Furfurilactobacillus, Zheng & Wittouck & Salvetti & Franz & Harris & Mattarelli & O’Toole & Pot & Vandamme & Walter & Watanabe & Wuyts & Felis & Gänzle & Lebeer, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6309919 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0389878A-FFA3-215F-DA0B-FECAFC48665F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Furfurilactobacillus |
| status |
gen. nov. |
DESCRIPTION OF FURFURILACTOBACILLUS GEN. NOV.
Furfurilactobacillus (Fur.fu.ri.lac.to.ba.cil’lus. L. masc. n. furfur bran, relating to the origin of furfurilactobacilli from cereal fermentations; N.L. masc. n. Lactobacillus a bacterial genus name; N.L. masc. n. Furfurilactobacillus a lactobacillus from bran).
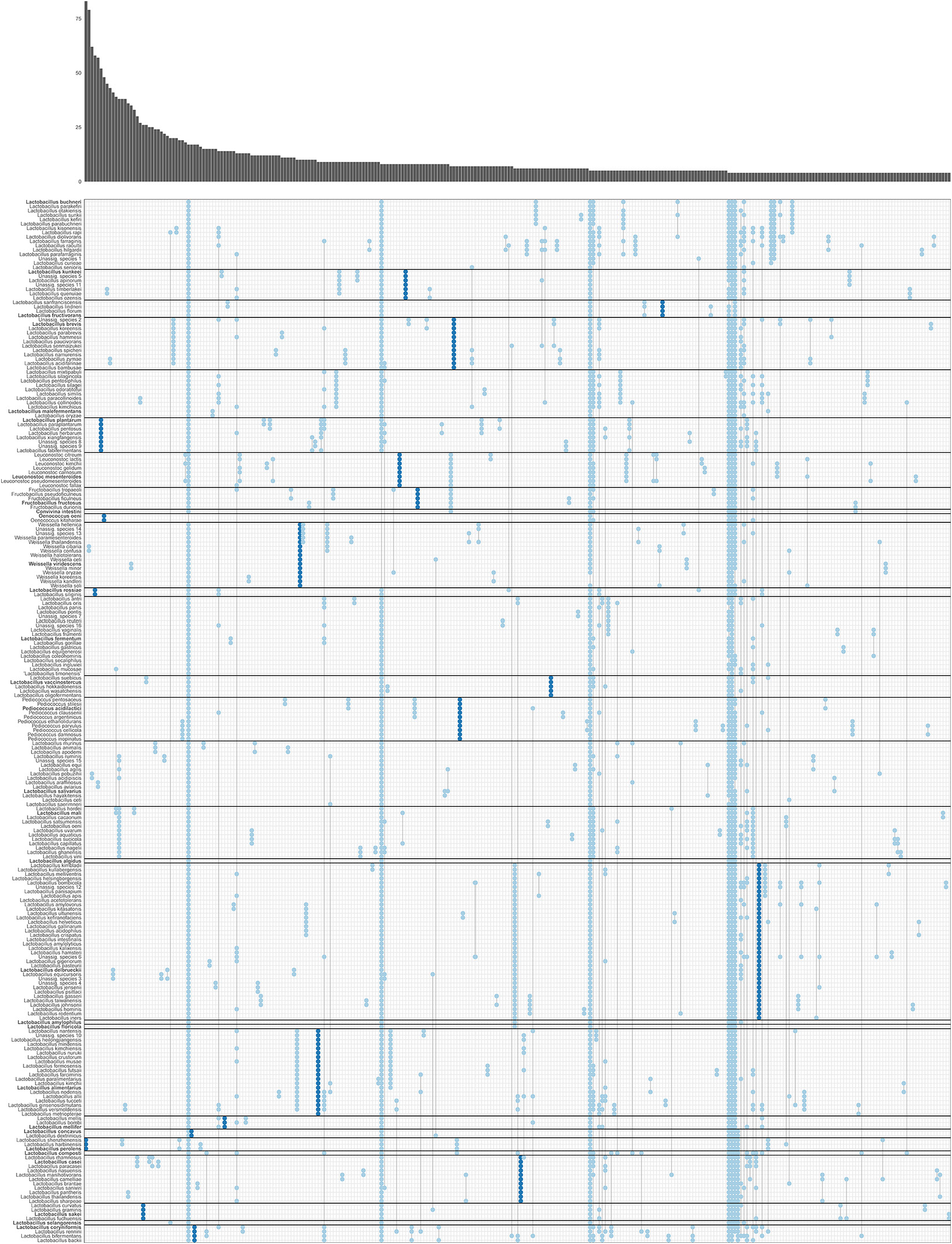
Heterofermentative and aerotolerant. Growth is observed at 15 and 37°C but not at 45 °C. The two species in the genus with genome sequences available have a genome size of 2.9–3.0 Mbp and a mol% G+C content of DNA of 43–44 %. Species in the genus were isolated from sourdough or spoiled beer and have an exceptional capacity to metabolize phenolic compounds [ 240, 241]. The ecology of the genus remains largely unexplored but appears to be similar to the nomadic lifestyle of L. plantarum .
A phylogenetic tree on the basis of 16S rRNA genes of all species in the genus Lactiplantibacillus is provided in Figure S 6L View Fig .
The type species of the genus is Furfurilactobacillus rossiae comb. nov.; Furfurilactobacillus was previously referred to as L. rossiae group.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.