Lacticaseibacillus, Zheng & Wittouck & Salvetti & Franz & Harris & Mattarelli & O’Toole & Pot & Vandamme & Walter & Watanabe & Wuyts & Felis & Gänzle & Lebeer, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6309692 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0389878A-FF90-216C-D94E-FD78FD1A67AE |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Lacticaseibacillus |
| status |
gen. nov. |
DESCRIPTION OF LACTICASEIBACILLUS GEN. NOV.
Lacticaseibacillus (Lac.ti.ca.se.i.ba.cil'lus. L. neut. n. lac milk; L. n. caseus cheese, referring to the casei-group lactobacilli; L. masc. n. bacillus a rod; N.L. masc. n. Lacticaseibacillus a milk-derived rodlet from the [ Lactobacillus ] casei group).
Strains of Lacticaseibacillus are homofermentative; some but not all species metabolise pentoses via the phosphoketolase pathway. The mol % G+C content of DNA is between 46 and 58.0. The genome size ranges from 1.93 to 3.14 Mbp. Strains are non-motile, oxidase negative, often producing D(−)- and L(+)-lactic acid from glucose. The temperature range for growth is variable, but never below 10 °C and never above 45 °C. One subspecies survives 70 °C for 40 s. Lys–D-Asp is the most common type of the peptidoglycan. The genus has considerable economic importance as it harbours several species that are used as starter cultures in dairy fermentations and as probiotics [ 58, 59].
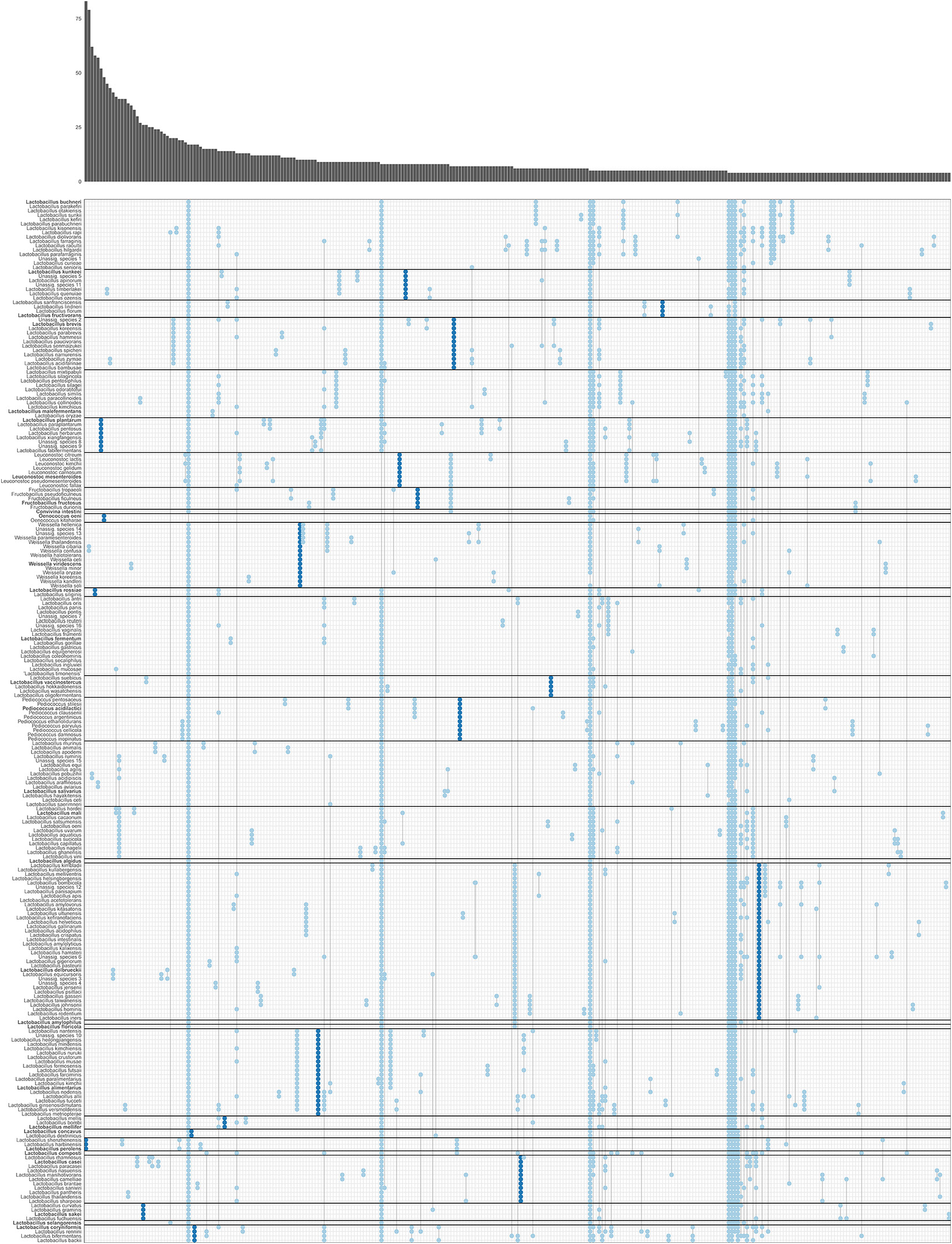
A phylogenetic tree on the basis of 16S rRNA genes of all species in the genus Lacticaseibacillus is provided in Fig. S 6F View Fig .
The type species is Lacticaseibacillus casei comb. nov.; Lacticaseibacillus was previously referred to as L. casei group.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.