Begonia cathcartii Hook.
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2018.396 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3794335 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0397A96F-2F70-FFF6-03A1-FAFAE5542D89 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Begonia cathcartii Hook. |
| status |
|
Begonia cathcartii Hook. View in CoL f. [sect. Platycentrum ]
Illustrations of Himalayan Plants: 13 ( Hooker 1855). – Platycentrum cathcartii View in CoL (Hook.f.) Klotzsch, Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin: 245 ( Klotzsch 1855 [‘1854’]). – Type: India, Sikkim, Darjeeling, Hooker s.n. (lecto-: K000373057, here designated; isolecto-: K000373056).
Begonia nemophila Kurz View in CoL , Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal 46 (2): 108 ( Kurz 1877). – Type: Myanmar, East of Tounghoo, Martaban Hills, Kurz s.n. (n.v.).
Citations in other publications
As B. cathcartii: Klotzsch (1855 View in CoL [‘1854’]: 245), de Candolle (1864: 349), Clarke (1879: 646), Clarke (1881: 119), Craib (1931: 772), Hara (1971: 84), Hara et al. (1979: 181), Grierson (1991: 244), Chauhan (1996: 175), Kress et al. (2003: 171), Uddin (2007: 593), Hughes (2008: 24), Dash (2010: 32); as Platycentrum cathcartii: Klotzsch (1855 [‘1854’]: 125); as B. nemophila: Clarke (1879: 646) View in CoL .
Other material examined
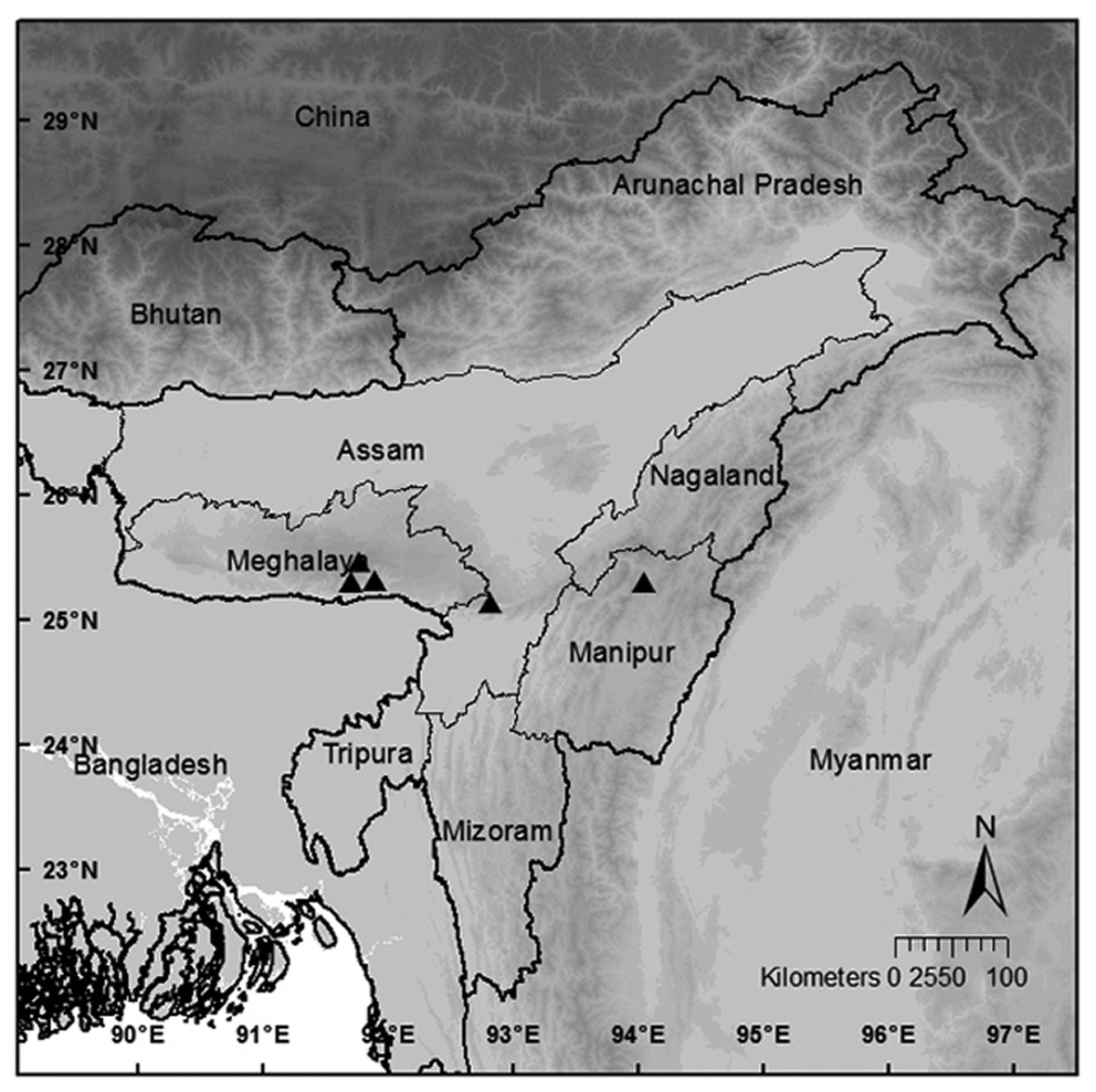
INDIA: Arunachal-Pradesh: Delei Valley, 16 Jul. 1928, Ward 8459 ( K).
Description
Rhizomatous, erect, monoecious herb, 30–60 cm high. Rhizome: ca 10 mm wide, densely strigose. Stem: stout, ca 5 mm wide, red reflexed strigose, internodes up to 23 cm long, much shorter at the rhizomatous base of the plant. Stipules: ovate, 9–10 × 3–4 mm, glabrous, semi-persistent. Leaves: petiole (3–)6–13(–20) cm long, red strigose; lamina ovate to broadly ovate, basifixed, base cordate with lobes not overlapping, 15–21 × 9–15 cm, asymmetric, upper surface green, sparsely red strigose all over, underside green, sparsely red strigose mostly on the veins, venation palmate, midrib 10–15 cm long; margin minutely serrate, with hairs; apex acuminate. Inflorescence: sometimes subtended with a pair of leaves; cymose, axillary, few; peduncles sparsely red strigose, branching 2–3 times, primary 4–8 cm long, secondary and tertiary peduncles ca 1 cm long, with 1– 3 female flowers and 1– 3 male flowers; bracts lanceolate, 7–11 × 2–4 mm, fimbriate. Male flower: pedicel 18–20 mm long, pilose; tepals 4; outer tepals ovate, 15 –24 × 10–20 mm, white, red pilose on reverse near the base; inner tepals lanceolateovate, 10–15 × 8–12 mm, white, glabrous; androecium with 60–80 stamens, symmetric; filaments ca 2 mm, anther oblong elliptic, 2 mm long, not hooded, connective extended. Female flower: pedicel 16–21 mm long, pilose; bracteoles absent; tepals 5, equal, ovate, outer tepals 20–25 × 12–15 mm, white, red pilose on reverse near base, inner tepals similar but smaller; ovary 2-locular, placentae bifid, capsule ellipsoid, densely red strigose, with one long oblong wing and two short triangular wings; styles 3, deeply forked once and twisted once. Fruit: recurved, 29–42 × 12 –16 mm; capsule ellipsoid, 18–20 × 7–9 mm, sparsely red strigose; wings extending along the pedicel slightly, subequal; longest rounded oblong, 15–24 × 11–15 mm; shortest triangular, 7–9 × 12–16 mm.
Distribution and phenology
Arunachal-Pradesh; also in Nepal, Sikkim, Bhutan, Myanmar and Thailand; 1800–2100 m. Flowering: April to June; fruiting: May to July.
Conservation status
Least Concern ( Hughes 2008). Begonia cathcartii is a widespread species with no significant change in distribution in recent years to warrant a change in its status. This species is known to occur in Doi Inthanon National Park in Thailand.
Remarks
Known in the study area from one specimen that lacked female flowers; the description was augmented using the protologue and specimens from the Eastern Himalayas. Begonia cathcartii is characterized by red reflexed hairs more or less all over the plant; B. thomsonii , also in B. sect. Platycentrum , shares having red hairs, but is a much smaller plant and the indumentum is denser and finer.
Begonia difformis (Irmsch.) W.C.Leong, C.I Peng & K.F.Chung [sect. Platycentrum ] Fig. 21 View Fig
Phytotaxa 227 (1): 86 ( Leong et al. 2015). – Begonia lacinata Roxb. var. difformis Irmsch., Mitteilungen View in CoL aus dem Institut für allgemeine Botanik in Hamburg 10: 531 ( Irmscher 1939). – Begonia palmata D.Don var. difformis (Irmsch.) Golding & Kareg., Phytologia 54 (7): 495 ( Golding & Karegeannes 1984). – Type: China, Yunnan, Sep. 1912, Forrest 16098 (lecto-: E00299196, designated by Leong et al. 2015; isolecto-: K n.v.).
Other material examined
INDIA: Assam: Cachar, Boro Lakha, 1 May 1951, Koelz 27847 (MICH1225785). Manipur: Karong, 8 Oct. 1950, Koelz 26470 (MICH1225756). Meghalaya: Khasi Hills, Cherrapunji, 17 Apr. 1952, Chand 5380 (MICH1225702); ibid., 14 May 1952, Koelz 29907 (MICH1225690); ibid., 29 May 1952, Chand 5779 (MICH1225812); ibid., 2 Jun. 1952, Koelz 30159 (MICH1225720); ibid., 18 Jun. 1952, Koelz 30311 (MICH1225719); Mawphlang, 15 Jul. 1953, Koelz 33304 (MICH1225704); Pynursla, 3 Aug. 1949, Chand 2127 (MICH1225687); ibid., 5 Sep. 1949, Chand 2170 (MICH1225688); ibid., Koelz 23758 (MICH1225747).
Description
Rhizomatous, erect, monoecious herb, 20 –80 cm high. Rhizome: ca 2 cm wide, internodes 1–2.5 cm long. Stem: 10–20 mm wide, sparsely hirsute, internodes 5–15 cm long. Stipules: narrowly ovate or ovate, 30 × 20 mm, caduceus. Leaves: petiole 10–30 cm long, sparsely to densely hirsute, ovate or oblate-orbicular, base cordate, lobes not overlapping, 7–17 × 5–11 cm, asymmetric, upper surface green, hispidulous along veins, lower surface paler green, hirsute; venation palmate, midrib 5–14 cm long; margin shallowly denticulate, usually divided to ¼ of the blade or more, apex acuminate to longacuminate. Inflorescences: cymose, protandrous; axillary, few; peduncle red pubescent, branching 1–2 times, primary 10–15 cm long, secondary 1–2 cm long, with 3– 4 female and 3– 4 male flowers; bracts ovate, 10–15 × 5–8 mm, upper surface sparingly hispidulous to nearly glabrous, margin ciliate, caduceus. Male flowers: pedicel 10–20 mm long, densely red puberulous; tepals 4, outer tepals obovate to orbicular, 12–23 × 8–20 mm, white to pink, red setulose on reverse, margin entire, inner tepals oblanceolate to narrowly obovate, 10–23 × 5–10 mm, white, glabrous, entire; androecium with 80–200 stamens, symmetric; filaments 1–2.5 mm long, unequal, fused at base into short column; anther narrowly obovate, 2 mm long, dehiscing through slits, not hooded, connective extended, acute. Female flowers: pedicel 10–20 mm long, densely red puberulous; bracteoles absent; tepals 5, unequal, oblanceolate to orbicular, 8–24 × 4–21 mm, red setulose on reverse to almost glabrous, entire, inner tepals similar but smaller; ovary 2-locular, placentae bifid; capsule oblong-ellipsoid, 5–8 × 3–4 mm, very sparse to dense red setulose, with one long wing and two short rounded wings; styles 2, forked once and twisted, caduceus. Fruit: recurved, capsule obovoid, ca 1.5 × 1 cm, sparse red setulose to glabrous; wings extending along pedicel, unequal; longest wing obliquely oblong, 10–30 × 5–10 mm; shorter wings oblong, ca 5 × 10 mm.
Distribution and phenology
Assam, Meghalaya and Manipur; also in China and Myanmar. Flowering: June to October; fruiting: August to November.
Conservation status
Least Concern. The species has an EOO of 179,130 km 2 and an AOO of 108 km 2. The range of this recently described species could possibly be extended further, as it is likely more specimens will be found which are currently identified as the similar B. palmata . The specimens we have cited are split between Yunnan, China and the study area which are linked by the Arakan Mountains and the eastern end of the Himalayas, providing suitable habitat which is currently under-explored botanically.
Remarks
Begonia difformis is very similar to B. palmata but differs in having leaves with deeper lobes and with the hairs on the upper leaf surface being restricted to the veins ( B. palmata has hairs all over). The most notable difference are the red setose hairs on the flowers and fruit; B. palmata has fine villose hairs. Also the largest wing of the fruit in B. difformis has a verrucose texture, unlike the smooth surface of the wings in the fruit of B. palmata . The description is augmented with information from the protologue.
| K |
Royal Botanic Gardens |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Begonia cathcartii Hook.
| Camfield, Rebecca & Hughes, Mark 2018 |
B. cathcartii: Klotzsch (1855
| Dash S. S. 2010: 32 |
| Hughes M. 2008: 24 |
| Uddin A. 2007: 593 |
| Kress J. W. & DeFilipps R. A. & Farr E. & Kyi D. Y. Y. 2003: 171 |
| Chauhan A. S. 1996: 175 |
| Grierson A. J. C. 1991: 244 |
| Hara H. & Williams T. S. & Williams L. H. J. 1979: 181 |
| Hara H. 1971: 84 |
| Craib W. G. 1931: 772 |
| Clarke C. B. 1881: 119 |
| Clarke C. B. 1879: 646 |
| Clarke C. B. 1879: ) |
| Candolle A. L. P. P. de 1864: 349 |
Platycentrum cathcartii
| 13 ( Hooker 1855 ) |
| 245 ( Klotzsch 1855 |
Begonia nemophila
| 46 (2): 108 ( Kurz 1877 ) |
Begonia lacinata Roxb. var. difformis Irmsch., Mitteilungen
| Phytotaxa 227 (1): 86 ( Leong et al. 2015 |
| 54 (7): 495 ( Golding & Karegeannes 1984 |