Antipathes furcata Gray, 1857
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4692.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F054DC68-6A7E-4C80-9094-8ECCA4502CD6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5688323 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038F878B-C914-FF9E-F9EB-FB73FDEDF4ED |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2019-11-05 07:30:49, last updated 2024-11-24 23:19:22) |
|
scientific name |
Antipathes furcata Gray, 1857 |
| status |
|
Antipathes furcata Gray, 1857 View in CoL View at ENA
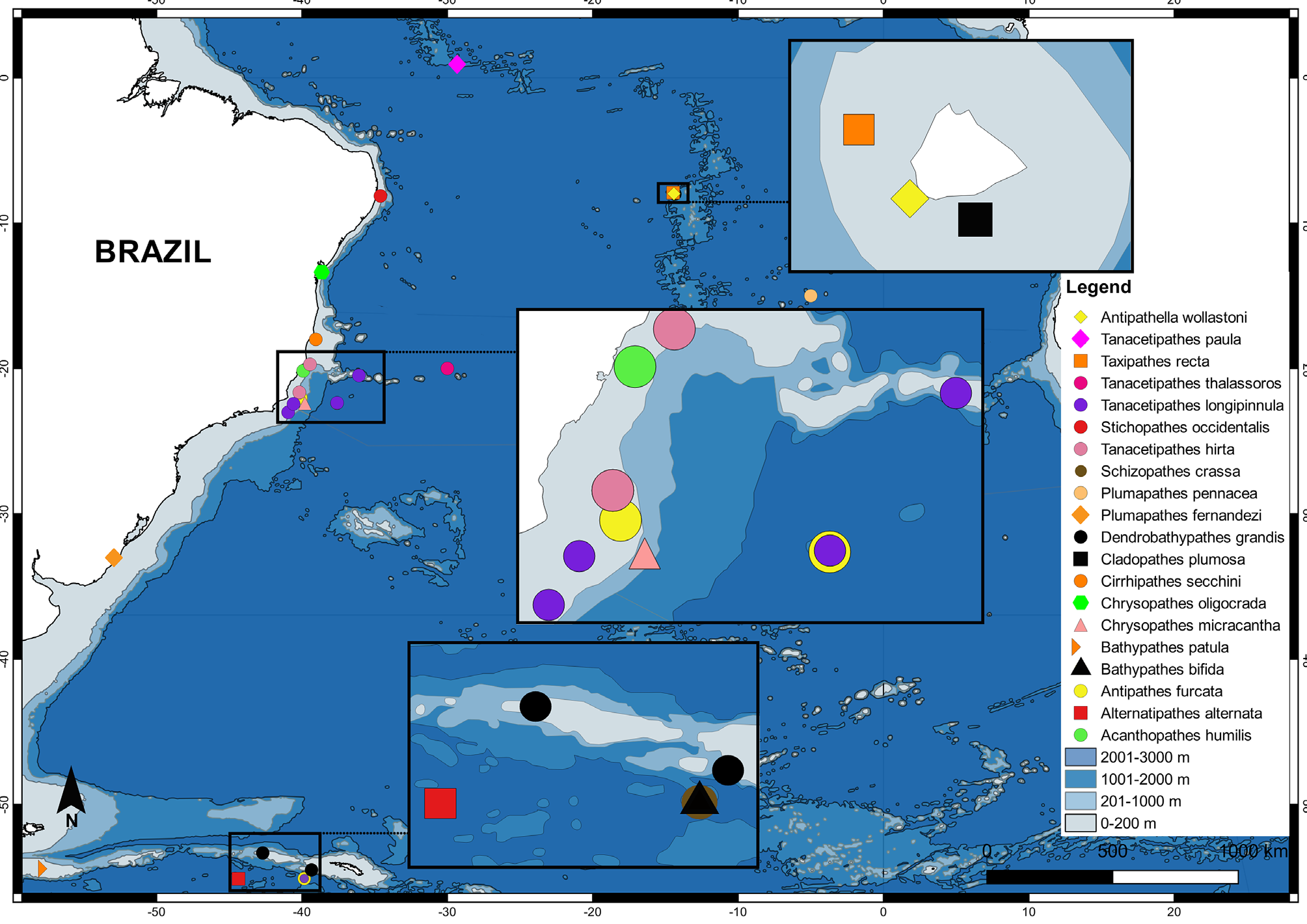
Fig. 35 View FIGURE 35
Antipathes furcata Gray, 1857: 291 View in CoL ; Schultze, 1903:92; Opresko, 1974: 60–67, fig. 2; Loiola & Castro, 2001: 2–4, figs 2, 3, 4; Opresko, 2003: 487, fig. 3d; Opresko & Sanchez, 2005: 497, fig. 4; Molodtsova, 2006: 148.
Type and type locality. BMNH 1843.2.6 or 8 (holotype, see Opresko, 2003), Madeira, depth unknown .
Diagnosis. “Small colonies (less than ~ 20 cm in height) fan-shaped, branched mostly in one plane; with very long, straight, ascending branches. Larger colonies (20–40 cm in height) densely branched, in a thick plane with numerous overlapping branches. Branches directed upward and away from the centre, with most reaching to the top of the corallum; branch angles very narrow, 30° or less. Spines short, triangular, smooth, 0.05–0.1 mm tall and 0.07– 0.1 mm wide at their base; arranged in 6–8 rows with 30–40 spines per centimeter in each row. Spines occasionally bifid or forked. Polyps 0.7–1.0 mm in transverse diameter; arranged in a single series on one side of branches; 6–8 polyps per centimeter. Colonies white in color when alive.” ( Opresko & Sanchez, 2005).
Distribution. Madeira Island ( Gray, 1857), Caribbean Sea ( Opresko, 1974; Opresko & Sanchez, 2005), and Brazil (fig. 35) ( Loiola & Castro, 2001); from 15 m, in Caribbean Sea ( Opresko & Sanchez, 2005) to 2480 m, in Northeastern Atlantic ( Molodtsova, 2006).
Gray, D. R. (1857) Synopsis of the families and genera of axiferous zoophytes or barked corals. Journal of Zoology, 25 (1), 278 - 294. https: // doi. org / 10.1111 / j. 1096 - 3642.1857. tb 01242. x
Loiola, L L. & Castro, C. B. (2001) Three new records of Antipatharia (Cnidaria) from Brazil, including the first record of a Schizopathidae. Boletim do Museu Nacional, Serie Zoologia, 455, 1 - 10.
Molodtsova, T. N. (2006) Black corals (Antipatharia: Anthozoa: Cnidaria) of the north-eastern Atlantic. In: Biogeography of the Atlantic Seamounts. KMK Press, Moscow, pp. 141 - 151.
Opresko, D. M. (1974) A study of the classification of the Antipatharia (Coelenterata: Anthozoa), with redescriptions of eleven species. Doctor of Philosophy dissertation, University of Miami, Miami, 149 pp.
Opresko, D. M. & Sanchez, J. A. (2005) Caribbean Shallow-water Black Corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Antipatharia). Caribbean Journal of Science, 41 (3), 492 - 507.
Opresko, D. M. (2003) Revision of the Antipatharia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa). Part III. Cladopathidae. Zoologische Mededelingen, 77, 495 - 536.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Antipathes furcata Gray, 1857
| Lima, Manuela M., Cordeiro, Ralf T. S. & Perez, Carlos D. 2019 |
Antipathes furcata
| Molodtsova, T. N. 2006: 148 |
| Opresko, D. M. & Sanchez, J. A. 2005: 497 |
| Gray, D. R. 1857: 291 |
1 (by plazi, 2019-11-05 07:30:49)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-11-05 07:42:27)
3 (by angel, 2020-01-16 15:21:40)
4 (by admin, 2020-01-20 22:56:39)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-11-09 18:33:37)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-11-10 09:04:53)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-11-13 05:11:46)
8 (by admin, 2023-10-01 00:49:20)
9 (by admin, 2023-10-01 01:41:44)
10 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-10-01 01:41:55)