Edwardsia californica ( McMurrich, 1913 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.183642 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5663819 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A431015F-FFBC-4B73-DFCC-1352FDF3F310 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Edwardsia californica ( McMurrich, 1913 ) |
| status |
|
Edwardsia californica ( McMurrich, 1913) View in CoL
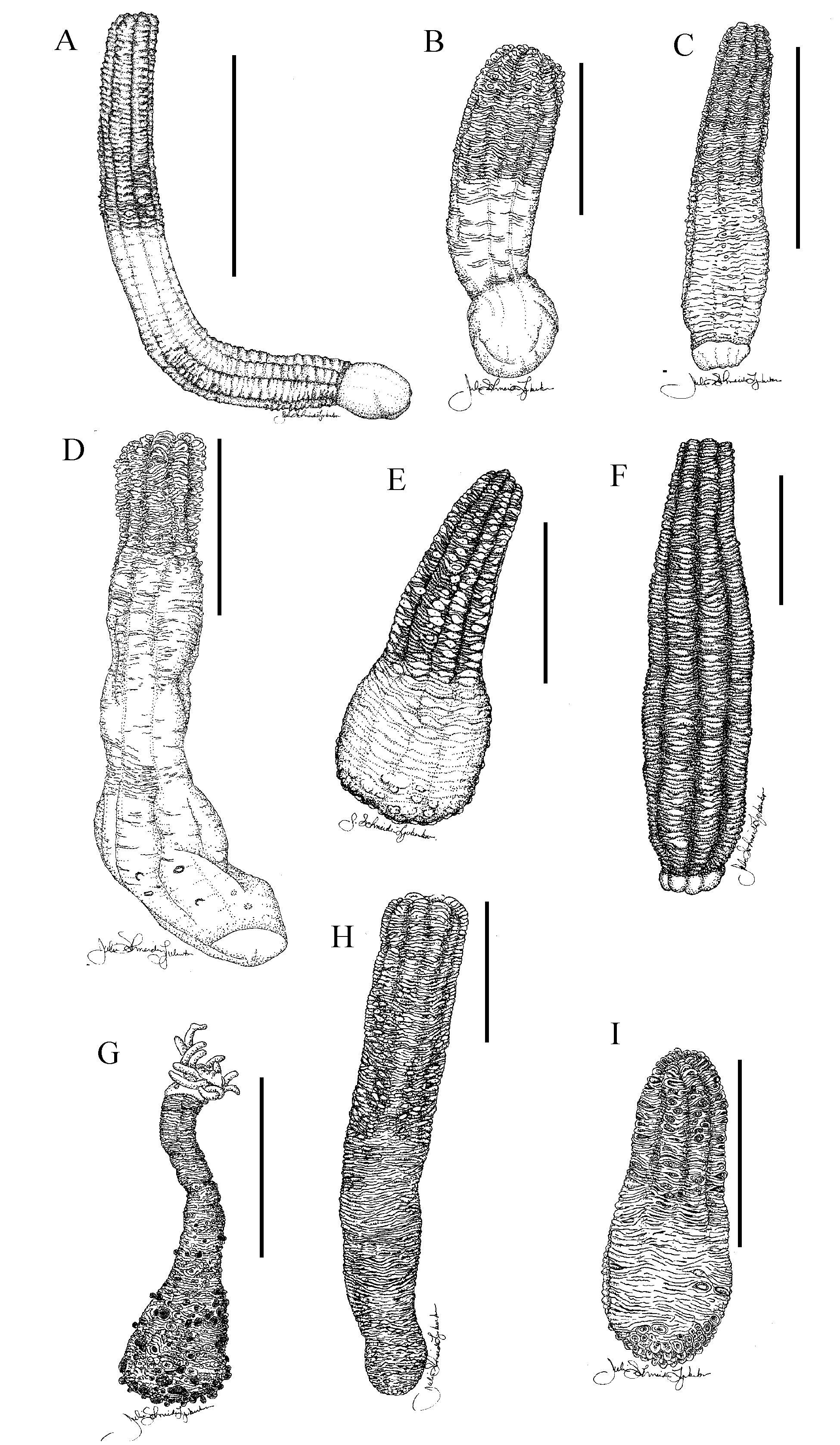
Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 3 View FIGURE 3 ; Table 1
Edwardsiella californica McMurrich, 1913 View in CoL ; Johnson & Snook 1927. Edwardsia californica: Carlgren 1936, 1949 View in CoL ; Hand 1955; Williams 1981; England 1987; pro parte Fautin 1998; Daly 2002.
Diagnosis. With large, single nemathybomes in two longitudinal rows between macrocnemes proximally. Nemathybome nematocysts of two sizes and morphologies, both longer than 40 μm. Length of whole animal in life to 100 mm ( Johnson & Snook 1927).
Material examined. Syntypes: Stingaree Hole, Anaheim Bay (Creek), Balboa, California ( SMNH 12830; USNM 30716). Other material: SBMNH 42858, Pacific Ocean, Santa Maria Basin, MMS Phase II Sta. PJ10, 34º53.63’N, 120º49.91’W, October 1986, 147 m.
External anatomy. Tentacles filiform, 16, in two cycles of eight. Scapus with eight rows of prominent nemathybomes ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 A, G); nemathybomes larger and forming double rows proximally. Periderm thin, fine; capitulum and tentacles pale beige, scapus taupe to grey. Mesenterial insertions visible as furrows with nemathybome rows forming ridges between them; highly contracted preserved specimens octagonal rather than circular in cross section. Physa naked, bulbous, with rugae and central invagination; physa may be retracted inside scapus or bear few grains of sand adhering to rugae ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A). Length of contracted type specimen 34 mm, diameter 3.5 mm.
Internal anatomy and histology. Parietal and retractor muscles strong ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 B, D). Retractor muscle with large pennon; pennon approximately equal in size to rest of retractor muscle ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B), branched on both sides of mesentery. Branches of retractor vary in height and degree of ramification: shorter and taller branches interspersed, closely spaced, those in middle typically simple, sometimes grouped into bunches, those at edges typically ramified. Parietal muscle ovoid to trianguloid; central lamella and lateral branches of approximately equal thickness ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 D). Gonochoric: all examined specimens either male or female.
Nemathybomes large, single, sunken into mesoglea, with top protruding into epidermis ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C). Scapular epidermis thin, highly irregular in outline; mesoglea of scapus thick, bilayered, becoming thinner and homogenous proximally. Epidermis of physa glandular, columnar, densely ciliated.
Cnidom. Spirocysts, basitrichs, microbasic p mastigophores, microbasic t mastigophores, pterotrichs ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 E–F, H–L; see Table 1 for size and distribution).
Distribution and habitat. Intertidal to subtidal, southern California including San Diego Bay, Mission Bay, and Anaheim Bay (JL, pers. obs.); northern limit probably Pt. Conception, southern extent of range unknown. Cooccurs with Scolanthus scamiti in coarse sediments near docks.
Similar species. Having 16 tentacles and large, single nemathybomes arranged in rows is the most common condition in Edwardsia , and thus E. californica superficially resembles many species. These characteristics, plus relatively large parietal muscles and slightly protrusive nemathybomes containing nematocysts of two sizes, ally E. californica with the beautempsi clade (Daly 2002), a group that includes the type species of the genus. It is distinguished from its closest known relatives by the sizes of the nemathybome nematocysts, which are notably larger in the specimens we measured than in E. beautempsii (36–65 μm and 36–86 μm: Carlgren 1921) or E. longicornis ( Carlgren, 1921) (39–65 μm and 45–64 μm: Carlgren 1921) and smaller than in E. claparedii Andres, 1880 (69–95 μm and 45–64 μm: Manuel 1981) or E. tuberculata Düben and Koren, 1847 (60–95 μm and 72–130 μm: Carlgren 1921). Its geographic range does not overlap with that of any other member of the beautempsi clade. Among species in California, it most closely resembles E. mcmurrichi , from which it differs in cnidom and muscle morphology. Like E. handi and E. olguini , E. californica has two sizes of nematocysts in the nemathybomes; it differs from these species in the arrangement of nemathybomes, sizes of nematocysts in the nemathybomes, and in morphology of the retractor muscles.
Tissue Cnida E. californica E. handi E. juliae
Tentacle Small basitrich (14.6) 17.2–24.6 x 2–3 (3.3) None seen 14.5–18.7 x 1.5–2.4 Large basitrich None seen 18.6–24.6 x 1.4–2.5 28.9–32.6 x 1.8–2.6 Spirocyst 12.6–18.4 x 1.9–3.6 11.7–18.3 x 2.1–3.7 8.7–12.6 x 1.6–2.7 (4.3)
Filament Small basitrich 17.8–23.3 x 2.5–3.3 13.9–16.7 x 1.7–2.4 (14.9) 19.1–21.7 x 1.4–
(3.3) 2.0
Large basitrich (34.4) 41.3–59.5 x 3.8–5.2 21–23.8 x 3.7–5.1 30.1–31.1 x 1.7–2.2 Microbasic p mastigophore None seen None seen 13.314.9 x 4.76.8 Remarks. Because it is not clear which specimens Carlgren used for various aspects of his description, and we cannot dissect or section all syntypes, we have chosen not to designate a lectotype from among the syntypes. Carlgren (1936) reported nematocysts 115–153 μm long from the nemathybome; these are significantly larger than any we found in the type specimens (see Table 1). No specimen we examined from southern California had nemathybome nematocysts as large as those reported by Carlgren (1936), although the largest nematocysts we found in the nemathybomes of E. handi are the same size as the smallest of those reported by Carlgren. Our measurements of nematocysts for E. californica were made from the type specimens deposited at the USNM; Carlgren provided no deposition information for his specimens, nor have any corresponding to the locality he cited been located. It is not clear whether the specimens Carlgren (1936) measured belong to E. californica , or whether the measurements are erroneous.
In the atlas of the benthic fauna of Santa Maria Basin, Fautin (1998) identified specimens from 147–900 m as E. californica . At the time of her report, this was the only species of Edwardsia described from this region. Only the shallowest of these specimens (SBMNH 42858, 147 m) belongs to E. californica ; the deeper specimens belong to E. profunda .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Edwardsia californica ( McMurrich, 1913 )
| Daly, Marymegan & Ljubenkov, John C. 2008 |
Edwardsia californica:
| Carlgren 1936 |
Edwardsiella californica
| McMurrich 1913 |