Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2020.698 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:623BBCE3-12A5-45A9-802A-2ED2E15164A3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4335440 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F52B791A-FFC8-E916-8115-FBA7C70BF209 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919 |
| status |
|
Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919
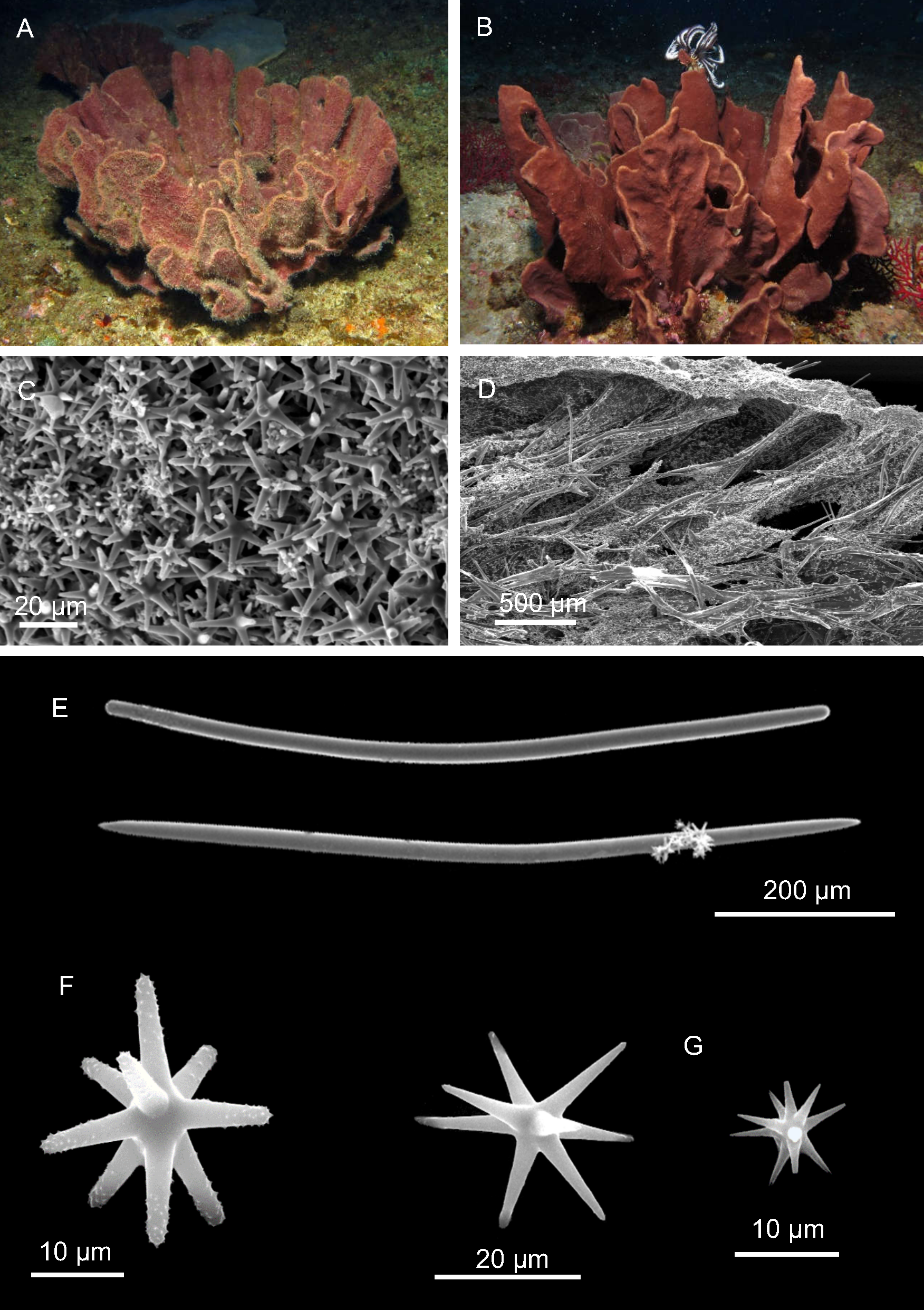
Fig. 27 View Fig
Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919: 7 , figs 2–5.
Material examined
PONTA DO OURO • 1 single, dried fragment of about 4 × 3 cm × 8 mm, several dried portions, 1 alcohol preserved; 26°46′39.864″ S, 32°55′25.284″ E; Cloud break; 34 m deep; 18 May 2015; Torsani leg.; IMG0516 GoogleMaps • 1 fragment, alcohol preserved, of about 11 × 5 × 4 mm; 26°50′36.881″ S, 32°54′54.478″ E; Atlantis; 40.7 m deep; 6 Feb. 2017; Cerrano leg.; PO20 GoogleMaps • 1 fragment, alcohol preserved; 26°46′38.829″ S, 32°54′17.387″ E; Waynes; 40.6 m deep; 17 Feb. 2017; Cerrano leg.; PO53 GoogleMaps .
Description
The sponge is lamellate, foliose; color is dark red to violet ( Fig. 27 View Fig A–B). On the surface, two specimens present algal turf. The samples preserved in alcohol changed color to beige; the dried samples are whitish, light brown; in the dried state, spicule tracts create an irregular pattern and thick lines on the surface. The samples have a micro-bristly surface and an elastic consistence.
SKELETON. The ectosome is constituted of a layer of densely packed euasters ( Fig. 27C View Fig ). the choanosome with plumo-reticulate tracts is formed by megascleres ( Fig. 27D View Fig ), without a well-marked differentiation between axial and extra-axial regions.
SPICULES. The megascleres are constituted by strongyloxeas and oxeas ( Fig. 27E View Fig ), with a wide range of intermediate forms, 590–(842.5, 100.8)– 980 µm ×10–(17.25, 4.3)– 25.5 µm; strongylasters with at least five rays ( Fig. 27F View Fig ) with microspined rays 7.5–(12.4, 3.6)– 20 µm, and smooth oxyasters 5–(8.9, 3.8)– 25 µm ( Fig. 27G View Fig ).
Remarks
The examined material fits with the species Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919 . This is a species with a strict distribution, confined to East Africa and Madagascar ( Burton 1959; Vacelet et al. 1976; Pulitzer-Finali 1993). This species is also similar to Hemiasterella vasiformis (Kirkpatrick, 1903) ( Topsent 1919) , recently recorded by Samaai et al. (2019) in South Africa; as a consequence, a revision of the genus Hemiasterella and a genetic analysis would be necessary in order to clarify the possible synonymy.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hemiasterella complicata Topsent, 1919
| Calcinai, Barbara, Belfiore, Giuseppe, Pica, Daniela, Torsani, Fabrizio, Palma, Marco & Cerrano, Carlo 2020 |
Hemiasterella complicata
| Topsent E. 1919: 7 |