Trididemnum hians Monniot F., 1983
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4114.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6EA59057-0E05-4AA5-8B84-327CBDB32E5B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6068882 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A25D4D00-D64B-7622-7BF3-FE9B7FEAFCBC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Trididemnum hians Monniot F., 1983 |
| status |
|
Trididemnum hians Monniot F., 1983
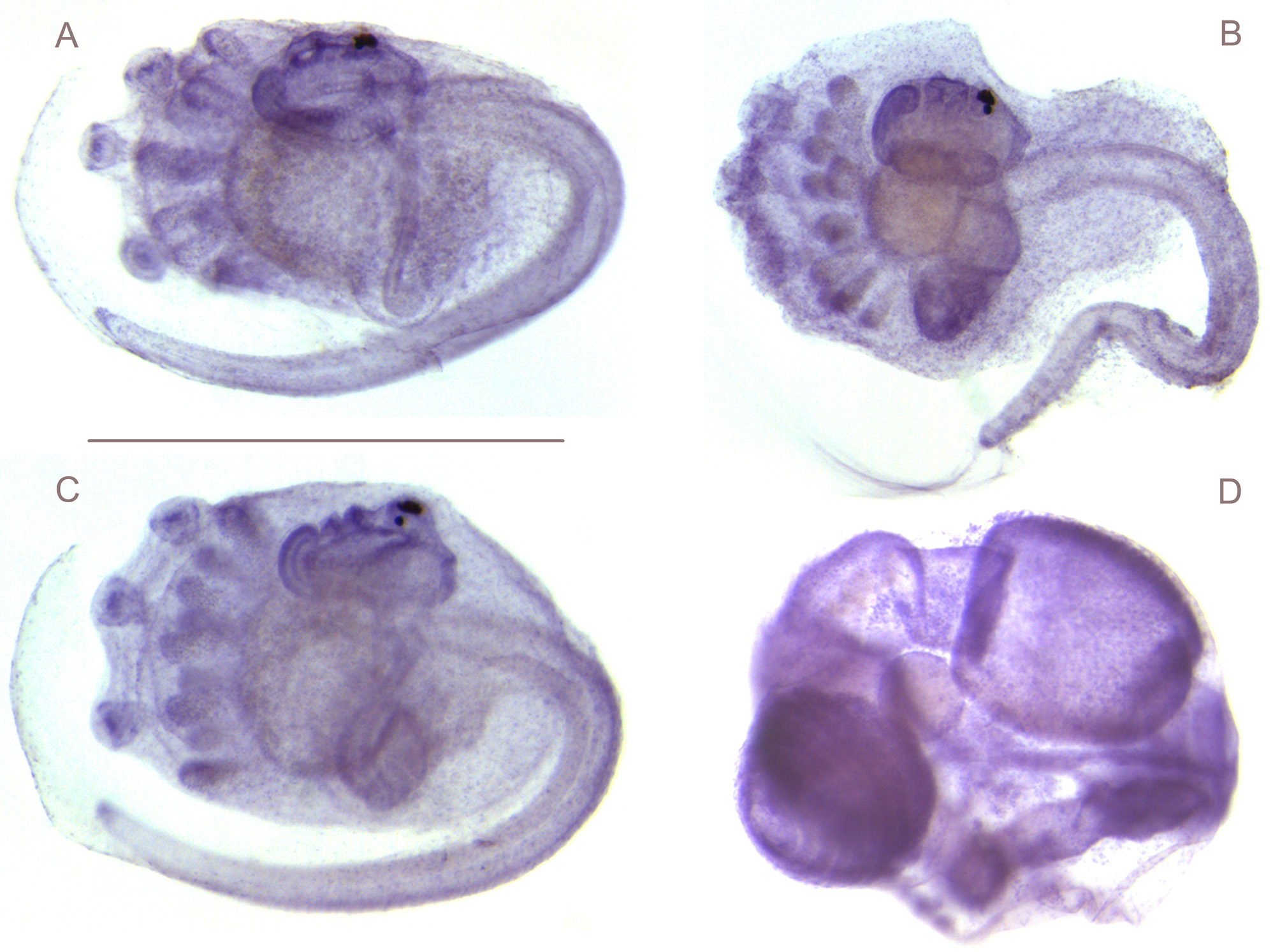
Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 .
Stations. SB3; SR8; SS1; SS3; SS4; SS5; SR14; SS11; SC6; SC12; SR23; CP4383.
The colonies are grey in formalin as the zooids contain abundant mud seen through the transparent tunic. They form soft crusts with sparse spicules in patches between groups of zooids. The oral siphon has 6 lobes, the atrial tube is always contracted. The thorax has some brown pigment in the body wall and an anterior black spot. Twelve stigmata were counted in the first half branchial row. The single testis lobe is covered by 8 to 9 turns of the sperm duct. A single oocyte is present with the testis in the intestinal loop ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 D). The larval trunk is 1mm long, the tail hardly reaches a half turn around it ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A,B,C). There are 3 divergent adhesive papillae generally lined by 6 ampullae on one side and 5 on the other side. Thorax and abdomen are already differentiated in these large larvae which have no bud. The spicules up to 50µm in diameter for the largest are composed of numerous blunt rays. The specimens from Guiana have been compared to the type material from Guadeloupe. They are recorded here for the first time in another location.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |