Diplonevra abbreviata (von Roser, 1840 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5138.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:11C1592C-6EB3-4705-A65A-F0589E602139 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6564866 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/97041566-516F-C750-78A6-FF08FAF3FE94 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Diplonevra abbreviata (von Roser, 1840 ) |
| status |
|
Diplonevra abbreviata (von Roser, 1840) View in CoL
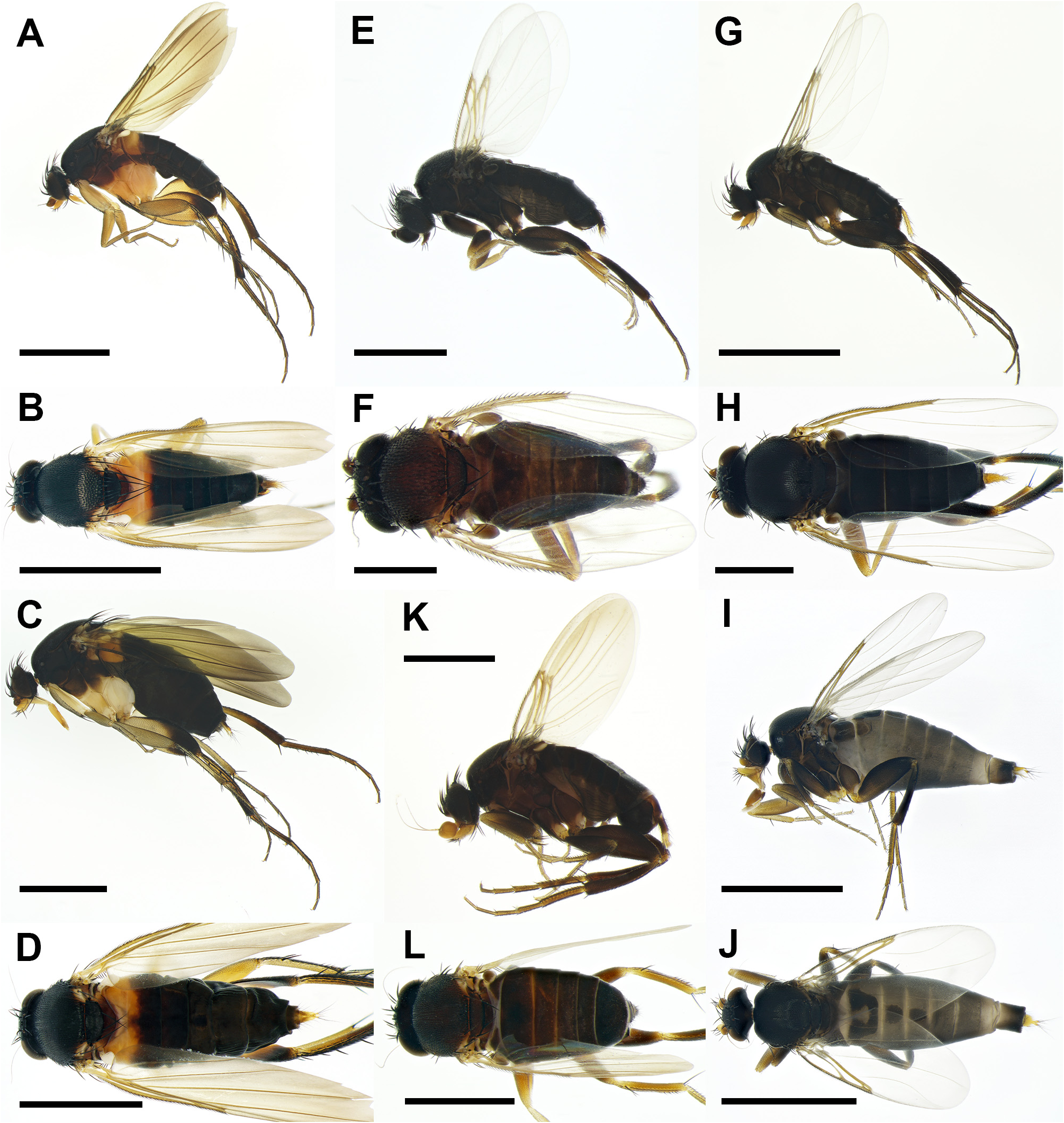
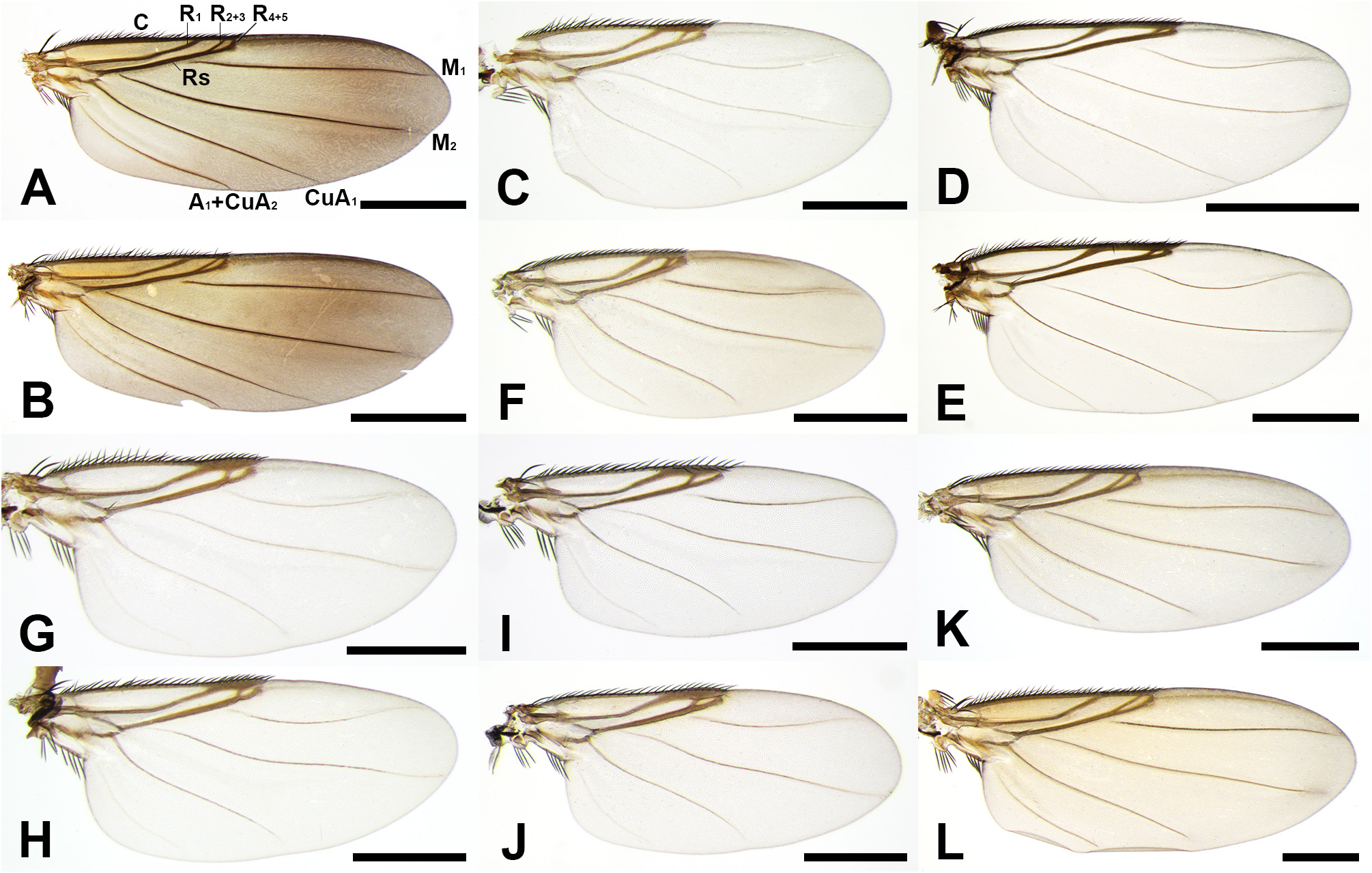
( Figs. 1A–D View FIGURE 1 , 4A–C View FIGURE 4 , 5A, 5B View FIGURE 5 , 6A, 6B View FIGURE 6 , 8A, 8B View FIGURE 8 )
Phora abbreviata von Roser, 1840: 64 . Type locality: Württemberg ( Germany).
Diploneura (Tristoechia) abbreviata: Schmitz, 1927: 47 (subgeneric assignment).
Phora sordipennis Dufour, 1841: 422 . Type locality: France (synonymy).
Diagnosis. This species can be distinguished from other Diplonevra species by the combination of the following characteristics: body uniformly blackish brown except abdominal tergite 1 and anterior half of tergite 2 yellowish orange; ventral margin of katepisternum and lower half of meron pale yellow; venter of abdomen blackish brown; inner face of male hind trochanter and femur without prominent strong setae; hind tibia with three dorsal longitudinal setal palisades and 3 or 4 strong anterodorsal setae; wing light brown, vein M 1 straight.
Description. Male. Body length 3.58–5.13mm (n=10). Head ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Frons blackish brown, shiny. Flagellomere 1 brown, as large as one-seventh of compound eye, subglobose, slightly pointed apically. Arista brown. Palpus yellow, as wide as maximum width of flagellomere 1, with six bristles apically and some short hairs ventrally. Labrum and labella yellow. Thorax ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Scutum and scutellum blackish brown. Posterior margin of scutum with three pairs of strong prescutellar bristles. Scutellum with two pairs of long bristles of subequal length; both anterior and posterior scutellar bristles apically crossing. Pleuron dark brown, brighter downward, ventral margin of katepisternum and lower half of meron pale yellow ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Legs yellowish brown, except entire coxae pale yellow, apical quarter of hind femur blackish brown, and color of hind tibia to tarsus gradually darker apically ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Fore tibia with one strong dorsal seta on basal half and one row of dorsal short setulae on apical half. Midtibia ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ) with two dorsal longitudinal setal palisades; anterodorsal one extending seven-eighths of midtibial length while posterodorsal one extending entire length of midtibia. Both of two dorsal midtibial bristles protruding at basal quarter of midtibia. Inner face of hind trochanter ( Fig. 6A, B View FIGURE 6 ) with single short, fine seta below joint of trochanter and femur, and numerous fine setae on ventral margin, without strong setae. Ventrobasal area of inner face of hind femur ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ) without stout setae but extending proximally into trochanter and highly sclerotized, with two hairs proximally and several hairs ventrally. Hind tibia ( Fig. 4B, C View FIGURE 4 ) with three dorsal longitudinal setal palisades, 3 or 4 anterodorsal strong setae, and one row of posterodorsal fine setae. Wing ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ). 3.06–4.17mm long (n=10). Costal index 0.46–0.50. Mean costal ratio 8.5:2.0:1; range 6.9–10.4:1.5–2.3:1. Costal setae of costal section III 0.06–0.09mm long. Vein of costal sections II–III not thickened. Base of Rs with single short hair. Vein M 1 straight. Vein dark brown and membrane translucent with yellow tinge, especially brown at marginal area. 3–6 (mostly 4) alular setae present, 0.09–0.15mm long. Halter white to pale yellow.Abdomen ( Fig. 1A, B View FIGURE 1 ). Tergites blackish brown except tergite 1 and anterior half of tergite 2 orange. Venter of abdomen blackish brown. Hypopygium ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ) dark brown. Epandrium without hairs dorsally. Left side of epandrium ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ) with thick, blunt epandrial lobe, bearing group of hairs basally and one strong seta apically. Right side of epandrium ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ) with numerous hairs on posterior half and small, hooked lobe on posteroventral corner. Hypandrium tomentose. Left plate of hypandrium ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ) with rounded, transparent posterior margin extending posterodorsally. Right plate of hypandrium ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ) tapering, with slightly curved upward, translucent posterior margin. Aedeagus with sharp, yellow plate protruding beyond posterior margin of hypandrium. Cercus with one pair of pale yellow sclerites mounted dorsally on brown stalk; length of cercus five times as long as maximum width of cercus; stalk with one pair of extremely long dorsal hairs protruding before base of cerci and several shorter hairs on surface except ventrobasal half bare.
Female. Body length 4.82–6.12mm (n=8). Head ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ) similar to male except flagellomere 1 smaller and darker, palpus broader, and clypeus and labrum greatly elongated (length of clypeus plus labrum about four times as long as palpal length). Thorax ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ) similar to male, except anterior scutellar bristles convergent but not crossing each other. Legs similar to male, except without structures on inner face of hind trochanter and femur. Wing ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ) similar to male, 3.74–5.17mm long (n=8). Costal index 0.47–0.50. Mean costal ratio 8.2:2.0:1; range 7.0–9.8:1.6–2.5:1. Costal setae of costal section III 0.07–0.10mm long. 4–6 (mostly 6) alular setae present, 0.11–0.15mm long. Halter pale yellow. Abdomen ( Fig. 1C, D View FIGURE 1 ). Tergites present only on abdominal segments 1–4 and 9. Tergite 1 orange, fully developed. Tergite 2 blackish brown or anterior half orange, with slightly extended anterolateral margin. Tergite 3 blackish brown, 0.6 times wide as posterior width of tergite 2. Tergite 4 small, bullet-shaped, blackish brown. Membranous area of dorsum and venter of abdominal segment 1–6 blackish brown. Abdominal segment 7 membranous, cylindrical, grayish brown. Abdominal segment 8 membranous, separated into gray dorsal portion with short hairs and brighter ventral portion with longer hairs. Abdominal segment 9 yellowish brown, flattened, triangular; tergite 9 with median ridge bearing one pair of long hairs posteriorly; sternite 9 with erected short hairs on surface. Cercus yellow, rounded, with two long hairs apically.
Specimens examined. South Korea: 1♂, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Daegwallyeong-myeon , Hoenggyeri , near National Institute of Highland Agriculture , 37°40′50.8″N, 128°43′51.1″E, 20.vi–4.vii.2018, Malaise trap, S. Nam leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 2♂ 1♀, ditto, 4–18.vii.2018, Malaise trap, S. Nam leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 2♂, Gangwon-do, Inje-gun, Buk-myeon , Hangye-ri , 38°08′46.5″N, 128°15′47.5″E, 24.vi–2.vii.2019, Malaise trap, Park & Nam leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, Gangwon-do, Chuncheon-si, Dongnae-myeon , Geodu-ri , Mt. Daeryongsan , 37°51′08″N, 127°48′22.2″E, 19– 30.viii.2019, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, ditto, 11–27.ix.2019, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee leg. ( NIBR) GoogleMaps ; 2♀, Gyeonggi-do, Yeoncheon-gun, Baekhak-myeon, Tonggu-ri , near Baekhak Reservoir , 38°01′43″N, 126°55′16.1″E, 28.vi.2020, sweeping, J. H. Lee & J. G. Lee leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, ditto, 28.vi–12.vii.2020, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, Chungcheongnam-do, Seocheon-gun, Pangyo-myeon, Sangjwa-ri , near Jongcheon Reservoir , 36°08′27″N, 126°39′20.7″E, 8.vii–6.viii.2020, Malaise trap, J. H. Sohn et al. leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂ 3♀, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Jinbu-myeon , Mt. Odaesan , near Odaecheon Stream , 37°44′21.5″N, 128°35′11.6″E, 15.vii– 14.viii.2020, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee et al. leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♀, ditto, pitfall trap, J. H. Lee et al. leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♀, Gangwon-do, Inje-gun, Buk-myeon, Hangye-ri , 38°08′46.5″N, 128°15′47.5″E, 20.viii–15.ix.2020, Malaise trap, Lim et al. leg. ( KNU) GoogleMaps .
Ecology. Adults can be found on leaves of broadleaf herbs or shrubs in shaded areas. Detailed ecological information of this species including feeding habits is largely unknown.
Remarks. This species is by far the largest Diplonevra species found in South Korea. This species is quite similar to D. bifasciata ( Walker, 1860) but can be easily distinguished by following characteristics: hind tibia with 3 or 4 anterodorsal stout setae (single seta in D. bifasciata ); abdominal venter blackish brown (pale yellow in D. bifasciata ). The previous Korean record of the species was based on a misidentification of D. bifasciata ( Kwon et al., 2018) .
Distribution. Korea (new record: widely distributed in South Korea), Europe, Russia, China, Japan.
| KNU |
Kyungpook National University |
| NIBR |
National Institute of Biological Resources |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Phorinae |
|
Genus |
Diplonevra abbreviata (von Roser, 1840 )
| Lee, Jun-Ho, Lee, Jun-Gi & Kim, Sam-Kyu 2022 |
Diploneura (Tristoechia) abbreviata: Schmitz, 1927: 47
| Schmitz, H. 1927: 47 |
Phora sordipennis
| Dufour, L. 1841: 422 |
Phora abbreviata von Roser, 1840: 64
| Roser, C. von 1840: 64 |