Coelorinchus kamoharai Matsubara, 1943
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/megataxa.3.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B711B23F-FF80-8648-DA3F-C681FDAB7A33 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2021-02-23 10:39:49, last updated 2024-11-28 19:05:39) |
|
scientific name |
Coelorinchus kamoharai Matsubara, 1943 |
| status |
|
Coelorinchus kamoharai Matsubara, 1943 View in CoL
[Japanese name: Ichimonji-hige]
( Figs. 34B View FIGURE 34 , 58–59 View FIGURE 58 View FIGURE 59 ; Appendix 3-3C)
Coelorhynchus kamoharai Matsubara, 1943:136 View in CoL , figs. 1B, 2B, 4 [original description; holotype: FAKU 2498 (ex. SKFC 4), from Kumano-nada; 14 paratypes from Kumano-nada and off Heta; new Japanese name: “Itimonji-hige”]; Matsubara et al. 1951:42 (listed; Mie Pref.); Kuroda 1951:391 (listed; Suruga Bay); Kamohara 1952:99 (spec. from Kochi Pref.); Matsubara 1955:1311, pl. 133, fig. 455 (in key; Japan); Kamohara 1958:73 (listed; Kochi Pref.); Okada et al. 1959:83 (listed; Kumano-nada); Kuroda 1962:8 (description of fresh color; 4 spec. from Suruga Bay); Kamohara 1964:95 (listed; Kochi Pref.); Matsubara 1965:505 (compiled; Japan); Okamura 1970a:159, pl. I, fig. b, text-fig. 64 (description; 111 spec. from Pacific off southern Japan from Heta to Kochi); Kataoka & Tomida 1981:78 (listed; Mie Pref.); Tominaga & Uyeno 1981:488 (listed; Japan); Ohta 1983: tables A–B (listed; Suruga Bay); Ozawa 1983:13 (listed; off Makurazaki, Kagoshima Pref., East China Sea); Akazaki 1984:265 (listed; Aoshima, Miyazaki Pref.).
Coelorhynchus (Quincuncia) kamoharai View in CoL : Okamura 1970b: table 1 (listed; Japan).
Coelorinchus kamoharai: Yatou 1984:221 View in CoL , 365, fig. 157 [brief description; 10 spec. from Okinawa Trough; photo based on BSKU 36042 (from Mimase fish market)]; Okamura 1984b:96, pl. 82, fig. I (compiled); Okamura 1988:96, pl. 82, fig. I (compiled); Iwamoto 1990:164, fig. 382 (synopsis); Suzuki & Kataoka 1997:83, pl. 33, fig. 179 (brief description; 1 spec. from Kumano-nada); Okamura 1997:126, fig. 6 (compiled); Shao et al. 2008b: table 2 (6 spec. listed from northeastern Taiwan); Shinohara et al. 2009:708 (listed; Pacific off Tohoku); Nakabo & Kai 2013:506 (in key; Japan); Fukui et al. 2015:182, fig. 11 (1 spec. from off Kuro-shima Island, Kagoshima Pref., East China Sea); Ikeda & Nakabo 2015:321, pl. 67, figs. 1–5 (brief description; spec. from Wakayama Pref.); Iwamoto et al. 2015:58 (brief description; 9 spec. from northeastern Taiwan and Philippines); Motomura 2020:38 (listed; Japan).
Caelorinchus kamoharai View in CoL : Nakabo 1993:366 (in key; Japan); Shao 1993:169, fig. 37-8 (compiled; Taiwan; photo spec. is C. formosanus View in CoL ?); Shinohara et al. 1996:169 (1 spec. listed from Pacific off Tohoku; 1 spec.); Shinohara & Matsuura 1997:290 (listed; Suruga Bay); Nakabo 2000:430 (in key; Japan); Shinohara et al. 2001:304 (98 spec. listed from Tosa Bay); Yoda et al. 2002:11 (listed; East China and Yellow Seas); Nakabo 2002:430 (in key; Japan); Nakajima 2003:54, pl. 15, fig. 87 (brief description; 1 spec. from Enshu-nada); Shinohara et al. 2005:416 (listed; Ryukyu Islands); Iwatsuki et al. 2017:32 (listed; Hyuga-nada).
Caelorinchus (Quincuncia) kamoharai View in CoL : Chiou et al. 2004a: table 1 (listed; Taiwan).
Diagnosis. Light organ tubular, completely covered with scales, externally represented by long black streak extending from immediately anterior to anus to chest just posterior to isthmus. Underside of head completely naked except for overlapping scales posterior to lateral nasal ridges; dorsal surface of snout broadly naked along each side of median rostral ridge. Snout long, sharply pointed, length 63–77% PRL, its dorsal profile straight in lateral view, with slight humplike rise above nostrils; terminal scute short, arrowhead-shaped, dorsoventrally flattened, length 6–11% PRL. Lateral nasal ridge incompletely supported by nasal bone. Anus abutting anal-fin origin. Premaxillary teeth small, slender, conical in moderately wide,long,tapered band,with outer series slightly enlarged; posterior margin of tooth band almost reaching lateral corner of mouth. Body scales covered with short, erect, narrowly triangular spinules in quincunx order; buttresses poorly developed. Second dorsal fin distinctly lower than anal fin. Orbit diameter 43–48% PRL; postorbital length 52–59% PRL; upper-jaw length 47–54% PRL; pectoralfin length 56–74% PRL; height of first dorsal fin 65–90% PRL; interdorsal length 41–58% PRL; length of gill slit 26–29% PRL; barbel length 14–24% PRL. Dorsal half of body with faint, dark, irregular blotches; lower half of head and body silvery white when viewed laterally; median nasal bone blackish; underside of head except mandibular rami densely covered with short, black, hair-like papillae; similar papillae also present over naked areas on dorsal surface of snout; lips blackish; oral cavity pale; gular and branchiostegal membranes heavily peppered with large melanophores; chest prominently dark; first dorsal fin dusky, but second spinous ray blackish; pelvic fin pale proximally, darker distally.
Material examined. 35 specimens. Paratypes of Coelorhynchus kamoharai: FAKU 2496 (1, 59.4 mm HL, 237+ mm TL), Owase fish market, Kumano-nada, bottom trawl, coll. K. Matsubara, 4–9 Jan. 1936; FAKU 1593 View Materials (1, 57.2 mm HL, 221+ mm TL) , * FAKU 1594 View Materials (1, 48.7 mm HL, 204+ mm TL) , * FAKU 1595 View Materials (1, 46.5 mm HL, 200+ mm TL) , * FAKU 1596 View Materials (1, 53.1 mm HL, 208+ mm TL), Owase fish market, Kumano-nada, bottom trawl, coll. K. Matsubara, 6–9 Dec. 1935 . Non-types : Japan : BSKU 106803 View Materials (1, 59.5 mm HL, 228+ mm TL) , BSKU 106804 View Materials (1, 62.8 mm HL, 252 mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshiki-jima Island, East China Sea , 31.5560ºN, 129.8847ºE, 415 m, F/ V Maruko-maru, tr. 4, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 106828 View Materials (1, 58.0 mm HL, 226 mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshiki-jima Island, East China Sea , 31.5658ºN, 129.8915ºE, 380 m, F/ V Marukomaru, tr. 1, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 106840 View Materials (1, 58.3 mm HL, 215+ mm TL) , BSKU 106841 View Materials (1, 44.3 mm HL, 184+ mm TL), southeast of Shimokoshiki-jima Island, East China Sea , 31.5675ºN, 129.8930ºE, 393 m, F/ V Maruko-maru, tr. 2, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Apr. 2012 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 112350 View Materials (1, 56.8 mm HL, 238+ mm TL) , BSKU 112923 View Materials (1, 75.8 mm HL, 300 mm TL) , BSKU 112924 View Materials (1, 72.3 mm HL, 290+ mm TL) , BSKU 112925 View Materials (1, 50.4 mm HL, 203+ mm TL) , BSKU 112926 View Materials (1, 66.0 mm HL, 269+ mm TL), off Okitsu, Tosa Bay , 280–320 m, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 24 Jan. 2014 ; BSKU 112428 View Materials (1, 56.7 mm HL, 226+ mm TL) , BSKU 112466 View Materials (1, 61.2 mm HL, 256+ mm TL), off Susaki, Tosa Bay , 320–380 m, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama et al., 9 Mar. 2014 ; BSKU 99361 View Materials (1, 32.3 mm HL, 128+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, 11 Jan. 2007 ; BSKU 89690 View Materials (1, 65.3 mm HL, 272+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, 15 Jan. 2007 ; BSKU 99410 View Materials (1, 34.6 mm HL, 140+ mm TL) , BSKU 99411 View Materials (1, 41.0 mm HL, 163+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, 19 Apr. 2006 ; BSKU 99238 View Materials (1, 64.8 mm HL, 259+ mm TL) , BSKU 99239 View Materials (1, 48.4 mm HL, 202+ mm TL) , BSKU 99240 View Materials (1, 54.7 mm HL, 220+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 31 Oct. 2007 ; BSKU 97005 View Materials (1, 53.2 mm HL, 209+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, 11 Dec. 2007 ; * BSKU 93575 View Materials (1, 59.6 mm HL, 248+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 21 Dec. 2007 ; * BSKU 94341 View Materials (1, 59.0 mm HL, 254+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 27 Mar. 2008 ; BSKU 108872 View Materials (1, 56.1 mm HL, 219+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, 22 Oct. 2012 ; BSKU 94344 View Materials (1, 61.8 mm HL, 239+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Kosei-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 27 Mar. 2008 ; BSKU 99284 View Materials (1, 49.6 mm HL, 206+ mm TL), Mimase fish market, F/ V Seiryo-maru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 14 Nov. 2007 ; BSKU 89490 View Materials (1, 39.7 mm HL, 160+ mm TL), Kochi, date unknown ; FRLM 34363 View Materials (1, 69.2 mm HL, 282+ mm TL), off Owase, Kumano-nada, coll. Iwata, date unknown ; BSKU 110036 View Materials (1, 60.2 mm HL, 247+ mm TL), Suruga Bay , 34.7127ºN, 138.4553ºE, 262–434 m, F/ V Hinode-maru, sta. 1, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama and R. Misawa, 23 Apr. 2013 GoogleMaps ; BSKU 110012 View Materials (1, 68.4 mm HL, 264+ mm TL) , BSKU 110020 View Materials (1, 44.1 mm HL, 174 mm TL), Suruga Bay , 34.7080ºN, 138.4587ºE, 200–450 m, F/ V Hinode-maru, sta. 2, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama and R. Misawa, 23 Apr. 2013 GoogleMaps .
Counts and measurements. Based on 30 specimens (32.3–75.8 mm HL, 128+– 300 mm TL). Counts: first dorsal-fin rays II,8–10; pectoral-fin rays i14–i17; pelvicfin rays 7; gill rakers on first arch (outer/inner) 0/9–11, on second arch 7–9/9–12; longitudinal scales 34–45; transverse scale rows below first dorsal-fin origin 4.5–6.5, below first dorsal-fin midbase 3.5–5, below second dorsal-fin origin 4–6, above anal-fin origin 11–20; pyloric caeca 10.
The following measurements are in % of HL, followed by those in % of PRL in parentheses: snout length 39–44 (63–77); orbit diameter 25–29 (43–48); postorbital length 32–36 (52–59); postrostral length 57–62; orbit–preopercle distance 35–39 (57–66); suborbital width 11–12 (17–21); upper-jaw length 28–33 (47–54); length of rictus 24–27 (41–45); length of premaxillary tooth band 20–24 (32–39); preoral length 32–37 (51–65); length of terminal snout scute 4–7 (6–11); length of lateral nasal ridge 26–31 (41– 54); length of suborbital ridge 94–100 (152–175); snout width 21–27 (35–45); internasal width 19–24 (33–39); interorbital width 24–28 (40–47); occipital width 6–8 (10– 13); body width over pectoral-fin bases 33–46 (54–74); body depth at first dorsal-fin origin 45–61 (73–99); body depth at anal-fin origin 34–46 (57–78); prepelvic length 101–110 (166–185); preanus length 142–156 (231–268); preanal length 144–159 (236–271); isthmus–pelvic distance 32–40 (53–66); isthmus–anus distance 71–90 (119–146); isthmus–anal distance 73–93 (121–150); pelvic–anal distance 43–57 (71–97); anus–anal distance 1–4 (2–6); pelvic-fin length 28–40 (46–65); pectoral-fin length 33–46 (56–74); predorsal length 104–110 (170–190); height of first dorsal fin 39–55 (65–90); length of first dorsal-fin base 18–22 (30–38); interdorsal length 25–34 (41–58); length of gill slit 15–18 (26–29); length of posterior nostril 4–7 (7–12); barbel length 8–14 (14–24).
Size. To 30 cm TL ( BSKU 112923, 300 mm TL, Tosa Bay, Japan).
Distribution. Restricted to Japan and Taiwan (Appendix 3-3C). Known from off the Pacific coasts of Japan northward to the Oshika Peninsula (38.32ºN), Okinawa Trough, and east of Tsushima Island, at depths of 110–450 m ( Shao et al. 2008a, 2008b; this study). One of the most abundant Coelorinchus found in southern Japan, but rare in the east of the Boso Peninsula (139.89ºE).
Remarks. Coelorinchus kamoharai was originally described by Matsubara (1943) based on 13 specimens collected from off the Pacific coast of southern Honshu, Japan (Kumano-nada and Suruga Bay off Heta). The type specimens of this species were believed to be lost during WWII (see the Comments on holotype of C. hige ), but five paratypes (FAKU 1593–1596, 2496, 46.5–59.4 mm HL, 200+–237+ mm TL; Fig. 59 View FIGURE 59 ) were rediscovered among the FAKU collection during the author’s visit in 2009 (Iwamoto et al. 2015:58).
For further morphological information see the original description (Matsubara 1943) and Okamura (1970a). This species is well represented in trawl catches from the Pacific off southern Japan at depths between 200 and 400 m (author’s pers. observ.).
Relationships and comparisons. Coelorinchus kamoharai belongs to the C. argentatus group (see the Relationships of C. formosanus ) and is most similar to C. argentatus Smith & Radcliffe in Radcliffe, 1912 known from the East Indies and Australasian waters. The two species are unique within the group in having short, black, hair-like papillae densely scattered over the underside of the head and the top of the snout. In C. kamoharai and C. argentatus , the gular membrane is overlain with fine striations or reticulations consisting of small black melanophores; this characteristic pigmentation is not found in other species of the C. argentatus group. Coelorinchus kamoharai differs most notably from large specimens of C. argentatus in having narrowly triangular spinules on the body scales (vs. broadly triangular and somewhat pyramidal). It is further distinguished from C. argentatus by having a larger orbit (43–48% PRL vs. 38–42%) and a shorter postorbital length (52–59% PRL vs. 57–64%).
Among Japanese congeners, C. kamoharai is closely similar to C. multispinulosus Katayama, 1942 in general appearance and coloration, with both species having similar dark spots or blotches dorsally on the body. However, the body markings of C. kamoharai are much larger and more obscure than those of C. multispinulosus ( Fig. 58 View FIGURE 58 vs. Fig. 72 View FIGURE 72 ), although the dark spots of C. multispinulosus are less pronounced when fresh. Spinulation of the body scales also differs between the two species: in C. kamoharai , the body scales are covered with short, erect, narrowly triangular spinules, whereas in C. multispinulosus , the spinules are much longer and needle-like ( Fig. 34B View FIGURE 34 vs. D). It further differs from C. multispinulosus in having a longer interdorsal space (41–58% PRL vs. 25–41%) and a wider gill slit (26–29% PRL vs. 21–27%). While their vertical distribution is broadly overlapping at depths between 110 and 400 m, C. kamoharai typically occurs on the continental slope at depths below 200 m, where C. multispinulosus is rarely distributed (author’s pers. observ.).
Akazaki, M. (1984) Aoshima fukin no kaisan gyorui [Marine fishes in the vicinity of Aoshima Island]. In: Miyazaki Linnean Society (Ed.), Natural History of Aoshima. Miyazaki Linnean Society, Miyazaki, pp. 149 - 266. [In Japanese.]
Chiou, M. - L., Shao, K. - T. & Iwamoto, T. (2004 a) A new species, Caelorinchus sheni, and 19 new records of grenadiers (Pisces: Gadiformes: Macrouridae) from Taiwan. Zoological Studies, 43, 35 - 50. http: // dx. doi. org / 10.1643 / ci- 03 - 128 r 1
Fukui, Y., Matsunuma, M. & Motomura, H. (2015) A list of demersal fishes collected from off Kuro-shima Island in the Osumi Group, Kagoshima Prefecture, southern Japan, with record of Hydrolagus mitsukurii (Chimaeriformes: Chimaeridae). Nature of Kagoshima, 41, 177 - 186. [In Japanese.]
Ikeda, H. & Nakabo, T. (2015) Fishes of the Pacific Coasts of Southern Japan. Tokai University Press, Hadano, xxii + 597 pp. [In Japanese.]
Iwamoto, T. (1990) Family Macrouridae. In: Cohen, D. M., Inada, T., Iwamoto, T. & Scialabba, N. (Eds.), FAO Species Catalogue, Vol. 10. Gadiform Fishes of the World. An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Cods, Hakes, Grenadiers and Other Gadiform Fishes Known to Date. FAO, Rome, pp. 90 - 317.
Iwatsuki, Y., Nagino, H., Tanaka, F., Wada, H., Tanahara, K., Wada, M., Tanaka, H., Hidaka, K. & Kimura, S. (2017) Annotated checklist of marine and freshwater fishes in the Hyuga Nada area, southern Japan. Bulletin of the Graduate School of Bioresources Mie University, (43), 27 - 55.
Kamohara, T. (1952) Revised descriptions of the offshore bottom-fishes of Prov. Tosa, Shikoku, Japan. Reports of the Kochi University, Natural Science, (3), 1 - 122.
Kamohara, T. (1958) A catalogue of fishes of Kochi Prefecture (Province Tosa), Japan. Reports of the Usa Marine Biological Station, 5, 1 - 76.
Kamohara, T. (1964) Revised catalogue of fishes of Kochi Prefecture, Japan. Reports of the Usa Marine Biological Station, 11, 1 - 99.
Kataoka, T. & Tomida, Y. (1981) Fish Fauna of Mie Prefecture. Mie Prefectural Museum, Tsu, 110 pp. [In Japanese with English summary.]
Katayama, M. (1942) A new macrouroid fish from the Japan Sea. Dobutsugaku Zasshi [Zoological Magazine, Japan], 54, 332 - 334.
Kuroda, N. (1951) A nominal list with distribution of the fishes of Suruga Bay, inclusive of the freshwater species found near coast (continued). Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 1, 376 - 394. [In Japanese with English abstract.]
Kuroda, N. (1962) On the life colours of some fishes-XV. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 10, 7 - 12. [In Japanese with English summary.]
Matsubara, K., Okada, Y., Suzuki, K. & Hashimoto, T. (1951) Cyclostoma and Pisces. In: Mie-ken Seibutsu Chosa Iinkai [Committee of the Biological Survey of Mie Prefecture] (Ed.), Mie-ken-san, Seibutsu Mokuroku [List of Organisms of Mie Prefecture], Mie Prefecture, Tsu, pp. 19 - 43. [In Japanese.]
Matsubara, K. (1955) Fish Morphology and Hierarchy. Ishizaki Shoten, Tokyo, xi + v + 1950 + viii pp., 135 pls. [In Japanese.]
Matsubara, K. (1965) Ostheichthyes [sic] [in part: Macrouridae]. In: Okada, K., Uchida, K. & Uchida, T. (Eds.), New Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Fauna of Japan. Hokuryukan Publishing Co., Ltd., Tokyo, pp. 504 - 510. [In Japanese.]
Motomura, H. (2020) List of Japan's All Fish Species. Current Standard Japanese and Scientific Names of All Fish Species Recorded from Japanese Waters. The Kagoshima University Museum, Kagoshima, 560 pp. [In Japanese.]
Nakabo, T. (1993) Macrouridae. In: Nakabo, T. (Ed.), Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species. 1 st Edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 353 - 371, 1276 - 1277. [In Japanese.]
Nakabo, T. (2000) Macrouridae. In: Nakabo, T. (Ed.), Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species. 2 nd Edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 417 - 435, 1494. [In Japanese.]
Nakabo, T. (2002) Macrouridae. In: Nakabo, T. (Ed.), Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species. English Edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 417 - 435, 1491 - 1492. [In Japanese.]
Nakabo, T. & Kai, Y. (2013) Macrouridae. In: Nakabo, T. (Ed.), Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species. 3 rd Edition. Tokai University Press, Hadano, pp. 493 - 512, 1872 - 1876. [In Japanese.]
Nakajima, T. (2003) Records of Fishes from Coastal and Offshore Waters of Aichi Prefecture, Honshu, Japan. Published by author, Toyohashi, 198 pp., 79 pls. [In Japanese.]
Ohta, S. (1983) Photographic census of large-sized benthic organisms in the bathyal zone of Suruga Bay, central Japan. Bulletin of the Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, (15), 1 - 244.
Okada, Y., Suzuki, K. & Mori, K. (1959) Kumano-nada engan no teisei gyorui [List of demersal fishes from the coastal waters of Kumano-nada]. Kumano-nada Engan Kokuritsu- Koen Chosa Hokoku [Survey Report in the Kumano-nada National Park], 11, 73 - 84, pls. 1 - 2. [In Japanese.]
Okamura, O. (1970 a) Fauna Japonica, Macrourina (Pisces). Academic Press of Japan, Tokyo, 216 pp., 64 pls.
Okamura, O. (1970 b) Studies on the macrouroid fishes of Japan: morphology, ecology and phylogeny. Reports of the Usa Marine Biological Station, 17, 1 - 179, pls. I-V.
Okamura, O. (1984 b) Macrouroidei. In: Masuda, H., Amaoka, K., Araga, C., Uyeno, T. & Yoshino, T. (Eds.), The Fishes of the Japanese Archipelago. 1 st Edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 93 - 99, pls. 79 - 83. [In Japanese.]
Okamura, O. (1988) Macrouroidei. In: Masuda, H., Amaoka, K., Araga, C., Uyeno, T. & Yoshino, T. (Eds.), The Fishes of the Japanese Archipelago. 2 nd Edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 93 - 99, 453, pls. 79 - 83, 344 - 373.
Okamura, O. (1997) Macrouridae. In: Okamura, O. & Amaoka, K. (Eds.), Sea Fishes of Japan. Yama-Kei Publishers Co., Ltd., Tokyo, pp. 124 - 129. [In Japanese.]
Ozawa, T. (1983) Studies on the bottom fishes of continental slope off Makurazaki, southern Japan I-Faunal composition and variation of abundance-. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Fisheries Oceanography, (44), 9 - 16.
Radcliffe, L. (1912) Description of a new family, two new genera, and twenty-nine new species of anacanthine fishes from the Philippine Islands and contiguous waters. Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 43, 105 - 140, pls. 22 - 31. http: // dx. doi. org / 10.5479 / si. 00963801.43 - 1924.105
Shao, K. - T. (1993) Gadiformes. In: Shen, S. - C. (Ed.), Fishes of Taiwan. Department of Zoology, National Taiwan University, Taipei, pp. 165 - 173. [In Chinese.]
Shao, K. - T., Iwamoto, T., Ho, H. - C., Cheng, T. - Y. & Chen, C. - Y. (2008 b) Species composition and distribution pattern of grenadiers (family [sic] Bathygadidae, Macrouridae, and Macrourididae [sic]) from Taiwan. In: Orlov, A. M. & Iwamoto, T. (Eds.), Grenadiers of the World Ocean: Biology, Stock Assessment, and Fisheries. American Fisheries Society Symposium 63. American Fisheries Society, Maryland, pp. 17 - 29.
Shao, K. - T., Ho, H. - C., Lin, P. - L., Lee, P. - F., Lee, M. - Y., Tsai, C. - Y., Liao, Y. - C., Lin, Y. - C., Chen, J. - P. & Yeh, H. - M. (2008 a) A checklist of the fishes of southern Taiwan, northern South China Sea. The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, (suppl. 19), 233 - 271.
Shinohara, G., Endo, H. & Matsuura, K. (1996) Deep-water fishes collected from the Pacific coast of northern Honshu, Japan. Memoirs of the National Science Museum, Tokyo, (29), 153 - 185.
Shinohara, G. & Matsuura, K. (1997) Annotated checklist of deep-water fishes from Suruga Bay, Japan. National Science Museum Tokyo Monograph s, (12), 269 - 318, pls. 1 - 2.
Shinohara, G., Endo, H., Matsuura, K., Machida, Y. & Honda, H. (2001) Annotated checklist of the deepwater fishes from Tosa Bay, Japan. National Science Museum Tokyo Monographs, (20), 283 - 343.
Shinohara, G., Sato, T., Aonuma, Y., Horikawa, H., Matsuura, K., Nakabo, T. & Sato, K. (2005) Annotated checklist of deep-sea fishes from the waters around the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. National Science Museum Tokyo Monographs, (29), 385 - 452.
Shinohara, G., Narimatsu, Y., Hattori, T., Ito, M., Takata, Y. & Matsuura, K. (2009) Annotated checklist of deep-sea fishes from the Pacific coast off Tohoku District, Japan. National Museum of Nature and Science Monographs, (39), 683 - 735.
Suzuki, K. & Kataoka, T. (1997) Marine Fishes of Mie Prefecture, Japan. Toba Aquarium, Toba, 297 pp., 152 pls. [In Japanese.]
Tominaga, Y. & Uyeno, T. (1981) List of Japanese fishes. In: Yasuda, F., Takagi, K., Tominaga, Y., Uyeno, T., Abe, T., Ishiyama, R., Iwai, T., Ochiai, A., Kuronuma, K. & Nakamura, M. (Eds.), Dictionary of Japanese Fish Names and Their Foreign Equivalents. Sanseido Co., Ltd., Tokyo, pp. 437 - 574.
Yatou, T. (1984) Coryphaenoides and Coelorinchus [in part]. In: Okamura, O. & Kitajima, T. (Eds.), Fishes of the Okinawa Trough and the Adjacent Waters I. Japan Fisheries Resource Conservation Association, Tokyo, pp. 218 - 223, 228 - 235, 224 - 245, 363 - 370.
Yoda, M., Tokimura, M., Horikawa, H. & Yamada, U. (2002) A Catalogue of Fishes from the East China and Yellow Seas with Their Local Names. Seikai National Fisheries Research Institute, Fisheries Research Agency, Nagasaki, 41 pp. [In Japanese.]
FIGURE 34. Scanning electron micrographs showing body scales (from the dorsum below the interdorsal space) of four species of the Coelorinchus argentatus group. (A) C. formosanus, BSKU 99863, ca. 72 mm HL; (B) C. kamoharai, BSKU 93575, 59.6 mm HL; (C) C. longissimus, BSKU 40448, 95.9 mm HL; (D) C. multispinulosus, BSKU 99273, 69.9 mm HL. Views from above. [Photos: N. Nakayama]
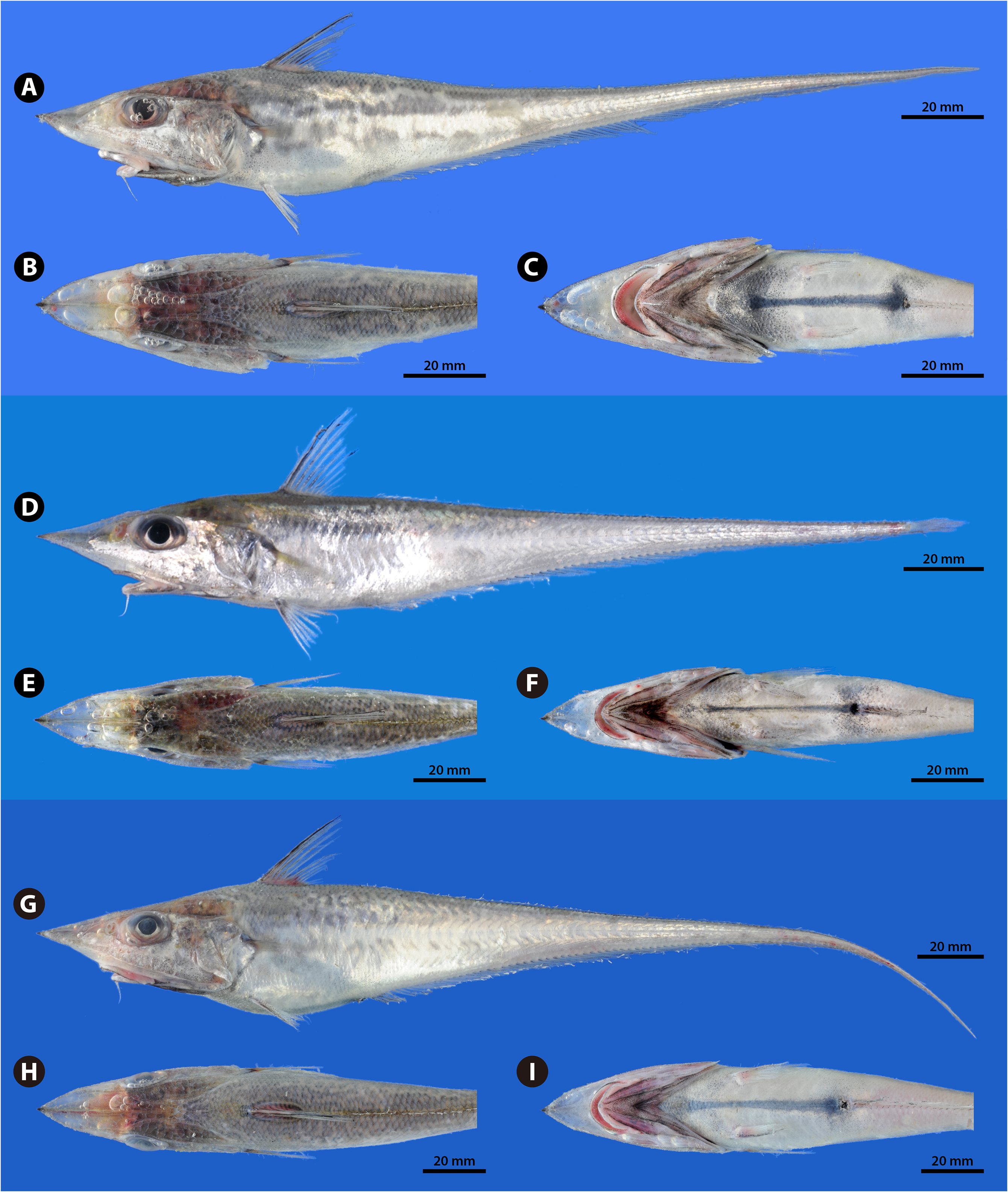
FIGURE 58. Fresh specimen of Coelorinchus kamoharai. BSKU 94341, 59.0 mm HL, 254+ mm TL, Mimase fish market, Kochi Pref., Pacific. (A) Lateral; (B) dorsal and (C) ventral views of the head and trunk. [Photos: N. Nakayama]
FIGURE 59. Rediscovered paratype of Coelorhynchus kamoharai (= Coelorinchus kamoharai). FAKU 2496, 59.4 mm HL, 237+ mm TL, Owase fish market, Mie Pref., Pacific. (A) Lateral, (B) dorsal, and (C) ventral views. Preserved condition. [Photos: N. Nakayama]
FIGURE 72. Fresh specimens of Coelorinchus multispinulosus. (A–C) BSKU 112572, 52.4 mm HL, 230+ mm TL, Etomo fish market, Shimane Pref., Sea of Japan; (D–F) BSKU 95364, 57.3 mm HL, 227+ mm HL, Mimase fish market, Kochi Pref., Pacific; (G–I) BSKU 112578, 64.3 mm HL, 292+ mm TL, collected with BSKU 112572. (A, D, G) Lateral views; (B, E, H) dorsal and (C, F, I) ventral views of the head and trunk. [Photos: N. Nakayama]
| BSKU |
Kochi University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Coelorinchus kamoharai Matsubara, 1943
| Nakayama, Naohide 2020 |
Caelorinchus (Quincuncia) kamoharai
| Chiou 2004 |
Caelorinchus kamoharai
| Nakabo 1993: 366 |
Coelorinchus kamoharai
| : Yatou 1984: 221 |
Coelorhynchus (Quincuncia) kamoharai
| Okamura 1970 |
C. formosanus
| : Okamura 1963 |
Coelorhynchus kamoharai
| Matsubara 1943: 136 |
Coelorinchus argus
| Weber 1913 |
1 (by plazi, 2021-02-23 10:39:49)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-04-12 20:43:48)
3 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-04-12 22:13:26)
4 (by diego, 2022-06-06 12:44:01)
5 (by diego, 2022-08-05 12:30:01)
6 (by diego, 2022-09-26 13:12:15)
7 (by plazi, 2023-11-01 21:45:09)
8 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-02 13:16:11)