 (0.7–1.0) | 0.75 | 0.9 |
| V 52.8 | - | 49.9 | - |
| G1 6.1 | - | 7.7 | - |
| G2 13.8 | - | 12.4 | - |
| Lip region width 8 | 7.25±0.5 (7–8) | 9 | 9 |
| Lip region height 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Amphid aperture | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Odontostyle length 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Odontophore length 12 | 10.6±0.57 (10–11) | 12 | 12 |
| Guiding ring from anterior end 10 | 10 | - | - |
| Nerve ring from anterior end 120 | 127±5.77 (120–130) | - | - |
| Neck length 583 | 527±35 (490–585) | 570 | 545 |
| Expanded part of pharynx 373 | 317±33.6 (290–375) | 360 | 320 |
| Cardia length 20 | 18±1.4 (16–20) | 18 | 17 |
| Body width at mid body 40 | 42±4.9 (36–47) | 49 | 39 |
| Body width at neck base 38 | 43±4.9 (37–49) | 47 | 37 |
| Body width at anus/cloaca 28 | 27±3.3 (25–32) | 32 | 62.9 |
| Anterior genital branch 87 | - | 130 | - |
| Posterior genital branch 200 | - | 210 | - |
| Vaginal depth 26 | - | 28 | - |
| Vulva from anterior end 763 | - | 840 | - |
| Prerectum length 200 | 180±20 (160–200) | 245 | 300 |
| Rectum length 35 | - | 40 | |
| Tail length 23 | 23.2±2.4 (20–25) | 24 | 27 |
| Spicules length - | 46.6±4.04 (43–51) | - | 50 |
| Lateral guiding pieces | 14.3±1.15 (13–15) | - | 13 |
| Ventromedian supplements - | (6–8) | - | 7 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |