Minibiotus xavieri, Fontoura, Paulo, Pilato, Giovanni, Morais, Paulo & Lisi, Oscar, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.190870 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5626503 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038C7144-B367-3E68-1B81-CE4ACC4CF84C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Minibiotus xavieri |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Minibiotus xavieri View in CoL sp. nov.
Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1. A – E View FIGURE 2. A – D
Material examined: 25 specimens and 15 eggs, one of them with fully developed embryo. Two specimens were mounted in polyvinyl lactophenol. All the other specimens and the eggs were mounted in Hoyer’s medium. One specimen was in simplex stage.
Type repository: The holotype (slide N. 5295), four paratypes and two eggs are deposited in the collection of Binda and Pilato (Museo del Dipartimento di Biologia Animale “Marcello La Greca”, Università di Catania); the other paratypes and eggs (slides CII-28 to CII-57) in the collection of P. Fontoura (Department of Zoology and Anthropology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto).
Specific diagnosis: Cuticle with variably shaped pores arranged in 9 wide transverse bands, the cephalic and caudal bands widest; granulation on legs absent. Eye spots present. Buccal tube narrow; buccal armature with peribuccal papulae as in all species of Minibiotus ; bands of teeth seem to be absent but this feature needs to be confirmed; two very fine latero-ventral transverse ridges and a single transverse dorsal ridge present; medioventral ridge not visible. Pharyngeal bulb with apophyses, three small macroplacoids and microplacoid. Robust claws of hufelandi type with well developed accessory points and smooth lunules. Eggs, freely laid, with long conical processes, with bifurcate apices and terminal filaments often broken; process surface and egg shell with widely spaced granulation.
Description of the holotype: Body length 369 µm, colorless; large eye spots consisting of a few pigment granules. Cuticle with small pores (longer diameter of elliptical pores up to about 2.0 µm long) arranged in 9 wide transverse bands, cephalic and caudal of which are widest; pores variable in shape: roundish, oval and, very few, trilobed ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1. A – E ). Ventral surface of body with few roundish pores. Pores also present on legs ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1. A – E ) where no granulation is present.
Mouth antero-ventral; buccal cavity very small ( Fig. 1B, C View FIGURE 1. A – E ); buccal armature without peribuccal lamellae and with peribuccal papulae as in all species of Minibiotus ; bands of teeth seem to be absent but this feature needs to be confirmed; two very fine latero-ventral transverse ridges and a single transverse dorsal ridge present; a medioventral ridge not visible.
Rigid buccal tube narrow, 32.7 µm long and 3.0 µm wide externally (pt = 9.2), with an unmarked anterior bend ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1. A – E ). Slight thickening of buccal tube wall present caudal to stylet supports ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1. A – E ). Ventral lamina not very long (pt = 55.7 measured in lateral view). Stout stylet supports inserted on buccal tube at 67.3 % of its length (pt = 67.3). Pharyngeal bulb with large triangular apophyses and three small macroplacoids and microplacoid ( Fig. 1B, C View FIGURE 1. A – E ); first macroplacoid, pear shaped, partially lying under apophysis as in other species of the genus, 4.5 µm long (pt = 13.8); second macroplacoid, roundish, 3.6 µm (pt = 11.0); third macroplacoid 3.9 µm long (pt = 11.9). Microplacoid 1.7 µm long (pt = 5.2). Macroplacoid row length, 12.6 µm long (pt = 38.5); entire row of placoids 13.9 µm long (pt = 42.5).
Robust claws of hufelandi type, with well-developed accessory points on main branches ( Fig. 1D, E View FIGURE 1. A – E ) particularly prominent on hind legs. External and internal claws of legs II and III 10.5 µm long (pt = 32.1) and 10.0 µm long (pt = 30.6) respectively, including accessory points and peduncle. Posterior and anterior claws of fourth pair of legs 13.0 µm long (pt = 39.8) and 12.0 µm long (pt = 36.7) respectively.
Smooth lunules, better developed on fourth pair of legs (about 3.0 µm longer diameter), present. Two small, faint cuticular bars, difficult to see, present below lunules on first three pairs of legs.
The measurements of some structures of holotype and four paratypes are shown in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov.
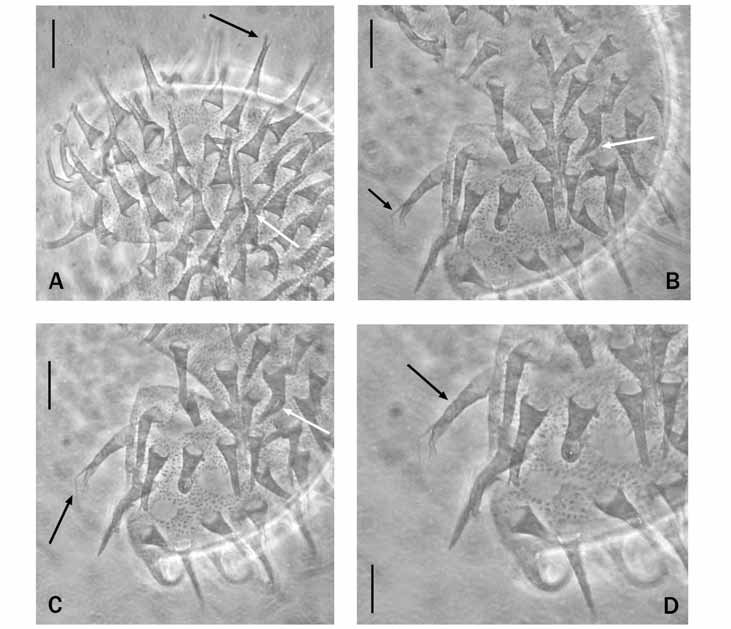
Eggs: Eggs, freely laid, spherical or slightly oval, with dotted shell and long conical processes with bifurcate apices and two or more terminal filaments (often broken) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2. A – D , black arrows); some processes forked in a more proximal position ( Fig. 2A–C View FIGURE 2. A – D white arrows). Diameter 56.0–79.0 µm excluding processes, 80 and 99.2 µm, including these structures. Processes, 20–23 around circumference, 75–95 in hemisphere, 10.6–19.0 µm high and basal diameter of 3.7–6.6 µm. Egg processes 3.3–5.8 µm apart. Egg process surface and egg shell with obvious, well-spaced granulation ( Fig. 2C, D View FIGURE 2. A – D ).
*) Unfortunately, due to a qui pro quo, Binda and Pilato, in the paper of 1992, wrote that the pt value relative to the buccal tube in M. furcatus is 7.94.
The paratypes are similar to the holotype in both qualitative and metric characters. The smallest measured specimen is 275 µm long (structures not measured) and the largest specimen 410 µm.
Etymology: The new species is dedicated in honor of Alberto Xavier da Cunha, pioneer in the study of Portuguese tardigrades.
Differential diagnosis: We compared Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. with the species of the genus having cuticular pores of variable shape (also trilobate) arranged in more or less defined transverse bands, buccal tube with an anterior bend and no posterior bend, and pharyngeal bulb with three macroplacoids and microplacoid. These characters considered, the most similar species are: Minibiotus eichorni Michalczyk & Kaczmarek, 2004 , M. orthofasciatus , M. vinciguerrae , and M. furcatus ; the new species differs from them in some qualitative and quantitative characters of both animals and eggs.
The eggs of Minibiotus eichorni are not known but the specimens of Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. differ from M. eichorni in the distribution of the cuticular pores (9 transverse bands instead of 8); in having smaller cuticular pores (longer diameter of elliptical pores up to 2 µm long in the holotype of Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. 369 µm long, up to 3.5 µm in specimens of M. eichorni 318 µm long); in lacking pores with 4 or 5 arms; in lacking granulation on the legs and in having claws with more prominent accessory points.
The new species differs from Minibiotus orthofasciatus in the distribution and size of the cuticular pores: Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. has a lower number of transverse bands (9 instead of 11) each with a higher number of pores; the diameter of pores is the same but in specimens of very different body length; in having longer microplacoid ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ); in having slightly longer claws ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 and Figs. 1D, E View FIGURE 1. A – E and 3A View FIGURE 3. A – C ) and in producing quite different eggs ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2. A – D and 3B, C View FIGURE 3. A – C ).
Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. differs from Minibiotus vinciguerrae in having shorter body length, in lacking granulation on the legs; in having the cuticular pores (never quadrilobate) clearly arranged in transverse bands; in having less slender claws ( Figs. 1D, E View FIGURE 1. A – E and 3 View FIGURE 3. A – C E, F), and in characters of the eggs (the processes are less numerous, 20–23 in the circumference, 75–95 in the hemisphere in M. xavieri sp. nov., 26 and 110 respectively in M. vinciguerrae ; they are longer, 10.6–19 µm in the new species, 8–9 µm in M. vinciguerrae ; the process surface and the egg shell are clearly dotted while they are smooth in M. vinciguerrae ) ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2. A – D and 3 View FIGURE 3. A – C D).
The new species differs from Minibiotus furcatus in having few trilobate cuticular pores and no quadrilobate ones; narrower buccal tube ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ), and very different eggs (the egg processes are up to 19 µm long, with a well-spaced granulation and bifurcate apex in M. xavieri sp. nov., while in M. furcatus they are up to 6 µm long, smooth and never bifurcate; in addition the egg shell is clearly dotted in M. xavieri sp. nov. and smooth in M. furcatus ).
As stressed by Pilato & Lisi (2006), by Guidetti et al. (2007) and by Fontoura et al. (2009), some species described as belonging to the genus Macrobiotus should be transferred to the genus Minibiotus . For this reason we think that it is appropriate to compare Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. with three species of Macrobiotus ( M. pustulaus Ramazzotti, 1959 , M. lazzaroi and M. pseudofurcatus ) which are similar to the new species, and whose systematic position needs to be analyzed because the examination of the type material did not confirm the presence of peribuccal lamellae (a generic character of Macrobiotus ).
Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. differs from Macrobiotus pustulatus Ramazzott i, 1959 in having eye spots, clearly smaller cuticular pores (diameter of largest pores in M. xavieri sp. nov. about 2 µm, in M. pustulatus up 6-7 µm), longer placoid row, and different eggs.
Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. differs from Macrobitous lazzaroi in having slightly smaller and more numerous cuticular pores ( Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1. A – E and 4A View FIGURE 4. A ), narrower buccal tube ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ), and quite different eggs.
Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. differs from Macrobiotus pseudofurcatus in having narrower buccal tube ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ), claws shorter ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ) and different in shape ( Figs. 1D, E View FIGURE 1. A – E and 4 View FIGURE 4. A B, C), (the difference in length between main and secondary branches is lower than in M. pseudofurcatus ), and in some characters of the eggs: they are slightly smaller (diameter 56–79 µm without processes in the new species, 83–90 µm in M. pseudofurcatus ); the processes are less numerous (20–23 in the circumference and 75–95 in the hemisphere in Minibiotus xavieri , 30–31 and about 130 respectively in M. pseudofurcatus ); the process surface has a wellspaced granulation while it is smooth in M. pseudofurcatus ( Figs. 2C, D View FIGURE 2. A – D and 4 View FIGURE 4. A D); the proximal portion of the processes, below the bifurcation, is generally longer than in the eggs of Macrobiotus pseudofurcatus ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2. A – D and 4 View FIGURE 4. A D); the egg shell has a more evident granulation in M. xavieri .
Maucci & Durante-Pasa (1984a) reported M. pseudofurcatus from Portugal. Keeping in mind the similarities between Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. and Macrobiotus pseudofurcatus , we examined one specimen from Portugal attributed by those authors to M. pseudofurcatus . We can exclude the proposition that the Portuguese specimens recorded by Maucci belong to this species and state that they very probably belong to Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov.
Macrobiotidae Thulin, 1928 View in CoL
Calcarobiotus (Calcarobiotus) View in CoL sp. Dastych, 1993 Macrobiotus cf. harmsworthi Murray, 1907 View in CoL Macrobiotus hufelandi Schultze, 1834 View in CoL
Macrobiotus lusitanicus Maucci & Durante Pasa, 1984 View in CoL b Macrobiotus recens Cuénot, 1932 View in CoL
Macrobiotus cf. richtersi Murray, 1911 View in CoL
Minibiotus cf. intermedius ( Plate, 1889) View in CoL
Minibiotus orthofasciatus Fontoura, Pilato, Lisi & Morais, 2009 View in CoL Minibiotus xavieri View in CoL sp. nov.
Eohypsibiidae Bertolani & Kristensen, 1987 View in CoL (nomen novum for Amphibolidae Bertolani,1981 View in CoL ) Bertolanius weglarskae ( Dastych, 1972) View in CoL
Hypsibiidae Pilato, 1969 View in CoL
Hypsibius seychellensis Pilato, Binda & Lisi, 2006 View in CoL Isohypsibius josephi ( Iharos, 1964) View in CoL
Isohypsibius prosostomus ( Thulin, 1928) View in CoL
Isohypsibius sattleri ( Richters, 1902) View in CoL
Diphascon (Diphascon) patanei Binda & Pilato, 1971 View in CoL Diphascon (Diphascon) pingue ( Marcus, 1936) View in CoL Astatumen trinacriae ( Arcidiacono, 1962) View in CoL
TABLE 1. Measurements (in µm) of some structures of the holotype and four paratypes of Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov.
| paratype | paratype | paratype | holotype | paratype | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length | 275 | 305 | 335 | 369 | 410 |
| Buccal tube | 27.5 | 28.9 | 32.2 | 32.7 | 32.1 |
| Buccal tube external width | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| pt | 9.8 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 9.7 |
| Stylet supports pt | 66.1 | 67.9 | 67.6 | 67.3 | 66.7 |
| Ventral lamina pt | 56.8 | 57.4 | 55.2 | 55.7 | 56.9 |
| First macroplacoid | 3.6 | ? | 4.1 | 4.5 | 4.3 |
| pt | 13.1 | ? | 12.7 | 13.8 | 13.4 |
| Second macroplacoid | 2.9 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 3.3 |
| pt | 10.6 | 11.1 | 10.9 | 11.0 | 10.3 |
| Third macroplacoid | 3.0 | 3.2 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.6 |
| pt | 10.9 | 11.1 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 |
| Microplacoid | 1.5 | ? | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.0 |
| pt | 5.5 | ? | 5.0 | 5.2 | 6.2 |
| Placoid row | 10.9 | ? | 13.0 | 13.9 | 13.9 |
| pt | 39.6 | ? | 40.4 | 42.5 | 43.3 |
| Macroplacoid row | 9.8 | ? | 11.7 | 12.6 | 11.7 |
| pt | 35.6 | ? | 36.3 | 38.5 | 36.5 |
| External claws II, III | 8.8 | 9.4 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| pt | 32.0 | 32.5 | 35.4 | 32.1 | 34.0 |
| Internal claws II, III | 8.3 | 9.1 | 10.1 | 10.0 | 10.5 |
| pt | 30.2 | 31.5 | 31.4 | 30.6 | 32.7 |
| Posterior claws IV | 10.3 | 11.3 | 13.2 | 13.0 | 13.1 |
| pt | 37.5 | 39.1 | 41.0 | 39.8 | 40.8 |
| Anterior claws IV | 9.9 | 11.1 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 12.9 |
| pt | 36.0 | 38.4 | 40.4 | 36.7 | 40.2 |
TABLE 2. Measurements (in µm) of some structures of Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov., Minibiotus orthofasciatus, Minibiotus furcatus, Macrobiotus lazzaroi and Macrobiotus pseudofurcatus.
| Body length | Minibiotus xavieri sp. nov. holotype 369 | Minibiotus orthofasciatus holotype 186 | Minibiotus furcatus 280 | Macrobiotus lazzaroi paratype 235 | Macrobiotus pseudofurcatus holotype 342 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buccal tube | 32.7 | 22.6 | 30.1 | 28.1 | 36.8 |
| Buccal tube external width | 3.0 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 3.9 |
| pt | 9.2 | 8.0 | 11.2* | 10.7 | 10.6 |
| Stylet supports pt Ventral lamina pt | 67.3 55.7 | 66.8 58.4 | 64.1 62.0 | 65.3 55.4 | 67.7 56.5 |
| First macroplacoid | 4.5 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 6.0 |
| pt Second macroplacoid | 13.8 3.6 | 13.7 2.4 | 13.8 2.9 | 14.6 3.3 | 16.3 3.6 |
| pt | 11.0 | 10.6 | 9.8 | 11.7 | 9.8 |
| Third macroplacoid pt | 3.9 11.9 | 2.4 10.6 | 3.1 10.2 | 3.6 12.8 | 4.4 12.0 |
| Microplacoid | 1.7 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| pt Placoid row | 5.2 13.9 | 4.0 8.3 | 4.8 12.0 | 4.3 12.1 | 4.9 16.9 |
| pt | 42.5 | 36.7 | 39.9 | 43.1 | 45.9 |
| Macroplacoid row pt | 12.6 38.5 | 7.4 32.7 | 11.0 36.5 | 10.9 38.8 | 15.2 41.3 |
| External claw II, III | 10.5 | 6.8 | 9.4 | 8.2 | 13.8 |
| pt Internal claw II, III | 32.1 10.0 | 30.1 6.3 | 31.3? | 29.2 8.0 | 37.5 12.6 |
| pt | 30.6 | 27.9 | ? | 28.5 | 34.2 |
| Posterior claw IV | 13.0 | 6.8 | ? | 9.8 | 18.2 |
| pt Anterior claw IV | 39.8 12.0 | 30.1 6.9 | ? 11.6 | 34.9 9.6 | 49.5? |
| pt | 36.7 | 30.5 | 38.6 | 34.2 | ? |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Minibiotus xavieri
| Fontoura, Paulo, Pilato, Giovanni, Morais, Paulo & Lisi, Oscar 2009 |
Minibiotus orthofasciatus
| Fontoura, Pilato, Lisi & Morais 2009 |
Hypsibius seychellensis
| Pilato, Binda & Lisi 2006 |
Eohypsibiidae
| Bertolani & Kristensen 1987 |
Macrobiotus lusitanicus
| Maucci & Durante Pasa 1984 |
Amphibolidae
| Bertolani 1981 |
Bertolanius weglarskae (
| Dastych 1972 |
Diphascon (Diphascon) patanei
| Binda & Pilato 1971 |
Hypsibiidae
| Pilato 1969 |
Isohypsibius josephi (
| Iharos 1964 |
Astatumen trinacriae (
| Arcidiacono 1962 |
Milnesiidae
| Ramazzotti 1962 |
Diphascon (Diphascon) pingue (
| Marcus 1936 |
Macrobiotus recens Cuénot, 1932
| Cuenot 1932 |
Macrobiotidae
| Thulin 1928 |
Isohypsibius prosostomus (
| Thulin 1928 |
Macrobiotus cf. richtersi
| Murray 1911 |
Macrobiotus cf. harmsworthi
| Murray 1907 |
Isohypsibius sattleri (
| Richters 1902 |
Minibiotus cf. intermedius (
| Plate 1889 |
Milnesium tardigradum Doyère, 1840
| Doyere 1840 |
Macrobiotus hufelandi
| Schultze 1834 |