Bellulia fuscis Han & Kononenko, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4938.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C7BDCA9B-E754-4569-922A-539B71A3E07F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4561471 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B757711F-302B-FFD8-2981-FDA024D0B9B5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bellulia fuscis Han & Kononenko |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bellulia fuscis Han & Kononenko View in CoL sp. n.
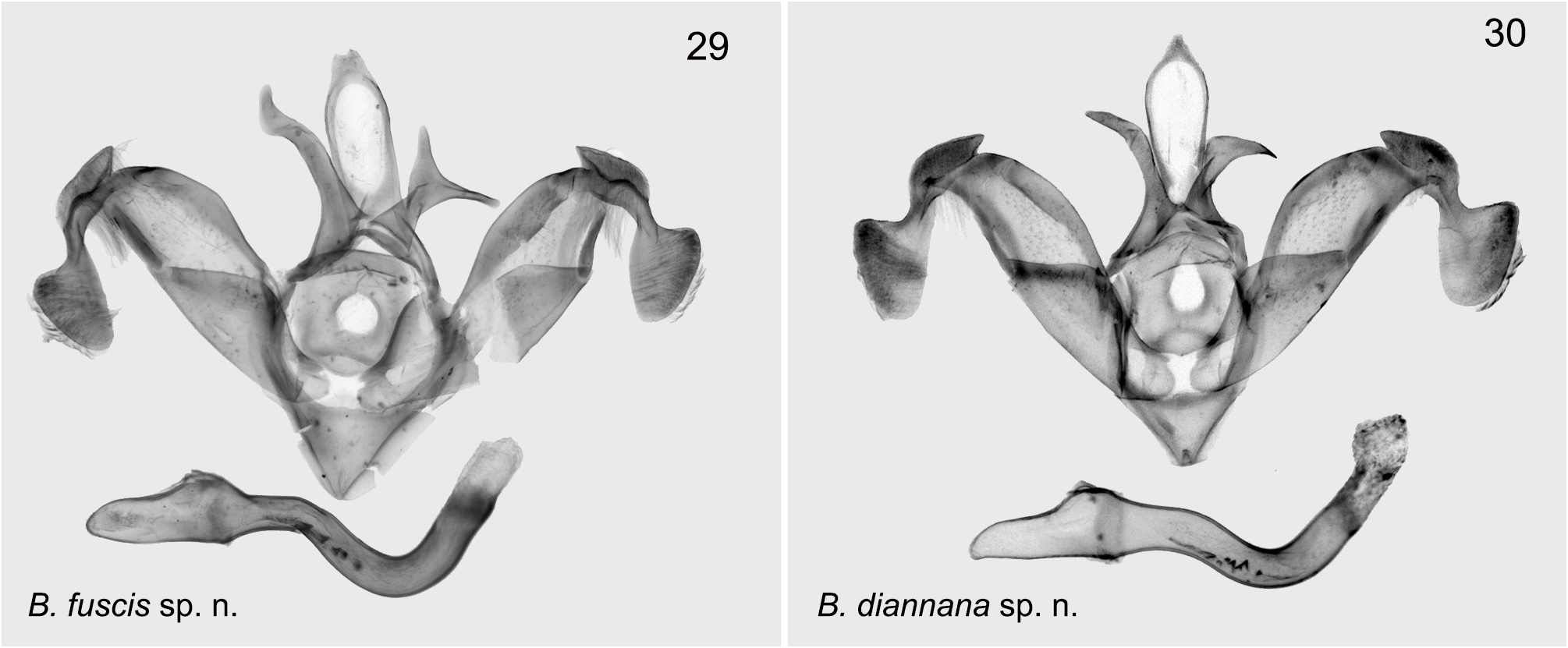
( Figs 14 View FIGURES 9-16 , 29 View FIGURES 29-30 )
Type material. Holotype: male, Cambodia, Prov. Mondul Kiri, Seima Biodiversity Conservation Area , 3-8.vii.2009, Y.S. Bae et al., genit. prep. hhl-2348-1, coll. NEFU.
Diagnosis. This species is similar to B. basalia Fibiger, 2010 ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 9-16 ) and B. wui Fibiger, 2008 ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 9-16 ), but differs from both species in the reddish-brown ground colour of the forewing (in B. basalia it is blackish-brown; in B. wui greyish-brown); the inner line of the antemedial line is very thin (in B. basalia and in B. wui it is more distinct), outer line bordering the antemedial line is broad medially (in B. basalia and B. wui it is regular); inner line of the postmedial line presents as a distinct broad black patch on the costal margin (in B. basalia black patch not expressed; in B. wui black patch weakly expressed); the reniform spot is small and irregular, yellow (in B. basalia larger, rounded, and muddy yellow; in B. wui it is small and white). In the male genitalia of B. fuscis ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 29-30 ) the ventral part of the tegumen fused to the fultura superior with prominent extensions, the right apically furcate (in B. basalia , Fig. 28 View FIGURES 23-28 ), the left one is pig ear-shaped, extended apically, sharp); the left sacculus is as broad as the basal part of valva (in B. basalia it is narrower than the valva); the vesica bears five cornuti of equal size (in B. basalia the vesica bears six cornuti of increasing size).
Description. Adult ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 9-16 ). Wingspan 11.0-12.2 mm. Head and abdomen blackish; thorax slightly russet, mixed with black. Forewing brownish and light russet, with black and dark brown scales throughout; basal line black, distinct, present only at costal margin; antemedial line black, double, smoothly curved, its inner line slender and indistinct, outer line broad medially; postmedial line black, double, waved, its outer line thin, indistinct, inner line as broad patch in costal area; subterminal line double, weakly waved, its inner line slightly darker than ground colour, thin, indistinct, outer line broad and black between costa and M2, otherwise indistinct; terminal line black; fringe same as ground colour; costal area smoky-black, with cyan and some whitish-grey, and slightly darker than reminder of wing; reniform spot small, irregular with yellow scalling, outlined with black. Hindwing lighter than forewing; discal spot present, tinged dark; outer margin slightly incurved at M2; fringe same as ground colour, mixed with greyish yellow basally.
Male genitalia ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 29-30 ). Tegumen broad, slightly longer than vinculum; ventrally fused to fultura superior with a prominent, log-shaped, curved process on each side, left one longer than right, pig-ear shaped apically, right process furcate. Vinculum broader than tegumen, V-shaped. Saccus broad V- shaped. Juxta ring-shaped, sclerotized, with full circular opening at center. Valva broad, weakly asymmetrical, left valva broader and shorter than right; sacculus slightly asymmetrical, left valva slightly shorter than right, about 3/5 as long as valva, somewhat narrower than base of valva, right sacculus broader than base of valva; ampullae slightly asymmetrical, rounded, with heavy setae, right ampulla slightly larger than left; costa thick and arched, broader on right valva. Aedeagus with coecum 1/4 as long as aedeagus, sclerotized, inbarely curved posteriorly; ductus ejaculatorius with large swelling; vesica with five tiny sclerotized cornuti medially.
Female genitalia. Female unknown.
Etymology. The species name derived from the Latin “ fuscus ” (brown) and refers to the brown colouration of the adult of the new species.
Distribution. Cambodia (Prov. Mondul Kiri).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |